Executive Summary
This report entails an analysis of HSBC Holdings, which operates in the banking industry. The firm has established a network of banks in different parts of the world. The report is organised into a number of parts. The first part outlines the company’s profile.
A brief background analysis of the company is illustrated by outlining the firm’s history, vision, mission, and organisational chart. The second part entails identification of the major challenges facing the firm.
The two main challenges identified related to employee turnover and exposure to risks associated with climate change. The report outlines and explains recommendations on the strategies that the firm should consider in dealing with the identified challenges.
The report also outlines how the firm can enhance implementation of the strategies identified by incorporating effective managerial roles. Finally, the performance measurement of the strategies and ethical issues that the firm might encounter are analysed.
Introduction
HSBC Holdings is a public limited company that operates in the global banking and financial services industry. The firm was founded in 1865 and it operated under the name “The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation” (Reuters 2013).
Its name was changed in 1991 to its current name, HSBC Holdings PLC. The firm has established over 9,500 financial institutions in Africa, South and North America, Asia, Europe, and the Middle East. The firm has a human resource base of over 310,000 employees.
HSBC has established a number of branches in the UAE. One of its branches is located at Abu Dhabi, UAE (HSBC 2013).
Vision
The firm intends to position itself as the leading international bank in the UAE.
Mission
Since its inception, HSBC has been focused on connecting customers with diverse opportunities, hence aiding them to achieve their dreams and ambitions. Moreover, the firm is committed towards supporting businesses in their operations.
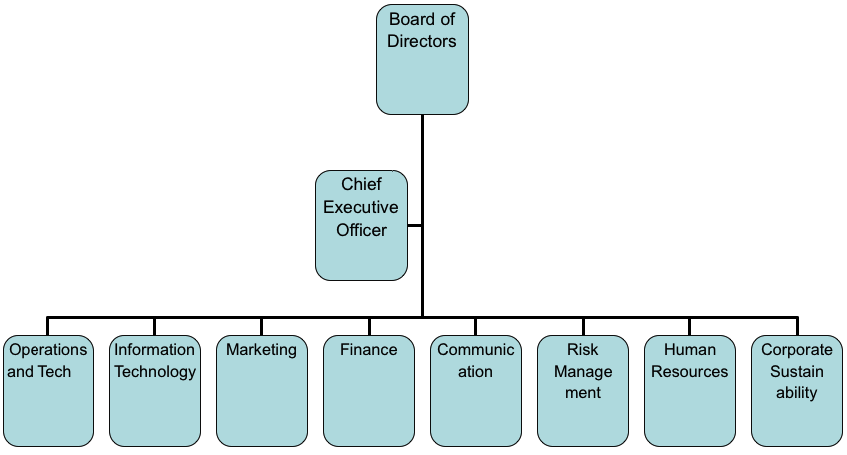
Challenges faced by the organisation
In the course of its operation, HSBC faces numerous challenges emanating from the external business environment. Employees play a critical role in organisations’ effort to develop competitive advantage.
Consequently, it is imperative for organisations to develop and maintain a strong human capital base. According to Griffin (2012), organisations should implement effective measures to discourage labour turnover.
A study conducted by Larissa (2012) shows that employee recruitment and retention are major challenges experienced by both private and public organisations in the UAE. Employee turnover has adverse effects on an organisations’ financial stability (Dan et al. 2013).
It is estimated that employee turnover cost organisations 15, 180 Dirhams annually. Apart from monetary cost, there are other non-monetary costs associated with employee turnover.
For example, employees who leave the organisation may join the competing firms. This aspect poses a major threat with regard to a firm’s competitiveness (Mollenkamp 2012).
By hiring employees who leave a particular organisation, competing firm may access knowledge and skills critical to an organisation’s competitiveness.
In a bid to achieve the desired level of competitiveness, HSBC should ensure that it develops sufficient competitiveness with regard to human capital, which highlights the need to formulate and adopt effective human resource management practices in the firm.
The second challenge facing the firm relates to the occurrence of climate change. HSBC operates as a credit lending institution. Consequently, the firm issues loans to both individual and institutional investors.
Firms in the banking industry are associated with climate change, as they provide financial capital to investors who in some instances, invest in activities that contribute to greenhouse gas [GHGs] emissions (Saleem 2010).
In line with its commitment towards improving the customers’ life, HSBC does not discriminate with regard to issuing loans. The bank issues loans to virtually all firms in different economic sectors.
In the course of operation, organisations have an obligation to operate in a corporate social responsible manner.
Lawson (2012) opines, “Management without caring needs and expectations of stakeholders in a community will not be competitive compared with those who do in the 21st century” (p.103).
Internal and external business environment
SWOT analysis
Internal business environment
The internal business environment is comprised of different elements, which include employees, corporate culture, the management and leadership processes, and employees (Hiriyappa 2008). Below is an analysis of the firm’s internal business environment.
Employees
The success of any business is dependent on the quality of human capital. Consequently, employees rank amongst the most important organisational assets. Therefore, it is important for organisations to ensure that their workforce has skills, attitude, and culture that align with the company.
