Introduction
In this laboratory work, the dynamics of linear motion of a cart on a horizontal plane were studied to determine the relationship between the position of the cart and time, which is then used to find the relationship between speed and time. To perform the experiment, a cart moving along the rails by a controlled fan was used. The position of the cart relative to the starting point was recorded every 0.10 seconds. The acceleration for a given cart was determined from the fact that visual dependencies were plotted using a linear fit.
Data and Analysis
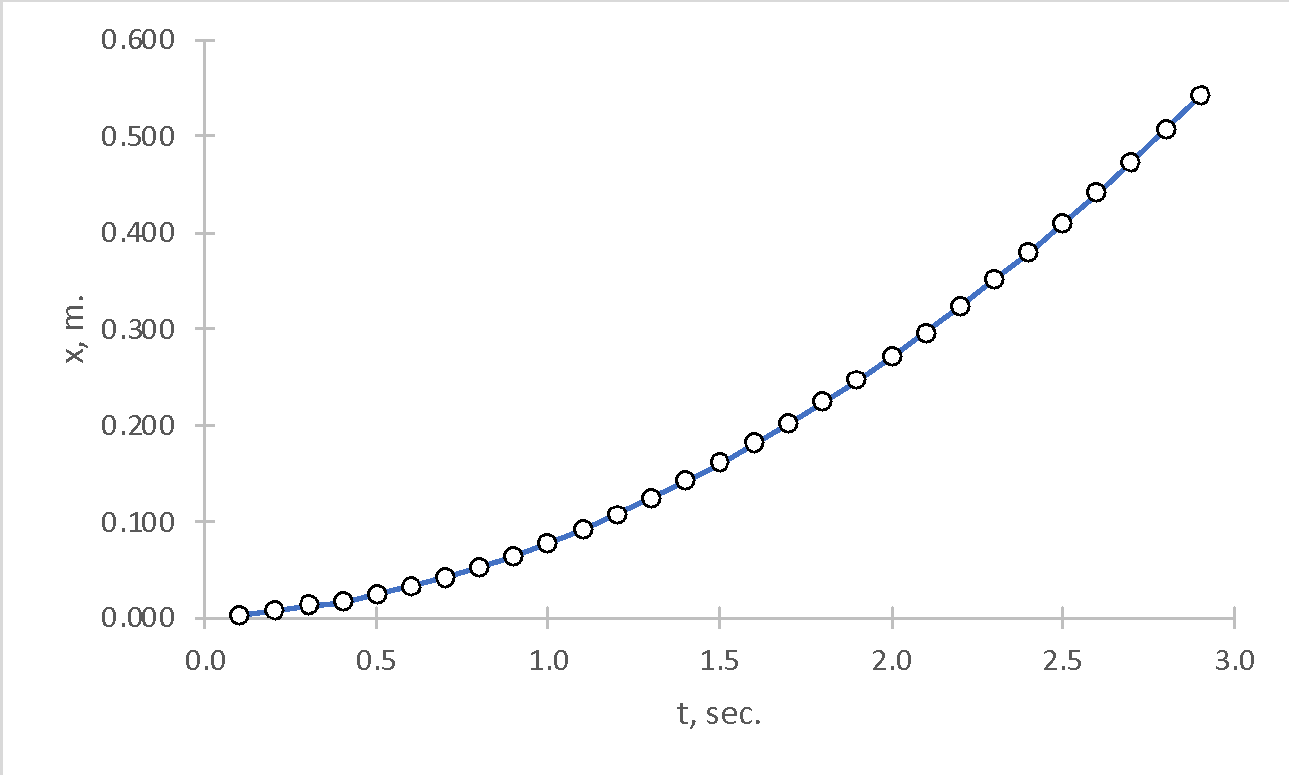
Table 1 shows the raw data that was obtained for the moving cart; in a general sense, Table 1 shows how far the cart moved over time. It can be seen that at the final time point (t = 2.9 sec.), the cart was 0.541 meters away from the starting point. Figure 1 visualizes this dependence and shows that with increasing time, the cart did move away from the starting point.
Table 1: Initial distance measurement results for a moving cart
Based on the data obtained using the formula ![]() , the average velocities for the points at the time
, the average velocities for the points at the time ![]() were calculated. It is worth clarifying, since the formula takes into account the average speed between the two points, the final number of points decreased to 28, because for the starting point the average speed was not determined. Fig. 2 is a graph of the dependence of the instantaneous speed of the cart on the time when the cart had this speed.
were calculated. It is worth clarifying, since the formula takes into account the average speed between the two points, the final number of points decreased to 28, because for the starting point the average speed was not determined. Fig. 2 is a graph of the dependence of the instantaneous speed of the cart on the time when the cart had this speed.
