Executive Summary
The University of Modern Sciences (Dubai) is a local-based institution of higher education in the UAE. The university mainly offers biotechnology courses and caters to the educational needs of a diverse student population. Although the university aims to create respectable and productive members of the society, this report shows that the institution’s strategic performance has been dismal. Indeed, after assessing its internal and external environments, this report shows that its corporate-level and business-level strategies have failed to exploit its core competencies. Instead, the institution has relied on traditional competencies for the improvement of its strategic performance. However, stronger foreign-based universities have overshadowed such strengths. Consequently, analysts have ranked the university behind its peers. Based on this performance, this paper recommends a strategic shift from the institution’s traditional competencies to its key resources (resource-based view). The success of this strategy depends on its effective implementation, at a business level.
Background
Through the patronage of the Abu Dhabi Chamber of Commerce, UMS (2014) started offering science-based courses in 2010. Since then, the organisation has grown to become a prodigious university in Dubai, and the wider Middle East region. Today, the university mainly offers biotechnology courses (during its inception, the University was called the Biotechnology University College). However, the institution also offers other courses, such as “Forensic sciences, Industrial engineering, Pharmaceuticals, and Business” (UMS, 2014, p. 1).
Aim
This paper aims to understand the strategic framework of UMS (2014) by evaluating its vision, core competencies, environment, and competitive position. To do so, this report uses strategic management tools, such as the SWOT and PEST analyses. Comprehensively, the findings of this report could provide its managers with a broader perspective of their performance. This way, they would adopt effective strategies of exploiting present and future opportunities for growth and excellence.
Scope
The scope of this report covers the internal and external environments of UMS (2014). Furthermore, this report covers the strategic position of UMS (2014) in its product and group segments.
Vision and Mission
According to the official website of UMS (2014), the organisation’s vision aims to provide an opportunity for students to create and produce new and innovative products in the society. Through this vision, the organisation strives to equip learners with new knowledge.
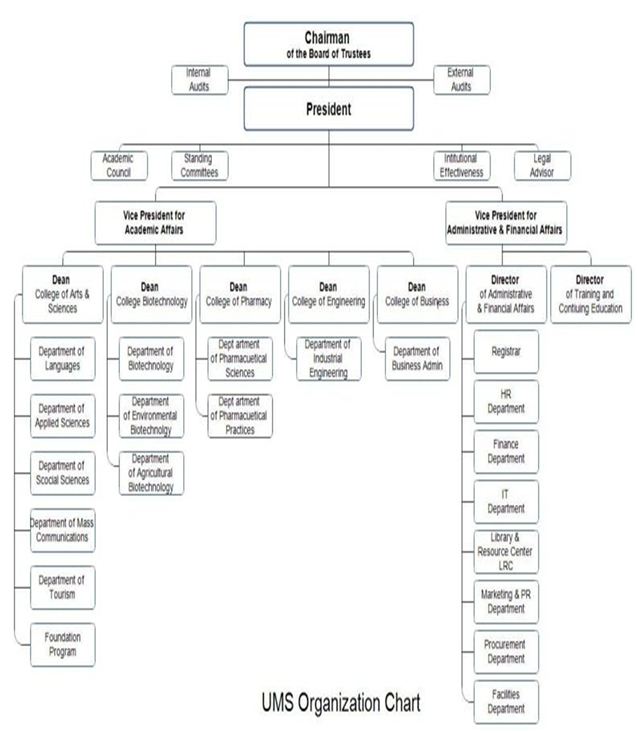
Organisation Chart
The organisational chart for UMS (2014) is broad and dynamic. However, at the helm of the institution is the chairperson of the board of trustees. The President of the institution operates under his leadership. Two Vice Presidents (Vice President for academic affairs and Vice President for administrative and financial affairs) support the functions and roles of the President. The Vice President of academic affairs oversees the roles and functions of five colleges – college of arts and sciences, college of biotechnology, college of pharmacy, college of engineering, and the college of business (UMS, 2014). Five Deans work under his leadership (the Deans supervise several departments). The Vice President for administrative and financial affairs manages the roles of two Directors – Director of administrative and financial affairs and the Director of training and continuing education. The Director of administrative and financial affairs manages different operational departments. The diagram below summarises this organisational structure.