HSBC is committed towards developing a strong human capital base. Moreover, the firm is cognisant of the importance of ensuring creating an environment conducive for working (Craig & Campbell 2012).
Corporate culture
It is important for firms to develop effective organisational culture. The organisational culture is comprised of a number of aspects, which include understanding the organisation’s mission, vision, values, and integrating effective management style.
In the course of its operation, HSBC has formulated organisational values that outline how its employees should interact with various stakeholders such as customers and regulators.
The firm’s organisational culture has played a critical role in establishing a strong relationship with its customers and the community.
Moreover, the firm has formed an organisational culture that is open to different cultures and ideas. In addition to organisational culture, a number of organisational principles guide the firm, which includes risk management, efficiency, speed, quality, customer-focus, integration, and sustainability.
Management and leadership
The firm has adopted an effective management and leadership style. The firm’s management style has enabled it to deal with changes emanating from the external environment.
On the other hand, the leadership style adopted by the firm has led to the development of an environment conducive for working.
Moreover, the management and leadership styles have contributed towards improvement in the employees’ level of job satisfaction (Tripathi & Reddy 2006).
Capabilities
In the course of their operation, it is important for organisations to focus on developing their core competencies. The firm has developed a number of core competencies, which include quality, efficiency, speed, customer focus, and performance focus.
These core competencies have contributed towards the development of a firm’s competitiveness.
External business environment
HSBC is affected by changes that emanate from the external business environment. According to Bates (2005), the external business environment can be categorised into two, which include the task and the general business environment.
The chart below illustrates the sources of external forces facing HSBC.
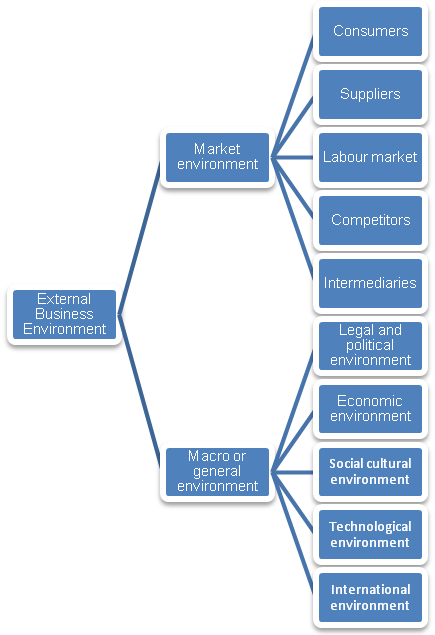
The chart above shows that forces emanating from the external business environment affect HSBC. The two main categories of task environment include customers, suppliers, competitors, intermediaries, and the labour market.
On the other hand, the general environment includes the political, legal, economic, social, technological, and the international environment (Ekins 2000).
Customers
Harrison and John (2010) posit that customers are a key component in the success of organisation in a particular industry.
In their pursuit for profitability, organisations have to ensure that their strategies are focused towards satisfying customers and ensuring that they achieve a unique customer experience.
Failure to meet the customers’ expectations may lead to a decline in the level of customer loyalty and hence the firm’s profitability.
Suppliers
HSBC is cognisant of the importance of developing a strong relationship with suppliers. The firm has formulated a comprehensive and inclusive procurement strategy.
The firm procures products and services from diverse suppliers and their relationship is robust. Moreover, the firm expects its suppliers to comply with the set of ethical standards.
Competitors
Businesses face direct and indirect competitors. HSBC may be affected by competition from both local and multinational companies.
The firm faces intense competition from a number of banks in the UAE, which include the Abu Dhabi Islamic Bank, Mashreq Bank International, National Bank of Abu Dhabi, Emirates Bank International, and the Dubai Islamic Bank.
Increase in the intensity of competition in the UAE will have adverse effects on the firm’s ability to maximise its profitability (Hashmi 2007). The chart below illustrates a summary of the external environment.
In addition to the above factors, the firm may also be affected by changes in the political, legal, social, economic, and technological environments.
Strategic considerations and planning
In a bid to address the challenges faced, the following strategies will be taken into account.
Organisational identification
The achievement of the set organisational goals and objectives is greatly dependent on the employees’ behaviour, which is influenced by the extent of employee and organisational identification.
Organisational and employee identification plays a critical role in motivating employees to continue staying in an organisation.
In a bid to develop organisational identification, the firm will focus on improving the employees’ behaviour, knowledge, and attitude towards the firm. The following strategies will be adopted in order to minimise employee turnover.
Reward management
The firm will formulate a comprehensive reward management policy. The policy will comprise both monetary and non-monetary benefits.
Some of the non-monetary benefits that will be considered include recognising employees who depict optimal performance and job promotions by conducting a comprehensive performance appraisal, thus ensuring that employees are fairly rewarded.
The firm’s management team will also ensure that it is effective in executing its organising functions. The firm will ensure that the jobs are designed in such a manner that they contribute toward enriching employees (Carpenter et al. 2011).
