Introduction
Dementia is one of the most common disorders in society that is associated with the loss of cognitive ability in aged adults. The condition may stem from brain injury or disease, which may interfere with the mind of an individual. Dementia presents a wide range of syndromes that entail language problems, memory loss, difficulties in communication, and problem-solving ability. To solve the problem, different measures are used with various levels of effectiveness. It is in this regard that is study highlights the management of dementia condition concerning the question stated below.
Framing of the Question
How effective is reminiscence group therapy in eliminating symptoms of depression in dementia patients?
The above-stated research question can be analyzed using the PICO model as stated below.
- Patient or Population: Patients with dementia
- Anticipated intervention: Reminiscence group therapy
- Current standard: Non-Pharmacological tool
- Outcome: Reducing depressive symptoms
Search Strategy
Five scholarly articles were identified for the topic. The articles presented information that could be used for evidence-based practice since the information provided the correlation between reminiscence group and its effectiveness as a non-pharmacological tool for reducing symptoms of depression. The scholarly articles include the following:
Blake, M. (2013). Group reminiscence therapy for adults with dementia: a review. British Journal of Community Nursing, 18(5), 228-233.
Bohlmeijer, E. Kramer, J. Smit, F. Onrust, S, & Marwijk, H. (2009).The effects of integrative reminiscence on depressive symptomatology and mastery of older adults. Community Mental Health Journal, 45(6), 476-484.
Croucher, M. (2009). Effects of reminiscence group in elderly people with Alzheimer disease and the vascular dementia in a community setting. Geriatrics and Gerontology International, 7(2), 167-273.
Robinson L, Hutchings D, Dickinson HO, et al. (2009). Effectiveness and acceptability of non-pharmacological interventions to reduce wandering in dementia: a systematic review. International journal of Geriatrics Psychiatry, 22 (1), 9–22
Van, P.J., & Maes, B. (2009). The Effect of Reminiscence Group Work on Life Satisfaction, Self-Esteem and Mood of Ageing People with Intellectual Disabilities. Journal of Applied Res Intellectual Disabilities, 22(1), 23-33.
Resources
Search Terms
To conduct an accurate search, appropriate guidelines were used as outlined in the table below.
Boolean Search Strings
