Introduction
Disintegration of constructions is no longer news in the current society since numerous incidences fill the media habitually. The increasing number of incidences continues afflicting the society as illustrated by material loss and fatality (Coppola, 2007). Countless factors have contributed to the occurrence of this phenomenon.
It is noted that the main known sources of building collapse include architectural malfunctions and unanticipated loads exerted on the structure. It is further asserted that sudden breakdown modes, as well as, mishmash of causes lead to subside of constructions. The normal collapse of the buildings can not deter the revisit of a critical scenario of Hyatt Regency Hotel. The exceptional collapse disaster occurred in Kansas City, Missouri, which led to the demise of 113 and over 200 sustained injuries (Morin & Fischer, 2006). The 1981, July 17 disaster, went into the annals of US history due to its extreme consequences on both human beings and other resources.
It is illustrated that the incident occurred when People gathered to watch music concert on the ground floor. The building had four suspended causeways from the ceiling, the forth course walk hanging directly on top of the second. On that fateful day, visitors thronged the hotel filling the concert area, plus, all the three walkways. It is imperative to note that the second and fourth course walks were full of dancing and cheering audience. Unfortunately, the fourth pathway fell on the one beneath reaching the packed first floor atrium (Morin & Fische, 2006). People were flabbergasted by the loud bang which led to death and injuries of many.
The blame is placed on structural failures of the building due to engineering negligence; furthermore, the building was inconsistent with Kansas City structure set of laws. The alteration of building design and plans led to the combination of the two walkways hanging on top of the other. It is indicated that the rectangular beams placed on the bearing shaft cores, as well as, washers got malformed thus failing to grip weight.
This led to the disjointing of the beams and the course walks from the ceiling bars thus falling on the atrium. It is indicated that the people in the second footpath and the atrium were more affected than others. The excess weight of the people on the fourth walkway exerted a lot of weight on the structural parts making it to smash. Great force from the two course walks coupled with the building materials led to the death of many people in the atrium (Baura, 2006).
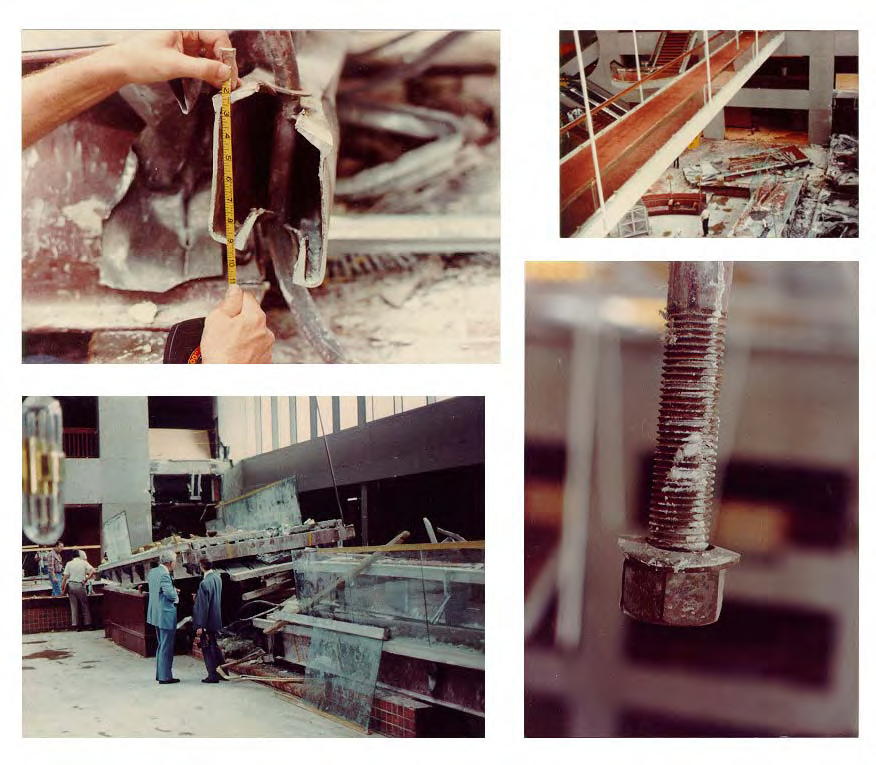
Pictures of the Hyatt Regency Collapse
The rescue squad reached the site soon after, and they included city fire, crisis recruits from the veritable army, doctors and paramedics from five region health hospices (Pfatteicher, 2010). The overwhelming situation prompted the city fire to invite workmen from a nearby construction corporation to give help.
