Introduction
Complexity of manufacturing recommendation requires specific planning such as automation of systems.

Examples of Inventory Management systems
- Material Requirement Planning (MRP);
- The Just-In-Time Purchasing/Production (JIT);
- Economic-Order-Quality Decision Model;
- Back-flush Costing.

Importance of the management systems
- Scheduling and recording of orders or raw materials;
- Managing demands;
- Maintenance of stock for the dependent demand;
- Maintaining of an optimal level of inventory;
- Enhancing purchase of new stock;
- Accurate delivery of finished inventory;
- Planning for the daily mechanizing processes;
- Reduces the cost of caring inventory;
- Reduces costs associated with long-term purchasing agreements;
- Limits extended purchase periods;
- Determining output requirements at each stage of production.

Entities of inventory management
- Planning procedures;
- Coordinating activities;
- Controlling activities.

Costs associated with control of inventory
- Purchasing costs;
- Ordering costs;
- Stock caring and quality costs.

Best inventory control and material planning requirement for Going’s Planes
- Quality management strategy;
- Biannual annual or multiple inventory analysis programs;
- Vender-owned management system.

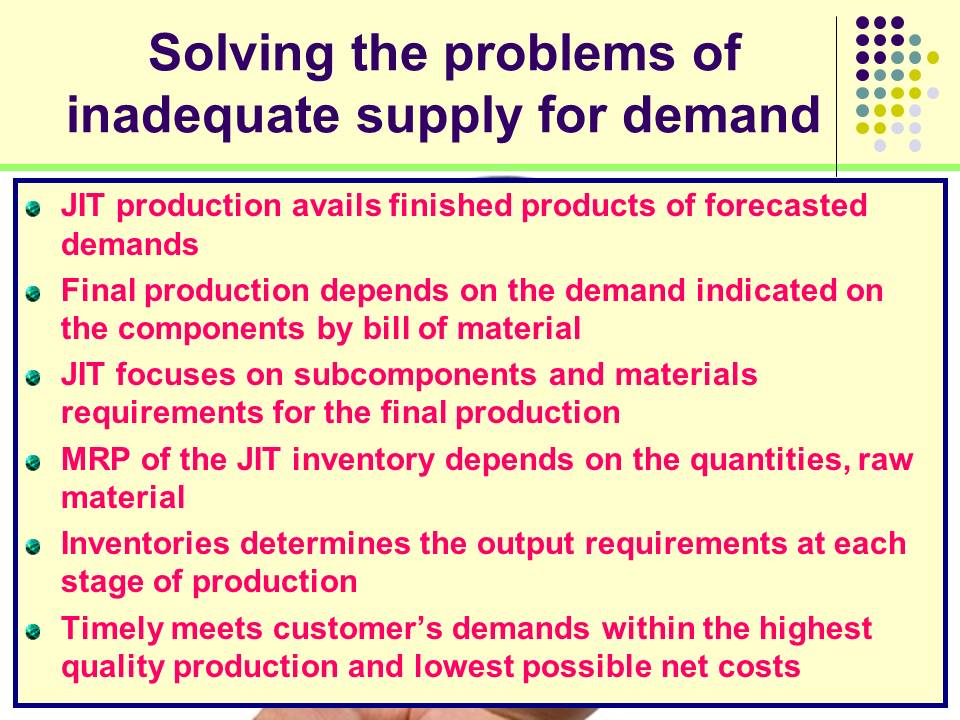
Solving the problems of inadequate supply for demand
- JIT production avails finished products of forecasted demands;
- Final production depends on the demand indicated on the components by bill of material;
- JIT focuses on subcomponents and materials requirements for the final production;
- MRP of the JIT inventory depends on the quantities, raw material;
- Inventories determines the output requirements at each stage of production;
- Timely meets customer’s demands within the highest quality production and lowest possible net costs;
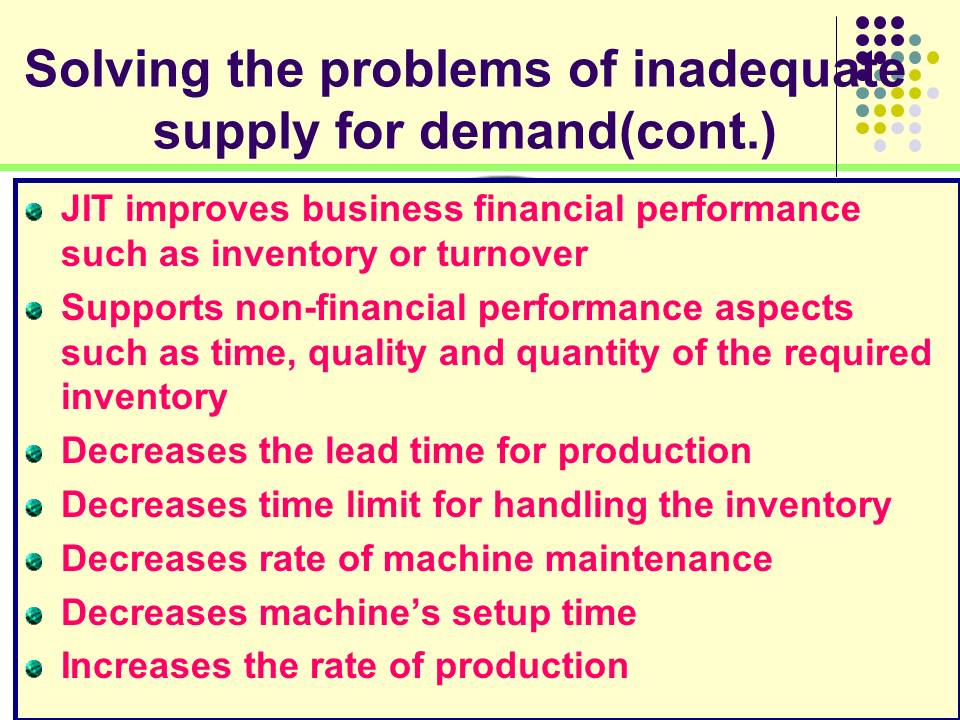
