Objectives and purpose of the report
The objective of this reflective report is to establish the relationship between various labor issues as component of decision science in management. The paper reflects on how motivation and participatory decision making processes impact on performance of an organization.
Summary of important recommendation
According to Bruce (1999), the best way to motivate employees is by giving them responsibilities for achieving something and the authority to do it in their own way. Through this approach, employees will be empowered and they will feel trusted and valued by the management personnel and the company as a whole. Naturally, human beings would wish for motivation through mutual consent and internalized empowerment and appreciation (Saunders, Lewis, and Thornhill, 27).
Empowerment unleashes plenty of energy and motivation (Bruce, 60). Reflectively, the motivational and energy aspects of appreciation functions simultaneously at micro and macro levels to facilitate optimal functionality or productivity. Empowering employees ensures a stable and sustainable a win-win situation as employees will be motivated to work without much supervision from the management or their supervisors.
When properly incorporated within and without different departmental segmentations as an active component of the company goals and vision, the complete manger between the management and other staff will contribute to value addition, good performance and healthy working environment (Bruce, 62).
In the end, the employees will form happy intra and inter personal working relationships and appreciate the need for quality service delivery along the production process channel. From the previous study conducted, the most important recommendations are summarized as stated below:
- To empower the employees to participate more in the decision making process
- To create more motivational programs involving outdoor activities such as sporting.
Illustration of the existing process
The process of motivating employees currently being used by the Bank can be represented using a data flow diagram as shown below.
Figure 1.2 Data Flow Diagram for the process of employee motivation

The diagram above illustrates the existing process of employee motivation. The motivational activities are predetermined by the management. The activities entail use of suggestion boxes, points rewards programs, get motivated programs, use of employee evaluation forms, sporting activities and get together parties. The end result is a team of motivated employees.
Problems and ways of changing them
From the previous study, there were still some problems with the motivational activities used by management. For instance, certain programs were viewed as a source of discouragement to employees while others were most preferred. For example, employee evaluation forms were seen as a doorway to retrenchment incase the employee was found liable.
From the sample picked, 75% rejected use of this method as a way of motivation. Further, the management was unable to motivate and retain employees with medicine qualifications. However, this was based on the assumption that maybe the employees with medicine qualifications were not well motivated to work in the banking environment and it was a wrong career choice for them therefore they had no choice but to quit.
Process of changing the problems
From the analysis above, there are two major problems that are inherent with the existing system. First, some motivational activities are not accepted by the staff members and the Bank was unable to motivate some employees especially those with medicine qualifications. In order to change the problems, the Bank has involved the staff members in decision making process. The employees are part of the evaluation program.
The human resource department engages the employees in setting their own targets and they also agree on the interval for evaluation. Further, the design of the evaluation form is changed to reflect what best suit the management and the employees. With this improvement, the employees are aware of what is expected of them during the evaluation period.
Further, they are more prepared for the evaluations and therefore there is likely to be minimal resistance as compared to the earlier situation. The Bank may also be in a position to attract and retain the employees with medical qualifications by engaging the decision making. The employees may be given the freedom to choose duties that would keep them motivated.
Diagram illustrating new process after the recommendations
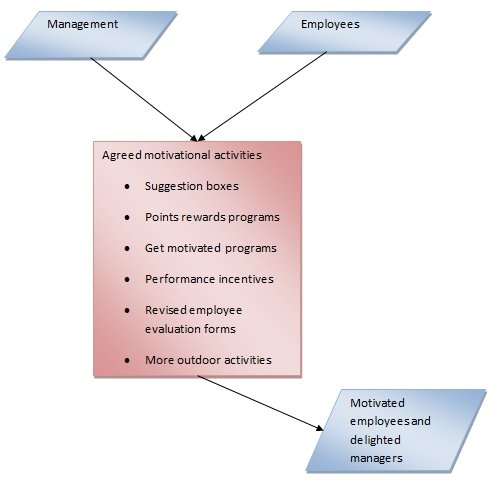
From the above diagram we note that the employees are involved in the decision making process. Therefore, the motivational activities are as agreed by both the management and the employees. The end result is a motivated workforce and delighted managers.
Benefit expected from each recommendation
The table below summarizes the benefits expected from each recommendation
Upon empowering employees to participate more in the decision making process, culture of independence in reasoning and consultative approach when handling work related duties will be internalized. In fact, the employees will appreciate the need for free consultation rather than doing the same as a condition imposed on them by their superiors.
In the process of carrying out consultative functionalism, the mind will be tuned to appreciate the need for flexibility in decision making science which is compatible with the goals and vision of the organization. In addition, the entire workforce operating under this approach is likely to positively embrace change element that may be introduced in the organization.