The invited team arrived with heavy machineries like bulldozers among other tools and equipment. It is further noted that the disaster team erected a temporary morgue at the site to hold the dead; consequently, other facilities were turned into triage quarters. It was unfortunate that the debris blocked the water pipes thus causing flooding in the lobby area (Morin & Fischer, 2006). This further worsened the situation for the survivors because they feared drowning. The bulldozer helped in breaking the door to allow out water, and this led to saving other twelve people from the debris.
Plant and Equipment
It is clear that structural and architectural failures led to the collapse of the hotel. The fabricator, Havens Company, changed the design and used a dual rod system so as to simplify the assembly (Morin & Fischer, 2006). The change from single threaded rode to double shaft make the structure weak hence was unable to sustain heavy weight. The hotel had shown engineering setbacks before when the atrium’s roof collapsed.
This is a clear indication that the builders were not following the required procedures. It is further noted that the walkways were not designed to carry excess weight like the one it contained on the collapsing day. The investigations revealed that the parties involved in the construction of the Hyatt Regency did not follow the prevailing building codes.
Physical environment
The regency collapse occurred at the heart of Kansas, and this enabled the rescue team to arrive promptly. Even though, the disaster team arrived in time, the situation in the hotel could not allow quick evacuation. Heavy debris caused deaths and injuries; consequently, heavy machineries caused further hurt to the victims buried in the debris. The heavy weight of the fourth walkway increased the severity of the individuals in the 2nd course way, as well as, the atrium.
The accumulation of water in the lobby caused suffocation to several survivors, and this complicated the rescue process (Baura, 2006). The closed building did not allow easy entry to the hotel to rescue the victims. The heavy machinery had to maneuver their ways into the atrium to extract the wounded victims. The location of the hotel allowed enabled the rescue teal to arrive the scene at an accelerated pace. Disaster personnel like the medics and other workmen needed not to cover long distances to access the scene.
People and skills
It is regrettable that the experts concerned with the construction of the hotel did not employ professionalism in their work. Simple design negligence by the builders led to the collapse of the hotel. The overcrowding of people in the walkways led to its collapse due to the increased weight exerted on the path. Consequently, overcrowding in the down floor led to the death of many since many could be trapped.
The presence of many people did not allow for easy escape, and this caused further injuries. It is imperative to note that the speedy disaster team helped in saving lives by offering basic support to the injured. The skilled workmen from a neighboring construction company offered additional support to the rescue team. Skilled teams countered the effects of the flooding in the lobby by breaking the door to let water out thus saving the drowning survivors.
Systems/methods
The Kansas disaster did not have a well prearranged system to ensure a reinforced structure. It is pertinent to note that the design and the materials used for the construction of the hotel were repugnant. They thus failed to offer a lasting structure. The disagreement between the two consultants led to the collapse of the hotel since the final decision led to the fixing of fake devices (Morin & Fischer, 2006). The suspending devices were unable to sustain the added weight of visitors on the walkways.
Contrarily, the coordinated disaster team from various fields with varied expertise led to successful rescue of the people trapped within the debris. Veritable army and the workmen involved in the evacuation while the health team concerned with offering fundamental life support and other medical interventions.
