Abstract
The present Information Technology sector has been growing rapidly, but here exists tremendous leadership gap in IT organizations and the concept of ICT leadership remains unclean; this study has aimed to identify the leadership styles and providing a clear understanding on the IT leaders at their organizations.
With these objectives, this paper has presented theoretical perspective of leadership styles, effects of leadership on organization, leadership styles and knowledge management, leadership styles and knowledge management, apposite leadership of IT firms, evidence of leadership gaps in the IT firms, leadership conflicts in the IT firms.
By interviewing 40 IT leaders of different firms, this study has identified that the modern IT firms need to have a new leadership approach rather than traditional leadership practice, which will focus on digital dynasty of this era.
Introduction
Background of Study
In the changing trend of the corporate world, leadership is a vital issue in organizational psychology; however, this chapter identifies the key challenges to the IT organizations to manage the performance of the human resources.
In addition, technological development from 1980s had made ICT a key element in the success of global business; therefore, great leaders are important to develop skilled workforce to manage different types of the activities of IT organizations.
At the same time, the effects of leadership in IT organizations include development the concept of ICT leadership, significance of team management, influence of leadership on knowledge management, change the role of leadership in the future, present trend of human resources of such companies and so on.
Statement of Problem
The capacity to attract and retain qualified employees is one of the key challenges to the IT organizations; however, previous research on the IT organizations have illustrated that staff turnover rate in this sector is extremely high, for instance, above 25% in India, 14% in China and more than 10% in the USA (Chandna & Krishnan, 2009).
However, it becomes difficult for the employees of such organizations to keep them up-to-date with the rapid technological development and innovation; in addition, it is also significant to note that the IT organizations need to transform operational efficiency due to change the business works for adoption of new technologies (Chandna & Krishnan, 2009; Pastore, 2000 and Kearney, 2004).
At the same time, these organizations need to concentrate on the knowledge management and efficiency development program to collaborate with new technologies (Chandna & Krishnan, 2009; Pastore, 2000; Kearney, 2004; and Den-Hartog & Koopman; 2011).
On the other hand, staff turnover rate had increased due to rapid expansion of IT industry in the global market; therefore, they have no effective commitment to the organization to reach vision of the companies (Chandna & Krishnan, 2009; Pastore, 2000; Kearney, 2004; and Den-Hartog & Koopman, 2011).
However, implementation of effective leadership styles can play vital role to mitigate above-mentioned challenges though investments in leadership and execution competencies are lagging far behind (Pastore, 2000; Chandna & Krishnan, 2009; Kearney, 2004; and Den-Hartog & Koopman; 2011).
Present IT organizations are not responding in accordance with the demands of their business by adopting new technologies (Pastore, 2000; Chandna & Krishnan, 2009; Kearney, 2004; and Den-Hartog & Koopman; 2011); most of these organizations in the developing countries have failed to meet future needs (Analoui, Doloriert & Sambrook, 2013; & Curraj & Vladi, 2013).
Purpose of Study
It is notable that leadership plays very significant role in engendering effective knowledge management function; the rationale of this study is to assess the leadership styles and their effects on IT organizations to contribute to theory by investigating magnitude of leadership; moreover, it provides analysis of different leadership styles particularly transformational style in IT organizations.
Research Question
There are many research have already conducted on leadership styles and their effect on organizations, but only few articles concentrated on the IT industry; however, this thesis considers the question how the organizational leadership styles will influence the performance of information technology organizations.
Literature Review
Theoretical Perspective of Leadership styles
Leadership style is an attribute, which received substantial attention in the management literature (Analoui, Doloriert & Sambrook, 2013; Politis, 2001; Adeyemi-Bello, 2001; and Curraj & Vladi, 2013); however, the following table will discuss on different types of leadership styles.
Table 1: Different types of leadership styles. Sources: Self generated from.
Effects of leadership on organization
Management theorists and researchers argued that profiles of leaders could reflect the performance of the companies as the leaders have the most important role in implementing an ideal leadership styles (Analoui, Doloriert & Sambrook, 2013; Adeyemi-Bello, 2001; Higgs, 2003; Dulewicz and Higgs, 2005; Chandna & Krishnan, 2009; Kearney, 2004; and Curraj & Vladi, 2013).