PEST Analysis
A PEST analysis evaluates the political, environmental, social, and technological analysis of an organisation. This section of the report uses this framework to analyse the university’s external environment.
Political
Politics affect the activities of UMS (2014) in different ways. For example, political intrigues often affect the student admission process (particularly, the international student admission process). For example, political processes often influence the visa requirements for international students. Similarly, political processes affect the process of accreditation and licensure. Particularly, this process affects the expediency of the process.
Environment
Environmental concerns affect different aspects of institutional governance. In this regard, UMS (2014) has to reflect these environmental concerns in all aspects of its operations. Particularly, environmental concerns influence the institution’s curriculum design because students have to learn why sustainable development is important in their learning process (through existing learning programs).
Social
Beyond academic pursuits, UMS (2014) understands why it is important to maintain a good relationship with the community and other external stakeholders. For example, the institution participates in cultural engagement programs with other organisations (within the region and outside the region). The institution also encourages both students and teachers to participate in similar programs.
Technological
Technological developments have helped UMS (2014) to improve its service quality and student learning experiences. Particularly, technological developments have helped the institution to improve its facilities and equipment to familiarise students with modern learning processes. For example, technological developments have improved the institution’s E-resources (audio and visuals) for teachers and learners (UMS, 2014). This environment supports the institution’s state-of-the-art learning environment.
SWOT Analysis
This section of the report analyses the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of UMS (2014). Broadly, this analysis evaluates the institution’s internal environment.
Strengths
Technological Advancement: Technological advancement (in learning) is a key characteristic of the operations of UMS (2014). According to the institution’s official website, its academic strategy strives to ensure the application of latest technologies in all aspects of curriculum development. The institution also uses the same strategy to improve its academic service quality (UMS, 2014). UMS (2014) implements this strategy by exposing learners and teachers to new trends in learning and teaching. These events occur through symposiums, workshops, and similar forums.
High Quality Academic Output: UMS (2014) prides itself in providing high quality academic services. For example, the university has also collaborated with several reputable educational institutions (like the Hong Kong University) to expose learners and teachers to global standards of research and learning. UMS (2014) also benchmarks its academic output quality by monitoring all academic processes through an internal quality assurance team.
State-of-the-Art Learning Environment: UMS (2014) prides itself in providing academic and learning services in a state-of-the-art environment. The creation of this environment aligns with the organisation’s technological empowerment strategy because the institution has upgraded most of its facilities (such as laboratories and smart boards) to reflect its goal of providing learning services in a state-of-the-art environment. This environment has helped to accommodate the changing needs of learners and teachers.
Weaknesses
Limited Scope of Courses: In today’s expansive and dynamic global environment, educational institutions need to equip their learners with sufficient and dynamic knowledge. However, UMS (2014) offers a limited scope of courses. For example, most of the courses offered in the institution are biotechnology-based. There is a need to expand the scope of the courses to meet the needs of a dynamic global environment.
Admission Process: Since UMS (2014) is a leading university in the region, the institution’s admission process is very rigorous and competitive. Consequently, the university admits only a few students, who meet their admission criterion. This situation excludes many learners who would have benefitted from the institution.
Opportunities
Expanding Multicultural Diversity: Although UMS (2014) admits several international students, the institution could still improve the number of international students to create a more global outlook of the institution. This opportunity would improve the institution’s image. Moreover, it would enrich the students’ learning environment because interacting with students from other cultures would help existing students to develop a broader perspective of their environment.