Table 2: Results of calculations of the instantaneous speed of the cart at the corresponding moments of time
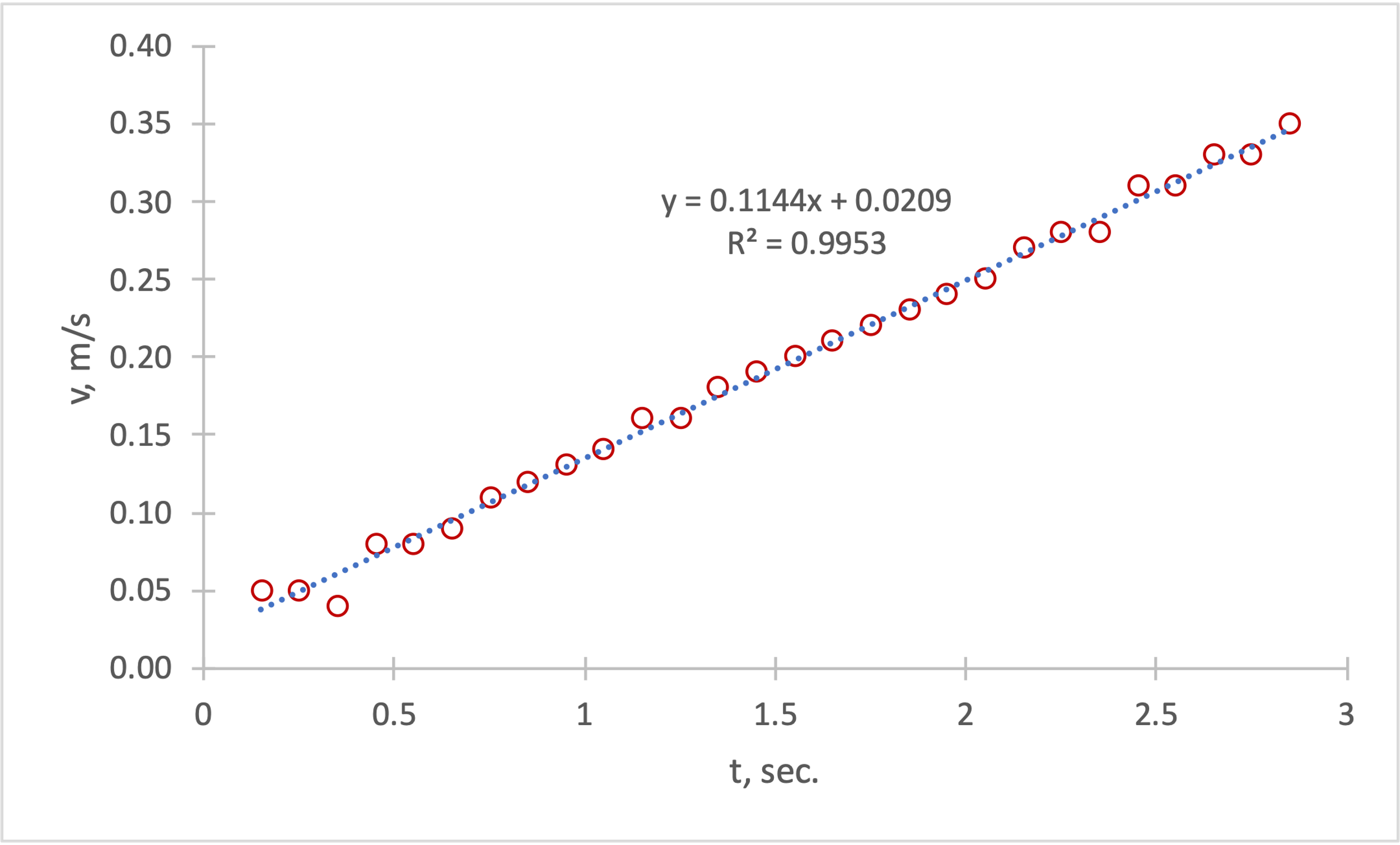
For the dependence shown above, a linear trend is evident: fitting shows that the coefficient of determination, in this case, is 0.9953. This means that up to 99.53% of the velocity variance is determined by this linear model, indicating an extremely high propensity for linearity in the distribution (Bloomenthal, 2021). From the constructed equation, it can be concluded that as time increases by one second, the velocity of the cart increases by 0.1144 m/s. This coefficient, the slope, also has a physical meaning. It is the acceleration of a given cart during motion. In contrast, there is no physical meaning to the y-intercept because otherwise, it means that at zero time, the cart had a non-zero velocity, which is not true.
Conclusion
In the present laboratory work, it has been shown that the dependence of the velocity of the cart as it moves in one dimension is linear with time. For this dependence, it has been shown that slope is an acceleration for motion, which means that this experiment can be used to calculate slope. It is worth pointing out that the uncertainties of direct measurements affect the accuracy of the results, so increasing these uncertainties may affect the accuracy of the conclusions.
Reference
Bloomenthal, A. (2021). Coefficient of determination. Investopedia. Web.