People-oriented or interaction-facilitative leaders concentrate more on the development of friendly and supportive environment and team efforts; however, people-orientation led to the higher level of performance though many research show different views (Adeyemi-Bello, 2001; Higgs, 2003; Dulewicz and Higgs, 2005; Analoui, Doloriert & Sambrook, 2013; Chandna & Krishnan, 2009; Kearney, 2004; and Curraj & Vladi, 2013).
At the same time, leaders of today’s business organizations have to demonstrate visualizing capability to design a clear portrait of the future to control their employees and enhance their expertise in the most attractive and efficient technique (Adeyemi-Bello, 2001; Higgs, 2003; Dulewicz and Higgs, 2005; Analoui, Doloriert & Sambrook, 2013; Chandna & Krishnan, 2009; Politis, 2001; and Curraj & Vladi, 2013).
In the era of globalization, skills are essential for effective leadership as they are responsible for managing change and leading employees in the competitive international business environment (Adeyemi-Bello, 2001; Higgs, 2003; Dulewicz and Higgs, 2005; Cacioppe, 1997; Analoui, Doloriert & Sambrook, 2013; Chandna & Krishnan, 2009; Kearney, 2004; and Curraj & Vladi, 2013).
Leadership Styles and Knowledge Management
Analoui, et al. (2013, p.4-37) conducted a landmark study in order to identify the appropriate leadership style for IT organizations with 153 companies of the UK involved in the business of Information and communication technology; most of them are engaged with web development, software solution, hosting, networking, and communication solutions, which are highly concerned with to knowledge management activity.
In the real life scenario, the ICT organizations are extremely well matched to the knowledge management area as they evidenced as knowledge demanding workplaces; however, most of their works and productions considered intellectual property and had taken the opportunity of copyright protection.
The implication of knowledge in the ICT organizations start from the customers’ demands with their selected primary knowledge and formulate digital products engendering effectual knowledge management activities in the manufacturing process where leadership has vital role to enhance apply existing knowledge and to contribute the ICT world by creation of new knowledge.
In the ICT organizations, the ‘Knowledge management’ is an umbrella term to understanding the capabilities of workforce for adoption of knowledge and it has been treated as a primary asset of the organization where leadership plays a critical role for maintaining and achieving competitive advantage by supporting effectual knowledge achievement and transfer.
Although there are very little works with the style of leadership that impact on knowledge management, the literature of knowledge management presented a strong accord of leadership with the knowledge management and argued that success and failure of such activities deeply concerned with the role of leadership (Analoui, et al. 2013, p.33).
Lakshman (2007, p.23) pointed out that among the different leadership concept and style, the categories of transformational and transactional leadership have been evidenced to put into practice of ICT organizations; at the same time, there are also some instance of amalgamating passive-avoidant style of leadership with the above two in order to raise further productivity of ICT firms.
However, the simple approach of transformational leadership presented five significant attributes, and these are presenting in the next table-
Table 1: five significant attributes of transformational leadership. Source: Self generated.
At the same time, the behavior and attitudes of such leaders attract and motivate the followers and team members to develop sense of power, self-confidence, improve values and beliefs to contribute increasing productivity of the organization.
Such leader himself inspires to improve the follower’s moral and ethical standards for decision-making, provides encouraging motivation and such leaders engage their highest efforts to motivate all around them by giving higher sense of understanding and attribute of taking challenges for their followers.
In the ICT organizations, transformational leadership also generates both individual and team spirit by encouraging the followers to visualize prospective future states that come from influential verbal communication, strong actions to construct confidence by inspiring eagerness to the intellectual incentive within the supportive environment for learning opportunities of the ICT organization.
On the other hand, the style of transactional leadership has two specific dimensions, such as, contingent reward and recognition reward; the first one approach of leadership illuminates expectations while the second one offers recognition while the ultimate goals are accomplished, the linked behaviors of such leadership approach provide support to others in exchange for their continuous efforts.
This approach also expresses contentment while the others meet up the targeted expectations of the management; the leadership clarifies values and principles for compliance, the leaders here formulate criteria to prevent ineffective performance, keep an eye to scrutinize performance as well as capture corrective action to attain higher performance.
Analoui, et al. (2013, p.4-37) and Lakshman (2007, p.23) pointed out that rather than the transformational and transactional leadership practice in the operation of IT firms; there is another approach of leadership named as ‘passive-avoidant leadership’ that amalgamated the first two approaches and lead to attain ‘management-by-exception’ through active structure of linked behavior.