Inclusive decision-making
HSBC will also incorporate employees in the decision-making process by seeking the opinion of the employees before implementing decisions that might affect them. Consequently, transformational leadership style will be integrated.
Employee inclusion will play a critical role in minimising resistance from the employees and to ensure that employees are integrated adequately in the decision making process, the firm will ensure effective directing by nurturing communication, leadership, and effective supervision.
Employee training
The firm will also focus on assisting employees to achieve their career goals by integrating comprehensive employee-training programs. Through the training program, the firm will develop the employees’ skills and knowledge.
Consequently, the firm will increase the rate of employee retention and undertake comprehensive control on its training program in order to ensure that it meets the desired results.
Environmental sustainability
The firm is aware that climate change may affect some of its customers and hence their ability to repay loans (Hitchcock & Willard 2012).
In order to deal with the risks associated with climate change, the firm will integrate the concept of environmental sustainability by ensuring that its operations do not contribute to environmental pollution, either directly or indirectly.
First, the firm will be committed towards ensuring that its customers do not utilise the loans issued in a manner that contributes to climate change.
Before advancing credit to its customers, the firm will require customers to outline how they will ensure that the loans issued do not increase environmental pollution.
Secondly, the firm will be committed towards minimising the number of greenhouse gases emitted in its operation, either directly or indirectly by setting a benchmark of reducing its greenhouse gas emissions by 30% within one year.
In a bid to achieve this objective, the firm will shift to utilising renewable and clean forms of energy such as biofuels, solar power, nuclear energy, and wind energy. By integrating such forms of energy, HSBC will minimise controls from the government (Luo 2011).
For example, the firm will avoid carbon tax and ensure that the employees are adequately motivated in order to continue working in the organisation.
Performance measurement
In a bid to determine its success with regard to implementing the above strategies, the following key performance indices will be evaluated.
- Improving the rate of employee retention with a margin of 40% by evaluating the rate of employee attrition per annum in order to determine the effectiveness of the strategies integrated in order to improve organisational identification
- HSBC will conduct a survey on its employees in order to determine their attitude towards the organisation and their job and evaluate the degree to which the strategies implemented have contributed towards improvement in the level of job satisfaction amongst the employees.
- The firm will also evaluate whether its environmental sustainability strategies have contributed to the reduction of ‘financed emissions’ by 30% within one year of its implementation.
- Evaluating the company’s rating by renowned rating agencies such as Moodys and Standard & Poors on environmental sustainability
Ethical issues that might arise
- Decision-making issues: some employees might compromise the decision-making process by making unrealistic recommendations and opinions, which may increase the amount of time required to implement a particular decision, and thus the intended outcome might not be achieved.
- Compliance and governance issues: despite integrating requirements for customers to utilise the funds issued in a manner that does not contribute to environmental pollution, some customers might not fully comply; thus, the firm might not achieve its goal.
- Integrity and trust: despite integrating a training program in an effort to increase the rate of employee retention, some employees might leave the organisation. Consequently, HSBC might not achieve its intended goal in designing the program.
Conclusion
This paper depicts HSBC as an organisation that is committed towards satisfying its clients. However, the firm might be subject to changes in the external and internal business environment.
Consequently, it is imperative for the firm to integrate strategies to deal with challenges that emanate from the external and internal business environments.
By integrating the concept of organisational identification and environmental sustainability, the firm will be in a position to improve its competitive advantage.
Reference List
Bates, B 2005, Business management; fresh perspectives, Pearson Education, Cape Town.
Carpenter, M, Bauer, T & Erdogan, B 2011, Principles of management and organisational behaviour, Deone Zell, New York.
Craig, T & Campbell, D 2012, Organisations and the business environment, Routledge, Chicago.
Dan, O, Muyia, F & Holmer, T 2013, Consequences of employee turnover in the banking industry; a review of selected literature. Web.
Ekins, P 2000, Economic growth and environmental sustainability: The prospects for green growth, Routledge, New York.
Griffin, R 2012, Management, Learning Customer Publishing, Mason.
Harrison, J & John, C 2010, Foundations in strategic management, Cengage, Mason.
Hashmi, A 2007, ‘An analysis of the United Arab Emirates banking sector’, International Business and Economics Research Journal, vol. 6 no. 1, pp. 1-12.
Hiriyappa, B 2008, Strategic management for chartered accountants, New Age International, New Delhi.
Hitchcock, D & Willard, M 2012, The business guide to sustainability: practical strategies and tools for organisations, Routledge, New York.
HSBC: Supplier information 2013. Web.
Larissa, Z 2012, Human capital retention in the UAE, a brief review. Web.
Lawson, K 2012, New employee orientation training, Routledge, New York.
Luo, Z 2011, Green finance and sustainability: environmentally aware business models and technologies, Business Science Reference, Hershey.
Mollenkamp, C 2012, High turnover among HSBC top cops. Web.
Reuters: HSBC Holding PLC. 2013. Web.
Saleem, S 2010, Business environment, Pearson, New Delhi.
Tripathi, P & Reddy, P 2006, Principles of management, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi.