Even the most satisfied customers posses the potential of abandoning a brand if given bigger incentive can easily convince them go somewhere else or buy something else. I think the main issue is not satisfaction of customer but about emotional attachment to the brand.
Many researches also shows that only 30percent of individual’s decisions and behaviors are motivated by rational contemplation meaning that more than 2/3 of customer loyalty and expenditure decisions are based on emotional features (Reinartz& Kumar, 2002, pp 34).
So, in this case, to measure customer satisfaction in order to determine customer loyalty will only lead to the truth. But when gauging customer satisfaction, it does tell about how customer feels about product, service and brand at that particular time. But there is no guarantee of loyalty, if they get a better deal in the same product line (McEwan, 2005, pp 8).
For instance, there is not much product differentiation in terms of electronics product design and technology. For instance, Sony has gained a lot of emotional attachment to the brand, but if brands like Samsung, LG and Philips is give better incentive or deal – customer will definitely consider buying.
In other words, customer satisfaction shouldn’t be confused with customer loyalty and bribe like single upset in delivering will be causing abandoning by satisfied customer but loyal customer is firm and has the emotional capability for seeing beyond the upset and maintains his resolute support for brand(Rozensher & Fergenson, 2008, pp36-38) and (Divett & Henderson, 2003, pp 66).
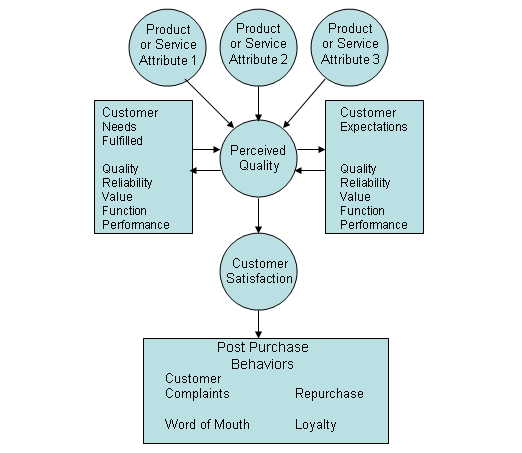
The following diagram shows that customer satisfaction is influenced by many factors like quality, service, features and benefits, but loyalty comes in the post buying behavior is only depends on satisfaction.
A survey was conducted in year 2007 by MM research and they also concluded that
“A loyal customer is certainly a satisfied customer, but a satisfied customer is not necessarily a loyal customer.”
Another important thing in this regard is loyalty schemes like incentives, gifts, and discounts are just to attract the customers and hence claiming more satisfaction. Whereas, loyal customer still does not switch the brand just because of the emotional bonding and strong relationship.
One of the best examples which can be present is Apple’s Macintosh cult. All the Mac customers bow to their products. Although they have seen hurdles in PC world but they have maintain their standards and brand loyalty. This is a result of building emotional connection between the brand and its customer, and then everything else will naturally follow(Rozensher & Fergenson, 2008, pp36-38).
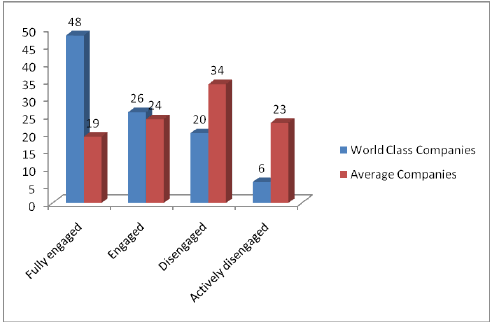
Gallup Consulting Group has also contributed a lot in doing research in the customer engagement sector. It has characterized four types of customer engagement:
- Fully engaged customers are the emotional and loyal, hence most precious consumers;
- Engaged customers, are the ones who have just started to feel the emotional attachment;
- Disengaged customers, are neutral when considers emotions and rationality;
- Actively disengaged customers who are not at all attached emotionally and also actively antagonistic (Reichheld, et al, 2001, pp 40- 45).
The fear of unknown also contributes to build the relationship of the customer and the brand. Whereas, the term ‘touch points’ is also necessary to talk about, these are those incidents or circumstances which cling customers or potential customers connect with the brand. While Positive or negative experience will result in loyalty or not.
For example, products like ice-cream or skin care product is when the customer gets immediate satisfaction and required result and at that particular time they decide to always get the same brand product(Shiller, 2000, pp53).
William J McEwan very briefly described that ‘satisfaction’ is not enough for measuring strength of a relationship of brand and the customer and “Good” presentation won’t convey brand passion. And yet, as Jim Collins (2001, pp 12) pointed out in his book Good to Great, too many companies have become content with pursuing “good” – the foe of ‘great’. Just like marriages needs extra loving not just liking.
References
Collins, Jim. 2001. Good to Great. Edition 1. Publisher: HarperBusiness.
Divett, M., Crittendon, N. and Henderson, R. 2003. Actively influencing consumer loyalty, Journal of Consumer Marketing, Vol. 20. Publisher: MCB UP Ltd
McEwan,J. Willaim. 2005. Married to the Brand. Why consumers bond with some brands for life. Gallup Press
Reichheld, Frederick F., Teal, Thomas A. 2001. “The Loyalty Effect: The Hidden Force Behind Growth, Profits, and Lasting Value”. Harvard Business School Press.
Reinartz, W., & Kumar, V. 2002. The mismanagement of customer loyalty. NewYork: Harvard Business Review.
Rozensher, G. Susan & Fergenson, E. P. 2008. The role of negative information in dissolving consumer identification with companies. Journal of Business &Economics Research, vol.6, 2008
Shiller, Robert.2000. Irrational exuberance. Princeton, 2nd ed. NJ: Princeton University Press.