In some contexts, ‘passive-avoidant leadership’ is totally different while the leaders merely engage with corrective action, the associated dilemmas turn out to be serious, final approach of this leadership is as much as accommodating that could be considered a situation of non-leadership, the followers stay away from leaders, lack of accountability and action could be significant issue in this regard.
Apposite Leadership of IT Firms
Curraj and Vladi (2013, p.301) pointed out that the developed countries are going through rapid technological boom due to quick technological development as well as user-friendly adoption of ICT in the academia, business, and real life practice, as a result, the ICT leaders are under pressure to improving their performance and increase sales revenue.
Due to backward linkage, the ICT sector in the developing countries had been improving remarkably to meet up the outsourcing requirement of the developed countries and continuously striving to deliver better service and improved quality of digital products where leadership quality is an important factor to that can accelerate the organizational decision-making aimed to produce better product and service.
Chandna and Krishnan (2009, p.1) pointed out the present extent of IT firms have been going through quick expansion and development where the importance of leadership has increased dramatically, the traditional approach of transformational leadership and even the transactional transformational leadership has very little impact on the information technology (IT) related organizations.
The transformational leadership along with its five associated work-related beliefs is less active in the IT firms than the non-IT sector and evidenced to have no straight cut effect on the commitment of the managers in non-IT and no effect at all in IT sector due to quiche technological advancement in this sector.
The leader’s motivation to adopt previous user-friendly technique rather than introducing new developments and reluctance to adopt and welcome the new technology could hamper the steady growth where working standard and ethic, Marxist views of workers, organizational values, spare time ethic, and humanistic considerations are required to restructure in the IT firms.
Karahanna & Watson (2006, p.171) presented a new model of Information system (IS) leadership, which is a very critical area within the practice of IT firms, due to the regular integration and practice, the IT firms are escalating their dependence on Information System for both the operational firmness along with increasing effectiveness of innovation practice with aim to implementing business strategy.
Here, IS Leadership style is totally different from the Leadership style of non-IT sector as the Chief Information Officer (CIO) is in the center of the model who engage his highest efforts to amalgamate the IS technical skills along with the practical understanding of the IT firms from their real-life experience.
The IT firms, from their corner to corner all functions of the company from operational management to the strategic would be interlinked with each other; as a result, a unique leadership challenges come into evidence within the technology dependant business interface that provide competitive advantages over the rivals.
Evidence of Leadership Gaps in the IT Firms
Leslie, Chandrasekar & Hannum (2008, p.5) had conducted a landmark study in developing and developed countries with the leaders from the east and west and identified that leaders from the Information Technology sector of developing countries like India and others are reflected themselves are not enough prepared to take the challenges of the quick shifting dynamics of this sector.
In the Information Technology sector globally, there exists a leadership in every country, the leaders from both the East and West have been assessed as ‘deficit’ of attributes and capabilities of strong leadership performance and most of them are laid behind the necessary level of leadership quality and emphasized to improve the leadership competence quickly.
The Center for Creative Leadership (2008, p.5) also added that competent leaders have to cheering the employees in order to build up their career in this sector could reduce staff turnover and it could be a better way out to overcome the major leadership gaps within the Information Technology sector (Leslie, Chandrasekar & Hannum, 2008).
However, lack of pressure and availability of job switching scope and moral dilemmas are the cause of lacking in this area, it is difficult to overcome such dilemmas until the industry as a whole do not agree to accommodate the switching employees without no obligation from the previous one.
Leadership Conflicts in the IT Firms
Curraj and Vladi (2013, p.309) pointed out another vital issue in the presents a conflicting situation while the CEO of the company comes from non-IT background and the leaders come from IT background, whatever the CEO’s competence includes there is no single element in this industry that can ensure steady growth that any CEO could ensure.
Within IT sector, CEO has no component to confirm higher productivity or he could not ensure competitive advantage without the continuous innovation of the IT leaders, the motivation for innovation and incentive attention to the necessary investment could ensure increasing productivity in the market; thus, the IT leadership has been gaining increasing importance in this sector with a superior magnitude.
It is also evidenced that the participation of the IT leaders in the corporate decision-making process has a positive impact on the growth and productivity of the company and could ensure right use of human capital utilized for innovation as well as higher return on investment.
