The seasonal club “9” has severe difficulties with the mode of work, caused by the organizational features of the company. Due to seasonality, emphasis on the local network, and a large number of clients with relatively small employees, the club has a problem achieving the necessary level of competitiveness. In particular, Rob Domore expresses his dissatisfaction with the fact that he has to visit his workplace to solve problems in bad weather, and, on the days when the club functions typically, he does not have enough time for office obligations. Obviously, this problem should be solved if the “9” company is interested in improving its performance: the ideal change strategy will be a remote network. The remote network mode will allow employees to get access to working materials from anywhere in the world so that the share of employees will be able to solve professional tasks right from home, as Domore would like. Moreover, when analyzing it, one can find that such a change will significantly reduce the financial and time spent by employees on the road. Plus, management will not have to spend money on office space rental if the work is done remotely.
Report
To eliminate the undesirable effects of the company’s current labor organization, it is necessary to develop a model of remote access. It is essential to recognize that the offer should be complex to satisfy the requests of clients and employees simultaneously. In particular, the clients of the club want quick and uninterrupted access to the services they pay for: swimming pool, golf course, and clubhouses. In turn, employees are interested in a quality network through which professional tasks can be solved remotely. For such purposes, the architecture shown in the figure below will be suitable: this remote access model demonstrates an encrypted connection between the client request and the work materials.
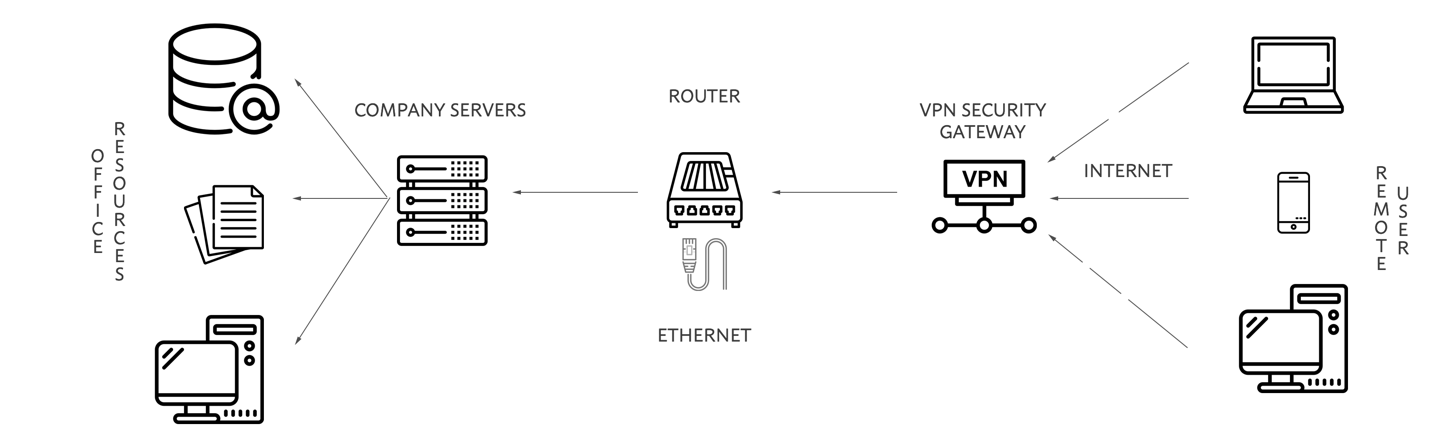
It is not difficult to imagine situations in which this architecture shows good results. The “9” employees, along with Domore, could connect to the WAN from home devices, send an encrypted request to the “9” ‘s server and access the materials (“Mobile device guidance,” 2020). On the other hand, customers who decide to visit the institution can pre-book a golf course through the application or site by remote access. In particular, the problem of creating such a model is solved by installing a VPN.
Indeed, the advantage of remote access becomes the main disadvantage: with a relatively open network, there is always a threat of hacking by fraudsters. Thus, through risk screening, one can find that the most significant threat is data leakage. Confidential information may include IP addresses of members of the network, personal data of the users, information about credit cards, and cases of club visits. Certainly, there must be a distinction between the data available to employees and customers. From a technical point of view, data is protected by double encryption, work materials are securely encrypted, and the user device sends an electronic key. From a personal point of view, each network member signs a non-disclosure agreement and refuses to transfer keys or information to third parties (“AUP,” 2020). It is worth acknowledging that this is quite common practice in private virtual networks.
As it is known, there are three states of data that include data at rest, on the move, and when used. Consequently, reliable double encryption of materials and automatic issuance of disposable randomized electronic keys will achieve their virtual protection. To use the information, users need to pass two-factor authentication: a session password is created directly by the user on a unique physical device that only they have. This measure will achieve cybersecurity both when using work materials and at rest, especially in the event that an employee or customer’s device is stolen.
References
AUP. (2020). Computer. Hope. Web.
Mobile device guidance. (2020). National Cyber Security Centre. Web.