Decreasing Response Time: UMS (2014) offers an opportunity for people to contact the administration, through the university’s website. However, the response time for general inquiries is long. The university should dedicate more resources to reply to such inquiries (such as employing more workers). This opportunity would improve the organisation’s efficiency (especially, its relationship with external shareholders).
Threats
Lack of Adequate Financing: Although UMS (2014) receives funding from different sources, it does not have enough funds to undertake all its research and development projects. Consequently, the organisation does not operate at its optimum. Similarly, this limitation threatens its research process by limiting its viability.
Overall, the diagram below summarises the above SWOT analysis.
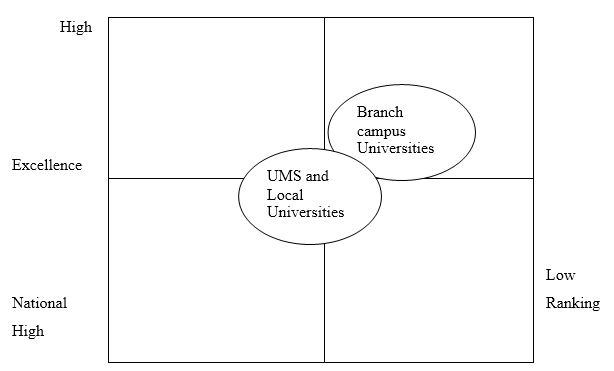
Strategic Group Mapping
Several universities in Dubai, and the wider UAE region, compete with UMS (2014). According to CSIC (2014), UMS (2014) ranks number 47 in the UAE ranking of the best universities. QS (2014) says UMS (2014) is among five local-based universities in Dubai that compete in offering educational products with 58 other branch campus universities in the Emirate. According to the latest university rankings, the branch campus universities have dominated the highest positions in university rankings (CSIC, 2014). UMS (2014) and other local-based universities have mainly trailed this list. The diagram below shows the strategic group map of UMS (2014), among its direct and indirect competitors.
Product Positioning Map
UMS (2014) mainly offers biotechnology courses. The institution is among five similar institutions, in Dubai, that offer the same product (biotechnology courses) (Swan, 2011). According to the product positioning map outlined below, “the American University of Ras Al Khaimah, the University of Sharjah, Manipal Dubai, and Amity University Dubai” (Swan, 2011, p. 14) offer direct competition to UMS (2014). The diagram below shows the performance of UMS (2014), compared to other universities that offer the same product
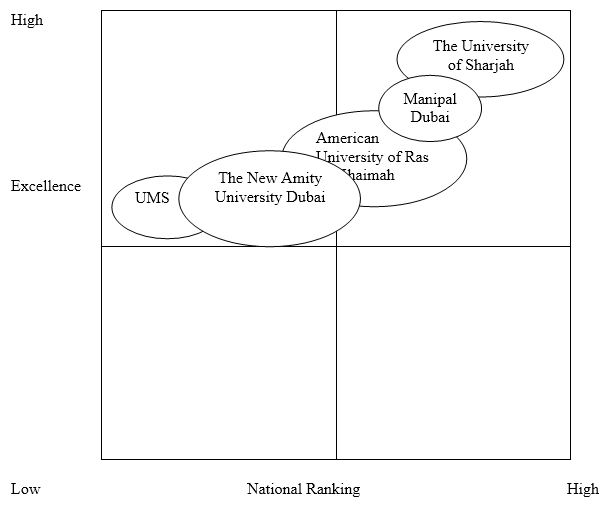
The diagram above shows that UMS (2014) trails the five institutions that offer biotechnology courses in the UAE. Stated differently, among the five institutions described above, UMS (2014) has the lowest excellence record and national ranking. This analysis shows that UMS (2014) needs to improve its product position among its competitors.
Strategic Analysis
Corporate-Level Strategies
Michael Porter (a renowned theorist) said businesses could increase their competitive advantages by adopting two strategies – cost differentiation and product differentiation strategies (Mind Tools, 2014). Through his generic theory, the diagram below explains these strategies.