Irrespective of the consequences of the change element, the dynamic essence of change proponent would not facilitate any state of quagmire or conflict as the unnecessary pressure associated with change would be integrated. Moreover, creation of more involving motivational activities outside the work schedule would facilitate team building and the spirit of self discipline. For instance, recreational activities such as an organizations sports day involve planning direct participation by all stakeholders of an organization.
During such activities, employees are either divided in groups or assigned a part to perform. To make this more interesting, the management could involve themselves in this as equals.
Repeat of such fun days minimizes pressure and inferiority complex that might be hiding in the workforce due to the bureaucratic hierarchy ladder. In the end, the concept of physical, mental, and social heath would be activated and the company is likely to benefit from the same especially on the facets of value addition as a result of good health and fitness.
Action Plan
Across the globe, organizations irrespective of their sizes or nature of activity they perform have direct need for top performance and optimal service delivery within sustainable and friendly limits. Supported by strong decision making science, the project of motivational functioning depends upon effective management strategies presented in a quantifiable action plan (Bloom, 30).
In order to actualize the above recommendations, that is, empowering employees to participate in decision making and organizing recreational activities, proper research should be developed to streamline goal setting as a factor of friendly working environment and motivation (Bloom, 32). Thus, an implementation action plan specifically focuses on goals identification which is effective on performance orientation and motivational improvement.
The table below represents the components of an action plan for the implementation of motivational insight recommendations. Components of an action plan includes: feedback channel, goal setting (specific and difficult), exception criterion, and evaluation of success or failure.
In empowering employees to participate more in the decision making process, the organization should source for expertise training on consultative decision making process.
This expert will impart skills directly to the management and entire workforce. In the process of implementing this recommendation, training manager should be assigned the duty of organizing the workforce into groups and following up the success or failure of the training (Bowman, 23).
During the training process, simple activities such as solving puzzles and brainstorming in different topics are encouraged. In addition, every member of the workforce is expected to participate actively by assigning roles which are balloted. The implementation should be done in three phases with the first phase actively involving an outsourced expert in the field of decision making.
After a fortnight, the management should then design in house programs as a continuation of the first stage. In the last stage, the entire workforce is encouraged to internalize the concept initially introduced and deactivate fear and inferiority complex when addressing issues of interest to the organization and at personal level (Landsdale, 22).
Though this process should be continuous, the active part should not run for more than four months from commencement at a budget less than four percent of the company’s net revenue. In implementing the recommendation on motivation through participatory activities, the organization should factor in those activities which involve the entire workforce.
For instance, in the above example, the sporting event should be drawn in the annual timetable and everyone is to be encouraged to participate wholesomely. As the sporting event commences, management and the workforce may operate as small teams competing for prizes as designed by the organizing committee.
The organizing committee has power to decide on the prize to offer in consultation with the training manager. In the process of practicing this, team building and motivation spirit is revived and the entire personnel are likely to feel appreciated (Bowman, 21). Reflectively, a motivated workforce performs optimally within little or no supervision as work related activities are internalized and personalized. When the need to achieve is incorporated in the performance index, the organization is destined for sustainable productivity.
Action Plan Tabular representation
Summary
In summery, these recommendations would directly impact on the feedback channel as employees will have motivational power to proactively participate in decision making process.
As a result, the learning oriented process will facilitate optimal performance which is specific to the goals and desires of the company as the workforce would have the feeling of being appreciated and recognized for every outstanding performance.
In addition, these recommendations facilitate detrimental creativity and positive attitude in organizational environment. In an organization setting, the need to motivate workers is essential to management team who aim at optimizing output within sustainable human resource functioning.
Generally, when these recommendations are actualized in the management system, companies are capable of predicting or forecasting the future and pillars of operation at optimal level. Employee motivation is necessary in managing labor retention.
Works Cited
Bloom, Paula. Circle of Influence: Implementing Shared Decision Making and Participative Management. Lake Forest, IL: New Horizons, 2004. Print.
Bowman, Singh. “Corporate restructuring: Reconfiguring the firm.” Strategic Management Journal 1.4 (2003): 5–14. Web.
Bruce, Ann. “Helping employees to accept responsibility for motivation.” Motivating employees 1.2 (1999): 59-72. Web.
Landsdale, Bruce. Cultivating Inspired Leaders: Making Participatory Management Work. West Hartford, CT: Kumarian Press, 2000. Print.
Saunders, Mark., Lewis, P, and Thornhill, R. Research Methods for Business Students. New York: Pearson Education, 2009. Print.