Introduction
The purpose of this report is to analyze political environment of Lebanon, business environment, principal business activities, exports, imports, balance of payments, social, technological and cultural environment, demographics, GDP growth rate for the last ten years, banking and tourism industry, Hofstede’s country characteristics (power distance, collectivism, masculine, uncertainty avoidance and long-term orientation) and so on.
Demographics
Lebanon is situated at the eastern basin of the Mediterranean Sea and surrounded by northern Israel as well as western Syria; from north to south it has two parallel mountain ranges along with fertile Bekaa valley with an aggregate area of 10452 square kilometers composed by 454 km land boundaries and 225 km Coastline (ILO 2010, p.4; ARTI 2009, p.18).
As per Indexmundi (2012) statistics, the country has a population of 4.140 million 23% infants up to 4 years, 68% mid-age from 15 to 64 years and 9% old-age 65 years and above with a birth rate of 1.492% and death rate of 0.663% that results a negative population growth rate of -0.38%.
The demography of Lebanon consist with a number of ethnic and religious groups where Arab 95%, Armenian 4%, other 1%, its rough landscape along with external and internal threats collectively driven the inheritance towards isolation pedestal on religion, and ethnicity where the literacy rate 87.4% and the rate of urban population is 87%.
Political Environment
The Republic of Lebanon was a historical part of Ottoman Empire in the ancient era and gained its independence from French mandates in 1943, but the economic prosperity and geopolitical of the western powers and their collaborators in the Middle East have seriously hampered its political stability of the country and thrown it into long term regional conflicts.
Following the independence Lebanon turned into the melting pot with a variety of cultural heritage with huge immigration from neighboring countries for its economic growth and democratic practice with boost of academic and medical centers, but the birth of Israel, Arab-Israeli War, Palestinian refugees, Lebanese Civil War, Revolution Hezbollah, and regional and international interference destabilized the socioeconomic condition of Lebanon.
AMBCI (2012, p.4) pointed out that the wave of Arab Spring flourished in the Arab world have generated greater risk for Lebanon in the concurrent situation while the present government composed with Hizbollah along with its pro-Syrian associates, the western political actors like Sunnis are in tension and couldn’t cooperate the government to overcome crisis.
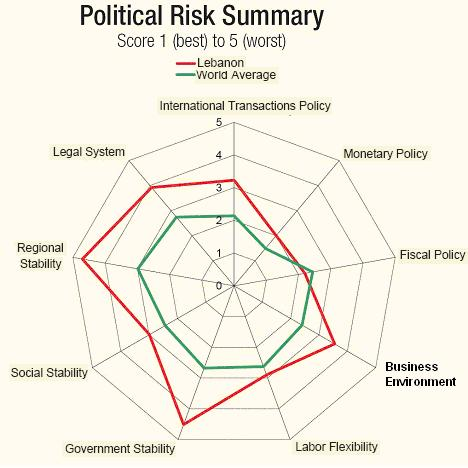
At the same time, improving relation of the government with Syria to allow to interfering in the domestic affairs, rising budget deficits, the decline in foreign and political pressure from the donor agencies have generated further challenges for Lebanon to melt down the socioeconomic unrest, the political risk summary has presented in the following diagram-
Cultural Environment
The historic and cultural heritage (cross culture of various civilizations) of Lebanon can be traced back from 6 thousand years ago; however, the following table gives more details in this regard –
Table 1: Cultural Environment. Source: Self-generated.
Technological environment
Development of information technology and communication technology helps the nation to improve efficiency in management (Ministry of Finance 2010, p.85).
Economic/Business Environment
The business environment or national economy of Lebanon based on some features, such as, long tradition of domestic free trade, no restriction on foreign investment to welcome foreign investors, exclusive monetary policy, and service-oriented economic activities, favor a strong role for the development of the private sector and no limitations on the movement of capital and goods Indexmundi (2013).
In addition, the Ministry of Finance (2010, p.22) reported that the government of this country provides facilities to the private business sectors because more than 85% of the total expenditures derived from this segment; however, the economy of this country is now facing difficulties due to the global financial crisis, unrest economic growth of Syria and downtrodden electricity sector.