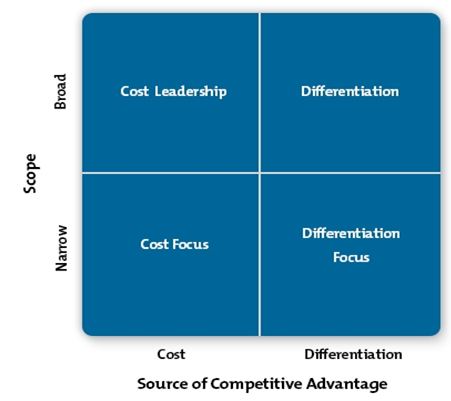
Already, this report shows that UMS (2014) trails other universities in offering educational products. Therefore, at a corporate level, the institution’s strategies have failed to increase the university’s profile in the regional and global ranks. A deeper analysis of the university’s differentiation and cost strategies appear below.
Differentiation Strategy: Based on the generic framework described above, UMS (2014) differentiates itself from other universities because it is local-based and specialises in offering biotechnology courses. However, based on the increasing number of universities that offer similar courses, UMS (2014) may soon lose this advantage.
Cost Leadership: Public universities in Dubai charge the lowest tuition fees. Comparatively, private universities, like UMS (2014), charge relatively higher tuition fees. Since there are more private universities in Dubai, than public universities, UMS (2014) does not enjoy the advantage of cost leadership. Instead, public universities enjoy this advantage.
Business-Level Strategies
The successes of corporate-level strategies often depend on the efficiency of business-level strategies. Based on the poor rankings of UMS (2014) in the regional and international education ranks, the marketing and quality assurance departments of the institution are responsible for the organisation’s success in this regard.
Recommendations
Adopt a Resource-Based View: This report shows that Porter’s generic theory outlines the use of differentiation and cost strategies to improve an organisation’s competitive advantage. However, these strategies do not appeal to UMS (2014) because the institution does not enjoy cost leadership (because public universities exercise this advantage) and differentiation advantages (because of the increased number of universities that offer similar courses). To counter these challenges, the institution could adopt a resource-based view of the institution to guide future strategic decisions. This view advocates for the use of strategic resources to improve its competitive advantage. Therefore, UMS (2014) would easily exploit some of its key resources (including physical, human, and institutional capital) to improve its competitive position in the market.
Particularly, the institution should focus on exploiting institutional resources that are valuable, rare, and inimitable. As highlighted in this paper, the marketing and quality assurance departments need to champion this strategy change. Particularly, the quality assurance department needs to improve the institution’s academic output quality by focusing on its resource competencies. Since this change would occur internally, UMS (2014) needs to communicate its progress to external shareholders through its marketing department. This strategic redirection should help the organisation to neutralise some of its threats and weaknesses.
Conclusion
This paper sought to understand the strategic performance of UMS (2014) by evaluating its vision, core competencies, environmental influences, and competitive position. This report also used strategic management tools to analyse the institution’s strategic position and performance (based on its internal and external environments). Key tenets of this report show that UMS (2014) trails its peers in the education sector. Although the SWOT analysis shows that the institution enjoys several core competencies, they do not match to the competitors’ competencies. Therefore, UMS (2014) has a poor ranking (among Dubai’s universities). Furthermore, the university trails other universities that offer biotechnology courses, which is its key area of specialisation. Through Porter’s generic theory and the resource-based view, this report proposes a shift of strategic direction to exploit the organisation’s key resources (as opposed to competencies) to improve its overall competitive position. This strategic redirection would help UMS (2014) to exploit (fully) its present and future opportunities.
References
CSIC. (2014). United Arab Emirates. Web.
Mind Tools. (2014). Porter’s Generic Strategies. Web.
QS. (2014). Universities in Dubai. Web.
Swan, M. (2011). Biotech courses gain a foothold. Web.
UMS. (2014). About UMS. Web.