- JIT improves business financial performance such as inventory or turnover;
- Supports non-financial performance aspects such as time, quality and quantity of the required inventory;
- Decreases the lead time for production;
- Decreases time limit for handling the inventory;
- Decreases rate of machine maintenance;
- Decreases machine’s setup time;
- Increases the rate of production.
Advantages of an Inventory Management system
- Provides details of manufacturing stages;
- Helps to determine requirements;
- It is a plan indicating the aspects of the manufacturing process;
- Keeps track of the inventory and material requirements;
- Maintains a level of stock to cater for emergency cases;
- Ability to plan for future deals or requirements such as raw materials.

Challenges of an Inventory Management system
- Need for accuracy to avoid poor planning or overstocking;
- Need for accurate master schedule;
- High implementation costs;
- Time consuming;
- Expensive to put into practice;
- Discipline or inaccurate record keeping procedures;
- Involves lack of standardized measures;
- Venerability to risks.

Recommended solution
- Proper calculation of the Return on Investments (ROI) for the inventory system to implement;
- True cost of a solution must be lower than the risk exposure.

References
Albrecht K. (2008). Eight “super-trends” you must master to succeed in business. Web.
Griffin, R.W. (2007). Fundamentals of management. Cengage Learning Publishers.
Khosrow-Pour, M. (2004). A Case Study on a Security Maturity Assessment of a Business-to-Business Electronic Commerce Organization. Journal of Electronic Commerce in Organization. Vol 2 (No 4), Idea Group Inc.
McNamarra C. Key concepts in the design of an organization. Web.
Sonnenreich, Wes & Albanese, Jason. (n.d.) Return On Security Investment (ROSI): A Practical Quantitative Model. New York, NY, SageSecue, LLC publishers.