Introduction
McDonald’s in Germany is a part of the successful chain of fast-food restaurants that closely follow the other American and the European model. There are more than 1211 McDonalds restaurants in Germany and the restaurants cater to millions of customers. The business model followed in Germany is a mix of company-owned restaurants and franchised restaurants. This paper provides an analysis of the McDonalds restaurants in Germany with special emphasis on the advertisement features and campaign that the company uses.
ich liebe es (I love it)
The ‘I love it’ campaign was launched on September 22, 2003, and this was a global campaign targeted at Mcdonald’s customers across all countries. The German advertising company, Heyes designed the campaign. The budget for the campaign was 100 million Euros. The campaign was aimed at the 15 to 24 age group and included a number of print, TV, and banner Ads. A public casting call was announced for people to participate in the Ads and over 15,000 applications were received out of which 24 were chosen to appear in the Ads. Sample images of the Ads are given in the following table (ich Liebe es, 22 September 2003).
Table 1. Sample Ads from the ich Liebe es Campaign (ich Liebe es, 2003)


Schro¨der (Schro¨der 2005) has argued that McDonald’s is the single largest fast food retail chain in the world. The core brand philosophy is defined into three easy concepts: Food, people, and fun. The brand essentially stands for a combination of unique food products, customers, employees, and the atmosphere in which this happens. The brand stands for one of the easiest everyday pleasures in life. It conveys the philosophy that Ray Croc wanted to convey when he set up McDonald’s as a lifestyle brand. The author suggests that Consumer value plays a crucial role at the heart of all marketing activity of Mcdonald’s as it refers to things of value that have been created for a specific market.
Product Levels
Consumer value is a very complicated concept as it integrates a number of possible product quality attributes, process-related attributes and less tangible sources of value, and the brand image. The product level is defined at different levels such as nutritional, sensory, and hygienic. In addition, there are other attributes such as credence attribution, ethical attribution, and environmental protection (Dibb 2001). The standard McDonald’s menu of burgers and fries has been supplemented with chicken breasts, salads, fruit, organic milk, and free-range eggs for breakfast. The company distributes leaflets that promote the daily consumption of five portions of fruit and vegetables. The following table gives a broad breakdown of various product and menu items that the company provides. The offerings shown may differ be different in some restaurants and some of them may not have all the items that are mentioned.
PEST Analysis
The PEST analysis of the political, environmental, social, and technological factors that drive the business is given in the following section.
Political
McDonald’s has been faced with increased allegations about the vast natural resources that are being depleted to provide the restaurant with products such as meat, potatoes, and other forms of food. The mad cow disease scare hit the business hard, as customers were not avoiding beef products. The company has been accused of endangering large areas of South American forests that are cleared up to breed animals and to plant crops that are used by McDonald’s (Horovitz 2002).
Economic
According to Datamonitor (Datamonitor July 2006), the German fast food industry of which McDonald is a part has grown by 1.9% in 2005 and is worth 3.462 billion USD. By the year 2010, the market is forecast to have a value of $3,810.7 million, and this is an increase of 10.1% from 2005. The volume of transactions in 2010 is forecasted to be 2031.5 million and this is an increase of 4.1% from 2005. The fast-food market is defined as the sale of food and drinks for immediate consumption either on the premises or in designated eating areas shared with other foodservice operators or for consumption elsewhere. This means that the market share of Mcdonald’s is expected to grow in the coming years.
Social
There have been increasing outcry against the dangers of obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol levels that fast food in general and McDonald’s, in particular, have brought. There has been major criticism about health problems associated with continuous eating of high-fat restaurant food and victims of obesity have filed many billion-dollar suits. But the phenomenon of fast-food restaurants is here to stay and many companies such as McDonald’s, Burger King, Taco Bell, Subway, etc. have set up multi-billion dollar enterprises across different countries (Schlosser Eric, 2001).
Technology
McDonald’s has taken extra efforts to keep up with the best in technology and has used innovative IT solutions to increase its competitive advantage. A few years back, the company initiated the Project Seer that was intended to upgrade and overhaul the IT systems. The company used a Business Intelligence tool called Business Objects that helped the internal operations to be made more transparent. The implementation has allowed the company to improve the manner in which data from everyday sales is handled. This allows the strategic management team to understand which products are moving fast, which have lower sales, how much time is taken to complete an order, and so on.
The implementation also allows promotion offers to be more focussed. When a special promotion item is introduced, it is possible to know how the promotion has impacted the sales of other items, what items can be bundled to make the offer profitable, and so on. The implementation has also simplified the accounting procedures and the made customer complaint resolution much easier. The innovation allows the company to compare the sales figures of branches that have fewer complaints with sales figures of branches that have higher complaints. The company has also used technology innovations by using the web-based Restaurant Locator, using RFID tags, and the manner in which it makes the famous French fries that have the same taste no matter where they are eaten (Tiley 2004).
Five force analysis
Porter’s Five Forces analysis helps to identify the forces that influence the activities of Mcdonald’s in the market (Datamonitor 2006).
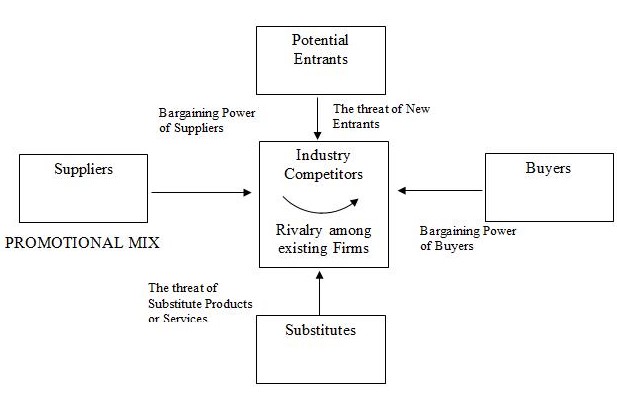
Promotional mix
Suppliers
McDonald’s supplier base is from third world countries and various ranches and farms in different countries. It is heavily dependant on the supplier who has to power to disrupt the operations and bring it to a standstill.