The increasing role of IT leaders in this sector could not be effective without the strong support and assistance from the CEO, any conflicting situation between the CEO and IT leader could hamper the steady growth of the company, thus, the management of the IT firms should consider relationship of CEO and IT leader as a ‘binomial key’ to success.
The joint efforts of the CEO and IT leaders could focus on the right investment decision, ICT infrastructural improvement, and sustaining innovation that ultimately generate new employment opportunities both in the developing and developed countries that would ultimately contribute to the macroeconomic factors of the nation through new project opening (Curraj and Vladi 2013, p.310).
Conclusion
The rising demand for competent leadership in the Information Technology sector has been meeting up by the less competence leaders and going through a severe gap; although, it necessitates critical for efficient leadership that would be capable to translate the corporate visions into pragmatic business strategies, higher effectiveness for quick problem solving, coup with changes.
In the Information Technology business of modern era required to have bilateral cooperation and live communication between CEO and IT leader and it would produce appropriate justification of the economic scales, political dilemmas and corporate social responsibility by addressing the underdevelopment in the economy.
Methodology
Research Design
The main objective of chapter three is to design a methodological framework to describe the leadership styles and their effects on Information Technology organizations; this thesis will use quantitative research approach to explain collected information regarding leadership approach on the performance of the IT organizations.
Data Collection
Primary data has used for the definite research purpose while secondary data is existing information (Malhotra, 2009 and Sekaran, 2006); however, this thesis will consider both types of data.
Here, the researcher will prepare a questionnaire for data collection to discuss different leadership styles and their effects on IT organizations; however, sample size is forty-five (50) employees and managers from five (10) information technology organizations and it is expected that 40 usable responses would be received.
In addition, it will use management books, different peer journal articles, for example, Journal of Management Development, Tecnia Journal of Management Studies, Leadershil & Organization Development Journal, Journal of Emerald publication, Procedia: Social and Behavioral Sciences, and so on.
Data Analysis
Collected data regarding leadership styles and their effects on Information Technology organizations would be analyzed using Microsoft excel software.
Results
What is your responsibility in your company and you the head of your department?
This is a formal question, which would ask to introduce with the respondents; however, most of the respondents are holding responsible position in the information technology department of the organizations; in addition, 20% respondents are leaders of IT department.
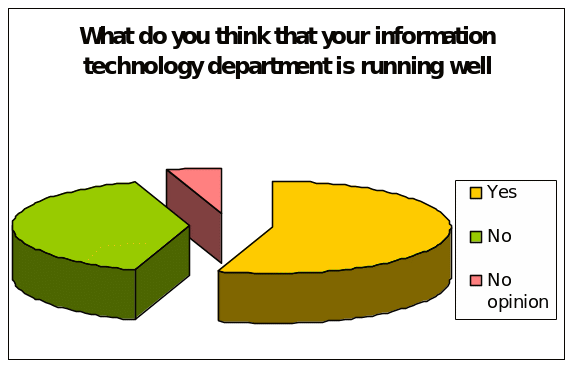
What do you think that your information technology department is running well?
In the support of this question, highest 55% of the total respondents or 22 employees argued that information technology department is running well; conversely, 40% respondents or 16 employees stated that information technology organizations department is not running well and only 5% respondents have no opinion in this regard; however, the following figure represents the result graphically:
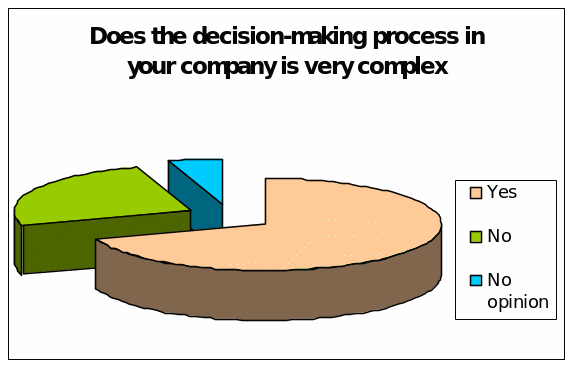
Does the decision-making process in your company is very complex?
According to the survey report on the employees and managers, highest 70% of the total respondents or 30 employees argued that the decision-making process of their company is very complex; on the other hand, 25% respondents stated that there is no complexity in decision-making process and 5% of the respondents have no idea or interest in this regard.