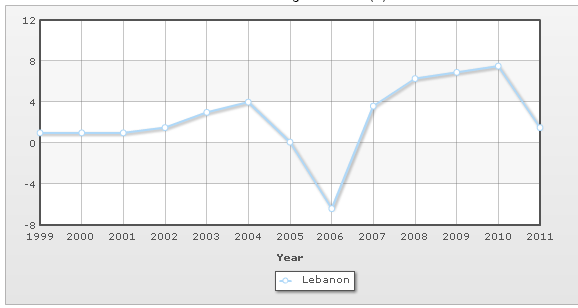
However, the following figure shows the GDP real growth rate for the last 13 years –
Principal Business Activities
According to the report of Ministry of Finance (2010, p.22), service sector is the main source of national economy particularly banking, tourism, insurance, and free port activities help the nation to face economic challenges; in addition, skilled manpower of this country able to use their innovative ideas to built an excellent reputation in the region.
In addition, Ministry of Finance (2010, p.33) stated that tourism segment becomes one of the most important segments of the national economy because mild climate and natural beauty, snow-capped mountains, Mediterranean Sea and modern and international hotels attract the tourist all over the world; however, this country generates more than 20% of the total national GDP from this segment.
At the same time, in 2009, Lebanon experienced the highest growth in this sector and expected to carry on this success in the future; however, the government and private investors are working to develop this sector, so, more than 1,851,000 tourists arrived in Lebanon in 2009, which was 39% greater than 2008.
Exports from Lebanon
Table 2: – Total exports. Source: – Self-generated from Simoes (2012) and Indexmundi (2013).
Table 3: – The main export collaborates of Lebanon. Source: – Self-generated from Simoes (2012).
Analysis of Imports
Table 4: – Total imports. Source: – Self-generated from Simoes (2012) and Indexmundi (2013).
Table 5: – The main Import collaborates of Lebanon. Source: – Self-generated from Simoes (2012).
Balance of payments
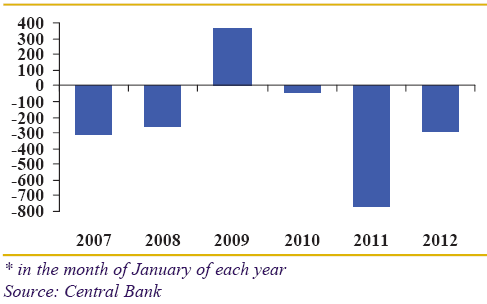
Central Bank of Lebanon estimates the balance of payment each January, and it demonstrates negative figures where expenditures exceed total revenues (though 2009 was a successful year); however, the following figure provides data for the last five years –
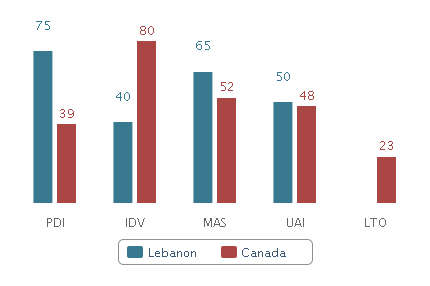
Hofstede’s Country Characteristics
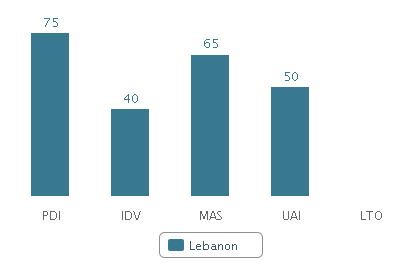
Table 6: Hofstede’s Country Characteristics – Lebanon. Source: Self-generated from Hofstede (2012).
Reference List
AMBCI. (2012). AMB Country Risk Report: Lebanon. Web.
ARTI. (2009). The Research and Innovation System in Jordan, Lebanon and the Palestian Territories. Web.
BYBLOS Bank. (2012). Lebanon This Week. Web.
Hofstede. (2012). Hofstede’s Country Characteristics – Comparison between Lebanon and Canada. Web.
ILO. (2010). Lebanon Country Profile 2010. Web.
Indexmundi. (2013). Country Profile of Lebanon. Web.
Ministry of Finance. (2010). Lebanon Country Profile 2010. Web.
Simoes, A. (2012). The Observatory of Economic complexity. Web.