Purpose of the Paper
Linear programming can be an excellent tool for solving economic problems and making optimal decisions. This quantitative analysis enables the identification of the most profitable or suitable option based on mathematical solutions (Chaudhuri et al., 2019). In this paper, a plan will be developed to maximize income from the sale of all manufactured products. This method can be applied at the levels of governments, large corporations, and small to medium-sized businesses.
Defining the Problem
- The farmer can produce two types of products: cucumbers and potatoes.
- The income from the sale of each type of product is known: cucumbers, $3,000; potatoes, $2,000. For growing vegetables, three types of fertilizers are used, with reserves of 7, 8, and 3 kg, respectively.
- The costs of each type of fertilizer for the production of every kind of product are known: one kilogram of the first type and two kilograms of the second type are used per 1 ton of cucumbers. For 1 ton of potatoes – 2 kg of fertilizers of the first type, 1 kg of fertilizers of the second and third types.
- The farmer must draw up a production plan to ensure the maximum income from the sale of all output.
Acquiring Input Data
- Data and limits are based on calculations provided for this project, considering the cost of goods and raw materials required for production.
Developing a Solution
Table 1 – Resource Allocation and Production Data
- Planned production volumes of cucumbers = x1; Planned production volumes of potatoes = x2. Objective Function = 3×1 + 2×2
- x1 + 2×2 <= 7
- 2×1 + x2 <= 8,
- x2 <= 3
- x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0.
Presenting the Results
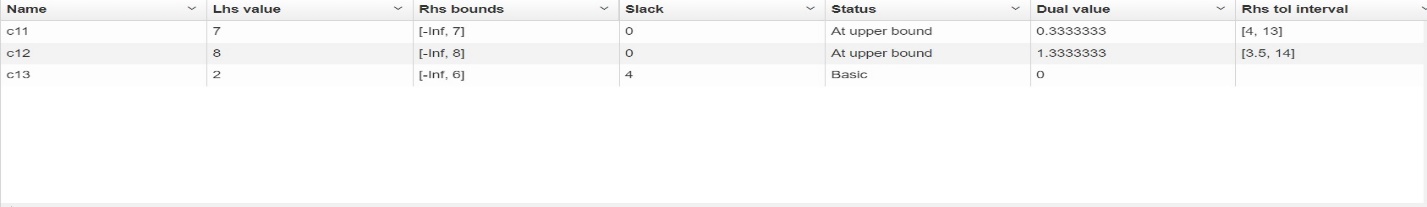
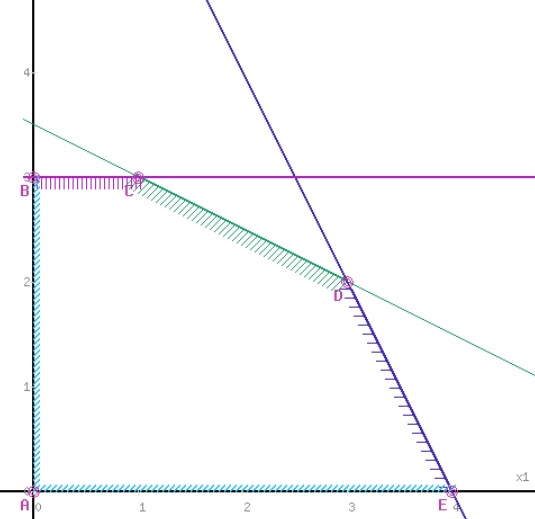
Sensitivity Analysis
Hatching indicates the half-planes corresponding to the inequalities. The set of all inequalities defines the polygon ABDE, which is the realm of feasible solutions. By changing the value of C, one obtains level lines that describe the behavior of the objective function (Feng et al., 2022).
Consequently, the objective function will reach its maximum value in the area of feasible solutions at point D. To solve the problem, it is necessary to find its coordinates. From an economic point of view, the optimal production volume of an agricultural object on one plot is three tons of cucumbers and two tons of potatoes. The maximum income from the sale of the crop will be $13,000.
Overall Recommendation
Subject to all the above conditions and considering the available fertilizers, the best option for a farmer would be to grow 2 tons of potatoes and 3 tons of cucumbers on each plot. With this option, the farmer can achieve a maximum profit of $13,000. It should be noted that the calculations might change if additional risk factors are included, such as price dependence on output, production restrictions, and (Cleff, 2019). Based on this calculation, modeling and programming are the primary methods for studying economic objects and processes since experiments on natural objects are either impossible or too costly.
References
Chaudhuri, M., Voorhees, C. M., & Beck, J. M. (2019). The effects of loyalty program introduction and design on short-and long-term sales and gross profits. Journal of the Academy of marketing science, 47(4), 640-658.
Cleff, T. (2019). Applied statistics and multivariate data analysis for business and economics: A modern approach using SPSS, Stata, and Excel. Springer.
Feng, Y., Niazadeh, R., & Saberi, A. (2022, July). Near-optimal bayesian online assortment of reusable resources. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM Conference on Economics and Computation (pp. 964-965).