However, the following figure represents the result graphically:
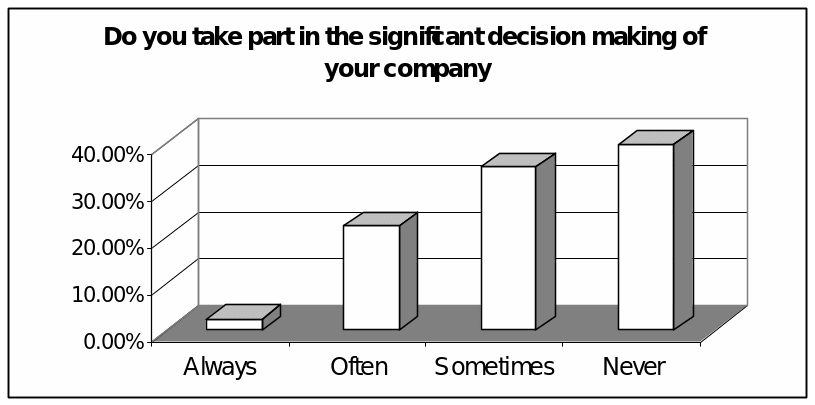
Do you take part in the significant decision making of your company?
In order to response this question, 2.5% respondent or only one respondent selected first option “always”, 22.5% of the respondents argued that the leaders often take opinion of the employees for decision-making purpose, while 35% respondents said leaders never consider their opinion and highest 40% respondents stated that leaders sometimes consider their view in case of organizational change and decision-making.
However, the result consistent with the secondary resources while management theorists and researchers argued that the leadership styles of information technology organizations are not based on the traditional approaches for which human resources of such organizations have limited scope to take part in decision-making.
However, the following figure represents the result graphically:
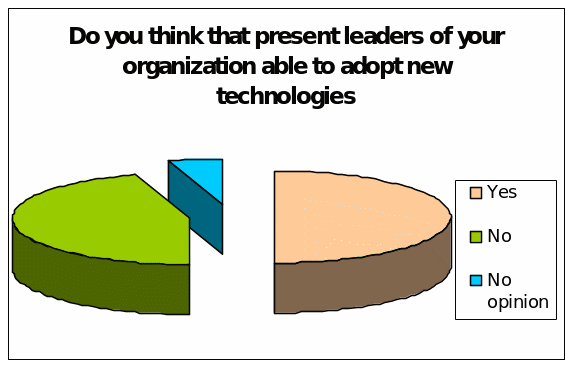
Do you think that present leaders of your organization able to adopt new technologies?
In the support of this question, highest 50% of the total respondents or 20 employees argued that information technology organizations are able to adopt new technologies; on the other hand, 45% respondents or 18 employees stated that information technology organizations have no ability to adopt new technologies with existing resources and only 5% respondents have no interest in this regard.
It is important to note that, the survey result consistent with the secondary resources since management theorists and researchers stated that today’s IT firms would not work tomorrow due to rapid technological development and lack of efficient human resources; however, the following figure represents the result graphically:
Do your leaders take any action for skills and knowledge development?
This is a significant question connecting with leadership style and knowledge management since the success of the IT organizations based on the performance of the skilled human resources since the business changes so fast, but the leaders get very limited time and resources to focus on the skills development and knowledge management.
In the response of this question, about 40% of the total respondents or 16 employees stated that the leaders of IT organizations are take any action for skills and knowledge development; in contrast, 55% respondents or 22 employees stated different opinion and only 5% respondents have no idea about the initiative of the leaders for skills development.

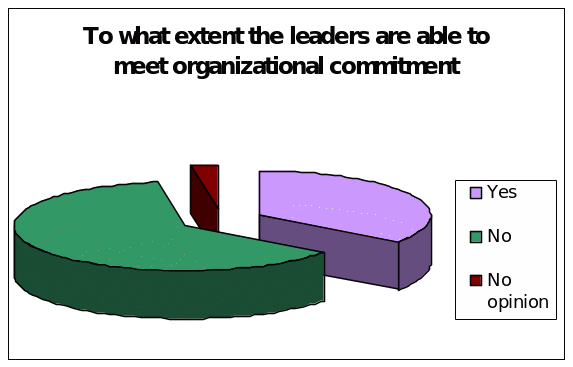
To what extent the leaders are able to meet organizational commitment?