The first step used in the search process entailed writing down the main phrase that was specific to the topic of the study. The phrase used in the search enabled the researcher to get the right information on the topic. The researcher typed the following phrase ‘Group reminiscence therapy for adults with dementia’ on the Google search engine. The next stage was the identification of a specific website that provided the required information. The researcher then proceeded to search for related terms from specific websites. Nice.Com was used as the website. The site provided information on other related issues of the topic such as non-pharmacological treatment. The search process can be justified as shown in the provided screen shorts.
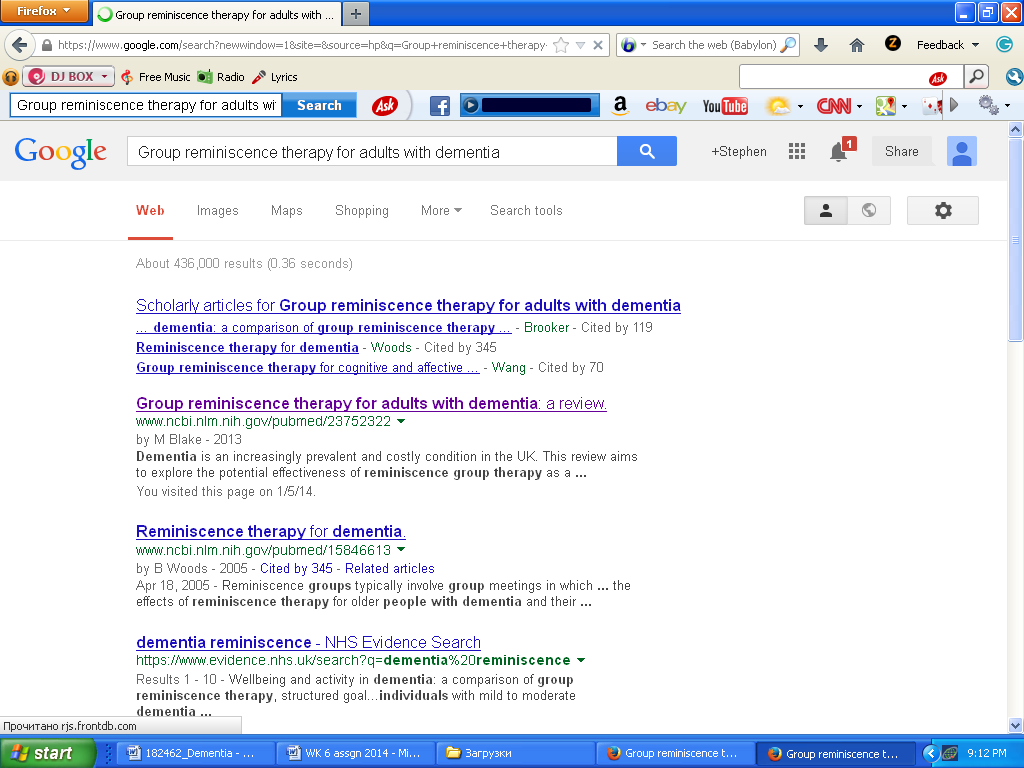
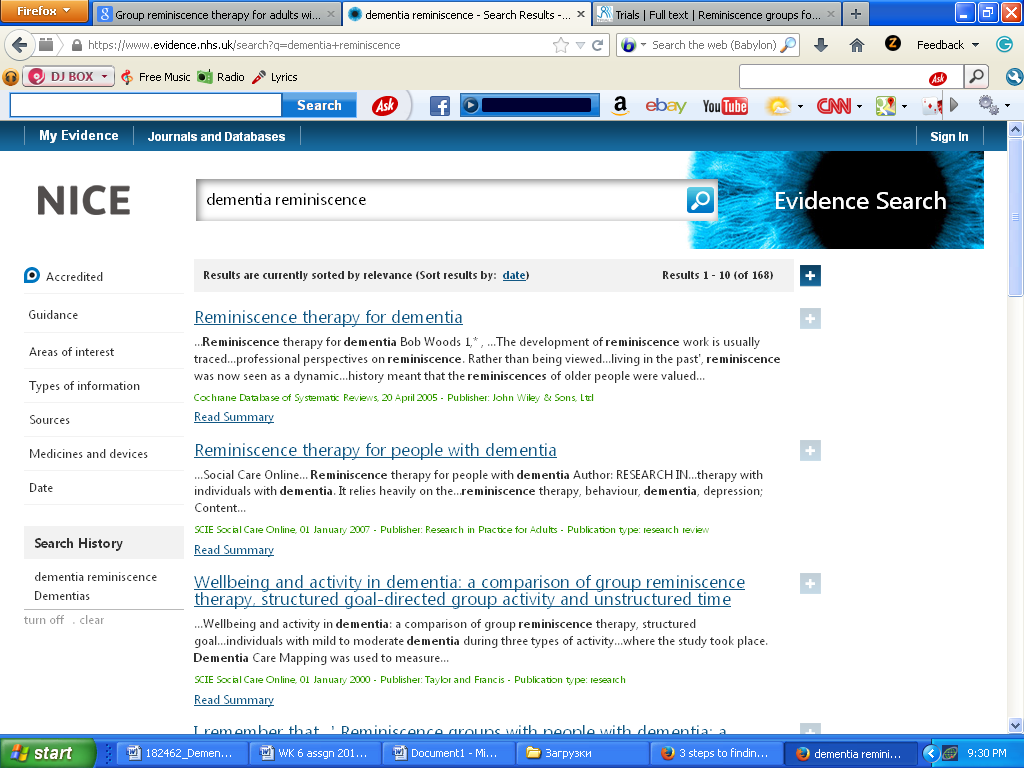
Literature Analysis
History and Purpose of the Research Question
Reminiscence group therapy is one of non-pharmacological approaches that was developed in the late 1990s to replace the use of pharmacological methods. Early researchers in the field of dementia discovered that pharmacological methods were not very effective in eliminating certain problems that affected dementia patients such as depression, low esteem, and self-confidence. The researchers also discovered that depression was one of the key problems that affect dementia patients. The position, therefore, justifies the ground for this research question.
Existing Literature
Gaps in the Current Literature
Current literature does not provide information on how non-pharmacological approaches such as group reminiscence can be used to ensure evidence-based practice in the management of dementia. The current literature tends to overemphasize the use of pharmacological methods in the treatment of dementia. Moreover, the current literature tends to over-rely on systematic reviews, which cannot provide adequate information on a given topic of research (Blake, 2013).
References
Blake, M. (2013). Group reminiscence therapy for adults with dementia: a review. British Journal of Community Nursing, 18(5), 228-233.
Bohlmeijer, E. Kramer, J. Smit, F. Onrust, S, & Marwijk, H. (2009).The effects of integrative reminiscence on depressive symptomatology and mastery of older adults. Community Mental Health Journal, 45(6), 476-484.
Croucher, M. (2009). Effects of reminiscence group in elderly people with Alzheimer disease and the vascular dementia in a community setting. Geriatrics and Gerontology International, 7(2), 167-273.
Robinson L, Hutchings D, Dickinson HO, et al. (2009). Effectiveness and acceptability of non-pharmacological interventions to reduce wandering in dementia: a systematic review. International journal of Geriatrics Psychiatry, 22 (1), 9–22.
Van, P.J., & Maes, B. (2009). The Effect of Reminiscence Group Work on Life Satisfaction, Self-Esteem and Mood of Ageing People with Intellectual Disabilities. Journal of Applied Res Intellectual Disabilities, 22(1), 23-33.