Introduction
The labor market is characterized by wage rate differentials. There exists more than one labor market since firms require different types of labor for different jobs and this implies that the demand and supply for labor is different for specific labor time. The wages paid to employees also vary with the labor service provided.
If all the firms wanted the same labor, then a common labor market would exist, however, there are variations in labor needs of the firms and employees want different jobs in different firms. These factors have led to payment of different wage rates. This papers seeks to explain the reasons for differences in wage rates and their implication
Factors Responsible For Wage Differential
There are various factors responsible for different wage rates as explained below.
Compensating wage differentials
Not all jobs or occupations are the same and the degree or level of risk or injury involved is different in both nature and magnitude. For example, considering the level of risk associated with an occupation such as electrical engineering and teaching is different, an electrical engineer is more prone to death risk as compared to a teacher.
However, more often than not, the engineer is paid higher wage to compensate for the risk involved as compared to the teacher. Compensating wage rates are normally applied if the degree of risk associated with the occupation is high or if working conditions are poor. The implication is that there is a tendency for people to want to venture in occupations associated with high risk and even work in poor conditions in pursuit of the additional income that come with such offers.
Competition
Competition both within the industry and among employees has also contributed to difference in wage rates. Competition within and across industries is important to the issue at hand since it has led to a distinction between successful and unsuccessful. Successful firms, regardless of their size are able to pay better and higher wages than the unsuccessful ones.
The issue here lies in the ability of a firm to pay. It is therefore possible that two or more businesses in the same industry and dealing with identical nature of goods and services will pay different wages to their employees depending ion a firms ability to pay.
Competition among employees has also become a very important factor in that. employee performance appraisal is used to determine additional benefits to employees. An employee achievements and efforts are evaluated and then additional benefits are given or rewarded by the organization to serve as an incentive.
Employee productivity
Difference in wage rates can also be explained by the value added by an employee. This is especially true in the manufacturing industries where value addition is important at every stage of production. For better understanding of this concept, value addition is defined as the contribution by factors of production to the value of the final product.
Amount of labor required in production varies with the type of industry. For example, in a cloth-manufacturing firm, the value added by labor is lower than value added by labor in a paper manufacturing industry. The challenge lies in differentiating the actual value added by labor and that added by use of machines since in most cases, the two go hand in hand.
Sometimes, employees work as a team and it is difficult to measure the exact value added by each employee to the final product. The implication is that active employees may feel demoralized and lack the incentive to work hard and give their best and this may detrimental to the overall performance of the organization. The role of trade unions cannot be ignored in creating wage differentials.
Most of the highly paid employees have trade unions that bargains or negotiates with employers for salary increment. More often than not, such bargains bear fruits. On the contrary, poorly paid employees are not even able to form trade unions that can act as their voice in bargaining for better pay. This implies that the poorly paid will continue to receive such pays since their bargaining power is weak.
Skills
Nature or characteristics of the employment and formal education required for the job. This aspect cannot be explored fully without considering individuals socialization. Socialization in this context focuses on individual’s ambitions, self-motivation, and their willingness to adhere to the authority structures in place at that time.
Productive socialization is normally associated with attainment of certified qualification such as a degree or having a good work experience record. Socialization of an individual therefore plays a part to difference in occupation wage rates through cost differentials. This can be explained further in that there are different job entry levels in almost all occupations.
A fresh graduate from school with no previous experience cannot be paid the same amount as a graduate with experience for the same job. This is because the latter has an additional advantage in that he requires less training. In addition, if an employer is interested in a candidate with both formal and practical experience, the costs associated with search for such a candidate are higher as compared to getting a fresh graduate since in the former a more porous screening process is applied hence increasing the costs.
From the discussion on socialization, it can be argued out that occupation requiring less formal or academic training and less experience tend to have lower average wage rate as compared to those that requires higher formal academic qualifications and experience.
Gender and Race
Another cause for differential in wage rate that does not reflect the skills and abilities of a person in performing a job is race and gender. The question rotates around socialization since a certain race may be perceived to have negative socialization. The implication is that before an employer gets to higher them, a thorough screening process will be employed and as if that is not enough, the employer will see to it that such employees are monitored and supervised.
This in return increases the costs to the organization and in order to recover for such costs or minimize them, lower average wage rates are applied as compared to those from a race perceived to have positive socialization. The implication of wage differential is that the employees who are underpaid will tent to be less productive.
Gender has also been a base for wage differential and with special regard to women of childbearing age and the traditional perception of their role. There is a preconceived idea that occupations in which women work tend to have a high turnover rate due to the time they take in maternity leaves and their inability to work for long hours since they have other family responsibilities. The implication is that such cost is borne by all the women across occupations leading to lower wage rate.
Differences in Wage Rates. Average full time wages paid per week (pounds).
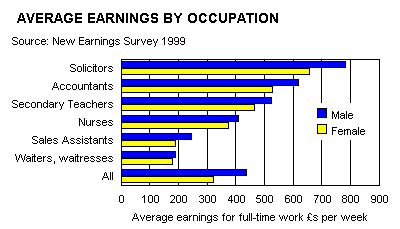
Wage Differentials in the Manufacturing Sector
To some extent, the wage differentials in the manufacturing industries are justified. This is because there are different departments and different processing stages and the skills required are different.
For example, there is need for unskilled labor to do those jobs that are not skill intensive, on the other hand, qualified personnel is required to perform the profession job. Therefore, the firm must be able to cater for all those labor expenses without passing a heavy burden on the consumer.
If the consumers are overburdened, the firm may be faced out by competition. In the manufacturing sectors, there is heavy capital investment on machines and technology that require special expertise and pose a great risk to the operators. Such employees will need an incentive to make them have the will to venture into such risky operations.
If the market forces of demand and supply continue to operate in determining the wages, then wage differentials will persist. This is because, it is difficult for the labor market to clear i.e. have supply equal demand. There will be increased and unskilled labor supply and the demand for the same will apply.
However, employers are interested in the marginal revenue product and will only employ it the marginal revenue product equals the marginal cost. With continued improved technology and better training facilities, the earnings of the skilled labor will continue and vice versa is true for the unskilled ceteris paribus.
Trends in Income Distribution and Wage Rates
From the study, it can be concluded that unequal distribution of income will continue to exist in the society with urban areas being in a better position as compared to the rural areas. This is because, most people prefer migrating to urban areas in search for better paying jobs since most industries and firms that can offer that are located in the urban areas.
Unless policies are implemented and incentives for delocalization are given, it will be difficult to achieve equality in income distribution. Difference in wage rates cannot be eliminated since it is not possible to pay common wages to all people since the nature of job and their requirements are different. It is possible that the gap between the highest and lowest paid employee will continue to expand.
Conclusion
Different occupations gave different wage rates since their requirements are also different and varied. Most employers pay wages based on the marginal revenue product gained from labor services offered and it should be equal to the marginal cost. Various factors such as difference in skills, competition, trade unions, nature of job and poor working conditions have accounted for the wage differentials.
Bibliography
Gleicher, D. L. Stevans, A classical approach to occupational wage rates,Greenwood Publishing Group, CA, 1991. Web.
Gottschalk, P., B. Gustafsson and E. Palmer, Changing patterns in the distribution of economic welfare: an international perspective, Cambridge University Press, NY, 1997. Web.
Holley, W., K. M. Jennings and R. S. Wolters, The Labor Relations Process. Cengage Learning, NY, 2008. Web.