This is one of the fundamental questions to assess the effectiveness of the leadership style in the IT organizations in order to make sure potential use of human resources.
According to the survey report on the employees and managers, about 35% of the total respondents or 14 employees argued that the leaders are able to meet organizational commitment, but 62.5% respondents or 25 employees stated that the leaders have no ability to meet organizational commitment and only 2.5% respondents had no idea in this regard.
Here, it is significant to address that, the survey result consistent with the secondary resources since Chandna & Krishnan (2009) researched on this issue and identified that transformational leadership has no influence at all in IT industry; in addition, Kearney (2004) argued that leaders of IT organizations could not be able to meet future demand.
However, the next figure represents the result graphically:
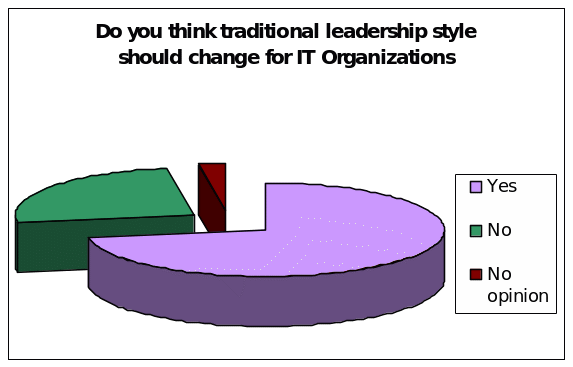
Do you think traditional leadership style should change for IT Organizations?
The aim of this question is to evaluate the effectiveness of the traditional leadership style in the IT organizations in order to find out a new leadership style for these organizations, such as, technology leadership, Information Systems Leadership and so on.
According to the survey report on the employees and managers, highest 72.5% of the total respondents or 31 employees stated that traditional leadership style should change for IT Organizations; on the other hand, 25% respondents stated that traditional approach should not change and 2.5% of the respondents have no idea or interest in this regard.
Here, it is significant to address that the survey result consistent with the secondary resources since the survey report of Kearney (2004) mentioned that more than 50% respondents support to change the traditional approach while Chandna & Krishnan (2009) stated that traditional approaches are very ineffective for IT organizations; however, the next figure represents the result graphically:
Reference List
Adeyemi-Bello, T. (2001). The Impact of Leadership Style on Organizational Growth. Web.
Analoui, B. D. Doloriert, C. H. & Sambrook, S. (2013). Leadership and knowledge management in UK ICT organizations. Journal of Management Development, 32(1), 4-17.
Cacioppe, R. (1997). Leadership moment by moment. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 18(7), 335-346.
Chandna, P. & Krishnan, V. R. (2009). Organizational Commitment of Information Technology Professionals: Role of Transformational Leadership and Work-Related Beliefs. Tecnia Journal of Management Studies, 4(1), 1-13.
Curraj, E. & Vladi, B. (2013). The Crucial Need for an Integrated ICT Leadership Approach toward Management with the scope of Improving Profitability into Local non-IT companies. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences , 75 (13), 308 – 317.
Den-Hartog, D. N. & Koopman, P. L. (2011). Leadership in Organizations. Web.
Dulewicz, V. & Higgs, M. (2005). Assessing leadership styles and organizational context. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 20(2), 105-123.
Higgs, M. J. (2003). Developments in leadership thinking. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 24(5), 273-84.
Karahanna, E. & Watson, R. T. (2006). Information Systems Leadership. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 53(2), 171-175.
Kearney, A. T. (2004). Why Today’s IT Organization Won’t Work Tomorrow. Web.
Lakshman, C. (2007). Organizational Knowledge Leadership: A Grounded Theory Approach. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 28(1), 51-75.
Leslie, J. B. Chandrasekar, A. & Hannum, K. (2008). Understanding the Leadership Gap A Quantitative Analysis of Leadership Effectiveness. Web.
Malhotra, N. K. (2009). Marketing Research- An Applied Orientation. New Delhi: Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Pastore, M. (2000). The value of word of mouth. Web.
Politis, J. D. (2001). The Relationship of Various leadership Styles and Knowledge Management. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 22(8), 354-364.
Sekaran, U. (2006). Research Method for Business. London: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.