Industry Competitors
The leading players in the German market are McDonald’s Deutschland, Burger King Holding, Yum! Brands, and Nordsee Group. The German fast food market is fragmented and hence competition remains intense. Consumers are deluged with choice, and the availability of substitutes is high. The threat of new entrants is also high, although stringent hygiene standards raise the entry costs somewhat. Consumer demand is critical and influenced by factors such as spending power – which is dropping in Europe – public perception, health trends, and so on. Food is perhaps of less cultural significance in Germany than in countries such as France, and fast foods are inexpensive compared to other forms of eating out. Slow growth in the German economy generally has led to greater price consciousness in many markets, and the fast-food companies have responded in some cases by introducing ‘budget’ menus (Datamonitor 2006).
Buyers
Buyers have a wide choice in the form of suppliers and menu items. The market is also price-conscious and they have become increasingly health-conscious of the food they eat. Increasing health awareness, in part due to the rise of obesity and obesity-related conditions across Western Europe, has impacted negatively on the fast-food market. Consumers are also increasingly demanding organic, ethical, and GM-free food, although the demand for low-carbohydrate food has declined. Companies such as Mcdonald’s are attempting to mitigate the effects of changing consumer preference by broadening their product and brand portfolios to include healthier options and therefore retain revenues. McDonald’s is also engaging in a campaign to educate European consumers about the health content of its food (Datamonitor 2006).
Substitutes
Other than the major retail chain restaurants, there are a number of local shops and chains that operate in a locality or a town. These units have lesser operational costs and are able to offer customized service to their customers in the form of different flavors, different beverages, different choices of toppings and fillings, and so on (Datamonitor 2006).
German market segmentation
The market is broken down into four segments: Quick Service Restaurants (QSR), Takeaways, Mobile & Street Vendors, and Leisure Locations. QSR’s areas are defined as locations where the primary function is to provide full meals but where table service is not offered. Takeaways are defined as: establishments that provide freshly prepared food for immediate consumption and where typically 80% or more of revenues come from consumers who take the food off the premises to consume. Mobile & street vendors are defined as: Either individual mobile stalls or vans that offer a limited range of freshly prepared food as well as beverages. Leisure locations are defined as locations serving food and drinks for immediate consumption on-premises within leisure outlets (such as Cinemas, Theatres, Racecourses, etc.) that the Leisure operator owns and operates itself. Quick service restaurant fast food sales form the German market’s most lucrative segment, generating total revenues of $1.8 billion in 2005. The market is forecast to accelerate its performance, with an anticipated CAGR of 1.9% for the five-year period 2005-2010. Franchising remains an important way for large players to expand the number of their outlets.
Factors affecting the German market
The German fast food market has seen some fluctuation in its growth within the last five years. People find quick-service restaurants the most convenient place to buy their fast food, and these outlets account for the highest volume of transactions and the most lucrative share of the market revenues.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis of the company is provided in the following table (McDonald Corporation, 23 June 2007).
Reason for adopting the same type of advertisement
McDonald’s is a global brand with commonly shared values across all its franchises when it comes to serving customers. To customers, the “real” McDonald’s is playful, optimistic, distinctive, delightful, and authentic, and caring. The rules of advertisement have changed and customers are smart about marketing. They don’t McDonald’s to advertise at them but they want to be part of the conversation. They want to connect to brands the way they connect to each other. By using a common theme of advertisement, it creates a uniform message of excellence in quality and service, wherever Mcdonald’s is sold (Dillion, May 2006).
Benefits of Branding
According to Dibb (Dibb 2001), Branding helps to create a sharp focus on the business and this increases the overall effectiveness. Marketing activities will attract the right prospects for the service. The business development strategy and plan will be aligned for increased success. Core communication would be created that reflects the benefits, features, and unique selling points of the product. The product will have a clear and consistent value and presence and this provokes customer confidence.
Conclusion
The paper has examined various features of the I Like it advertising campaign run by McDonald’s. The paper has also provided a PEST and SWOT analysis and examined the market segmentation and analyzed Porter’s Five Force analysis. The reasons for adopting a common advertising strategy have been examined and the benefits of branding have been studied.
References
- Buchholz Todd, 2004. Burgers, Fries and Lawyers. Journal Policy Review. 123. p. 45.
- Datamonitor (2006), ‘Fast Food in Germany’, Datamonitor Industry Report, Reference Code: 0165-2230.
- Dibb, S. (2001), ‘Marketing, Concepts and Strategies’, Boston, New York. Web.
- ‘ich liebe es’ (2003), ‘How one a 100-millions-euro-budget locally, nationwide and internationally looks’.
- Dillion, 2006, ‘Dillion WFA Speech-Draft 8’.
- Horovitz Bruce (2002), ‘McDonald’s looks beyond burgers’. Web.
- Lancaster, G., Reynolds, P. (1999), ‘Marketing‘, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford. Web.
- McDonald’s Corporation (2007), ‘SWOT Analysis of McDonalds’, Datamonitor, pp: 18-21.
- Online Translation (2007), ‘Prompt Online: German to English Translation’. Web.
- Schro¨der Monika J.A. (2005), ‘Fast foods and ethical consumer value: a focus on McDonald’s and KFC’ British Food Journal, Volume 107, Issue No 4, pp: 212-214.
- Tiley Steve, 2004, The Information Age Interview. Web.