Timeline of Events
The proprietor commenced the project of building Hyatt regency in 1976 and settled on G.C.E as the structural specialist which decided on a basic design in summer 1977. The project was set near the beginning 1978 based on the city’s building regulations, and the PBNDML Architects agreed to construct the building in April 1978. Actual construction began in the spring of 1978, and the Havens Company were contracted to erect and fabricate the atrium in December 1978.
This company changed the design of the 2nd and 4th walkways in February 1979 from solo to dual rod, and in October, the same year, the roof of the atrium collapsed. The construction of the hotel was completed in July 1980 and operations started the same time. On 17th July 1981, the two walkways collapsed killing 114 and wounding over 200 people. February 1984, professionals from various fields filed a case against the contractors and consultants of negligence and unprofessional move. November 1984, the builders were found guilty of the alleged unprofessional conduct (Baura, 2006).
Table 1: Timeline of the events
Table 2: Timeline of events continues
People and Organizations Involved
It is obvious that there were scores of players in the Hyatt Regency catastrophe including individuals and organizations. The proprietor of the building, Crown Center Redevelopment Corporation, is the chief player in the incident since the owner is directly affected. The consultants, G.C.E., and other contractors like the Havens Company were the chief parties blamed on the collapse of the hotel due to change of designs. Another crucial actor is the PBNDML Architects who constructed the 750m building thus they had a lot of information regarding the construction procedures.
The government officials concerned with the enforcement of building policies like architectures and surveyors were also involved during the period of construction. It is crucial to assert that the disaster team like the health professionals, city fire and authentic army among others played a crucial role in saving lives. Other imminent actors were the performers as well as visitors and the business community within the building. General public and the media were also considered key players (Baura, 2006).
Table 3: People and Organizations involved
Parties in the sphere of influence
More than a few parties were at the sphere of influence in the Hyatt collapse. The governmental departments like the architecture and survey were at the forefront of the disaster management. The authorities ensured that the regulations were followed to prevent future disasters. In particular, the national bureau of standard undertook an exploration to determine the causes of the collapse. The NBS further stipulated future precautions to the builders to prevent the same in the future.
The owner and other parties involved in the construction of the hotel were at the center stage in giving information during the investigation (Baura, 2006). They also played a crucial role in reconstruction of improvised walkways, which can resist such occurrences in the future. The performers and the audience remain the genesis of the disaster since their overwhelming number led to the fall of the 4th walkway causing serious catastrophe. Other survivors acted as bystanders who helped in the rescue of the affected as well as giving information.
It is imperative to assert that the disaster team like the health professionals, city fire and authentic army among others played a crucial role in saving lives. They employed their expertise in draining the flooded lobby and rescuing the trapped individuals, as well, as extraction of the dead. The media was another party due to the role of collection and dissemination of information. Updating the public through television and newsletters reduced the anxiety within the populace. The general public played a crucial role during the catastrophe in volunteering and dissemination of information to other concerned authorities since they were eye witnesses.
Solutions to the scenario
Several solution schemes can be devised to stop analogous incidences in the future. It is imperative to note that utilization of hierarchy of control can be exploited to formulate solutions to the incident. The use of Elimination is so far considered one of the best methods because it does not depend solely on people for it to control accident.
Risk elimination is considered the most practical means of preventing hazards from causing severe effects to human beings and machinery (Pfatteicher, 2010). This involves the abolition of poor technology like the hanging of causeways from the ceilings.
Consequently, materials like rods and bolts, which do not meet the dimensions, should be avoided. It is noted that the exclusion of poor engineering techniques could have save the situation. The walkways should not be directly above the atrium so that incase of an accident they do not fall on the lobby.
The next level of hierarchy of control involves the substitution of the dangerous by less hazardous so as to reduce the impact of the risk (Hughes & Ferret, 2009). The ineffective technology and equipment used in the construction of the hotel should be replaced with other effectual machinery.
The double rod used in hanging the walkway should be replaced with single rod, which proves more effective. It is further noted that the technology of hanging the walkways from the ceiling should be replaced. The best substitute is the construction of the walkways sustained by columns underneath at several points. Such supported course ways do not pose risks like the hanging paths.
Engineering is the third level of hazard control, and it involves upgrading of existing engineering appliances to deter future accidents (Ignacio& Bullock, 2009). This entails enhancing the effectiveness of the equipment to reduce the catastrophes in the future.
Engineers ought to have used the three shafts rising from the second flooring to the upper limit, instead of using a technology which sustained 60% of the least weight. Consequently, the designers should have avoided insertion the fasteners straight in a soldered joint since this is considered a weak structural plan. The welding should be improved to offer effective support to the metals and other joints.
The fourth level of control is administration which involves adequate training of personnel. The consulting and contracting firms should train their personnel so that they exude high levels of professionalism. Such actions enable the employees and workmen adhere to the guiding principles of construction. They can, therefore, apply appropriate technology where possible without compromising the quality of the structure.
The hotel management should also have fire extinguishers and other disaster response equipment. It should have trained personnel who can respond when disaster strikes. The last step accident control is the use of personal protective equipment (Ignacio & Bullock, 2006).
This is considered last in the hierarchy because it does not control the accident but reduces the severity of the impact after the exposure or accident. The building should store personal protective clothing like jackets and helmets so that people can wear when the house is collapsing. The people in the hotel should always be aware of the exit routes to escape when disaster strikes.
Best solutions for long and short terms
The key players during construction should apply appropriate long and short term solution to abate the accidents in the future. It is imperative to assert that elimination method is the best long term solution available since it does not depend on anything to control the hazard.
The consulting firm and other contractors are responsible for eliminating the possible future hazards to avoid loss of property and life. Designers should avoid the negligence in construction like using ineffective rods and nuts. The short-term method to be applied is the use of personal protective devices, and this should be implemented by all the key players plus the people who are likely to be victims of an accident.
Making the changes
The administration of the key players like the Havens, G.C.E. and others, should be responsible for implementing long-term changes. They are the designers during construction, so they are able to detect a wrong technology and eliminate it forthwith. They have expertise in recognizing the possible challenges in the future (Nadel, 2004).
It is further noted that the owner of the building is also responsible for implementing the long-term solutions since it is responsible for financing the development of the structure. Furthermore, the owner would not like to incur loses after the completion of the structure, hotel.
The government should offer supervisory and regulatory measures to ensure that all the requirements are met during the construction of buildings. The architectures, surveyors and other government officials should strive to offer advisory services to the developers to avoid incidences of collapse. It is imperative for the state to get involved because it is charged with the responsibility of safeguarding the lives of its people.
Furthermore, the builders should carry out research on the causes of collapse before making any adjustments. The implementation of short-term changes should be initiated by the administrations of the key players. The builders should seek advice on the possible personal protective equipment from the life experts (Nadel, 2004). The general public and the hotel visitors should be aware of the protective devices to reduce the impact severity in case of accident.
References
Baura, G. (2006). Engineering ethics: an industrial perspective. California: Academic Press.
Coppola, D. (2007). Introduction to international disaster management. Burlington: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Hughes, P. & Ferrett, E. (2009). Introduction to Health and Safety at Work. Oxford: Butterworth Heinemann.
Ignacio, J. & Bullock, W. (2006). A Strategy for Assessing and Managing Occupational Exposures, 3rd. Prosperity Avenue: AIAH.
Morin, C. & Fischer, C. (2006). Catastrophe: Kansas City Hyatt Hotel Skyway Collapse. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, Volume 6(2), 5-11.
Nadel, B. (2004). Building security: handbook for architectural planning and design. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Pfatteicher, S. (2010). Lessons amid the Rubble: An Introduction to Post-Disaster Engineering and Ethics. Baltimore: JHU Press.