Research Sample: the Spanish Multinational Companies (MNCs)
- Telefónica, S.A. It is the telecommunications company functioning in the Latin America and a list of the European counties.
- Atento. The company offers the telephone and informational technology support for businesses. Located in Argentina, Peru, Mexico, and Central America.
- IberdrolaGeneración, S.A.U. The energy and electricity company that operates in the USA, the UK, and Brazil.

The functions of the political system
- “In every political system, there is a set of political structures or institutions which initiates and processes inputs and converts them into outputs” (Jay, 2009, p. 105). The political structure converts demands into policies and regulations, the application of which leads to particular results.
- The political system interacts with its environment. It draws human and financial resources from the environments, i.e. taxes. At this stage, the organizational performance is assessed by governments, and the businesses can experience the increasing level of the political participation.
- The political system sustains itself through legislation and its adoption in the society.

The Political Risks in the International Business
- Overall, the political risk can be defined “in terms of loss of control over ownership or loss of benefits of enterprise by government action” (Fitzpatrick, 1983, p. 249).
- The causes of the political risks emergence include both the unexpected shifts in the political environment within the country and the changes in the form of relationship of the country to other countries (Butler, 2012).
- The risks involve the financial and operational restrictions. The government can limit the corporation’s freedom by imposition of the employment policies, exchange controls, limitation of the ownership and financial rights, discrimination through taxes, and even damage to property through riots or wars (Kim & Kim, 2009).
- The multinational companies also face the risk of expropriation. The government can confiscate the company’s assets or sale it to the local businesses.
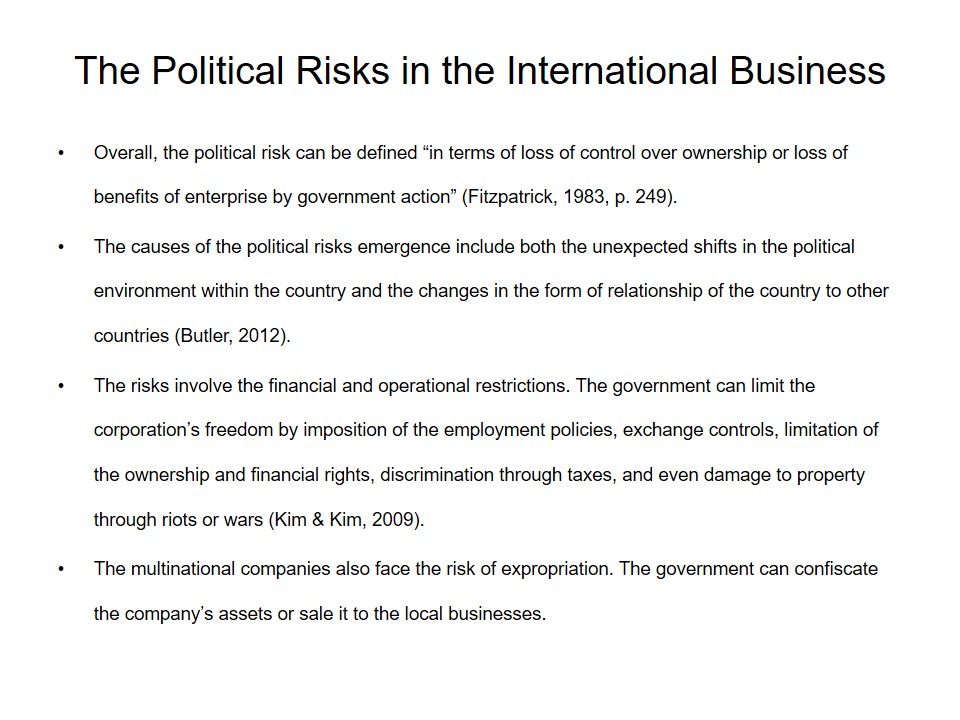
Telefónica, S.A.
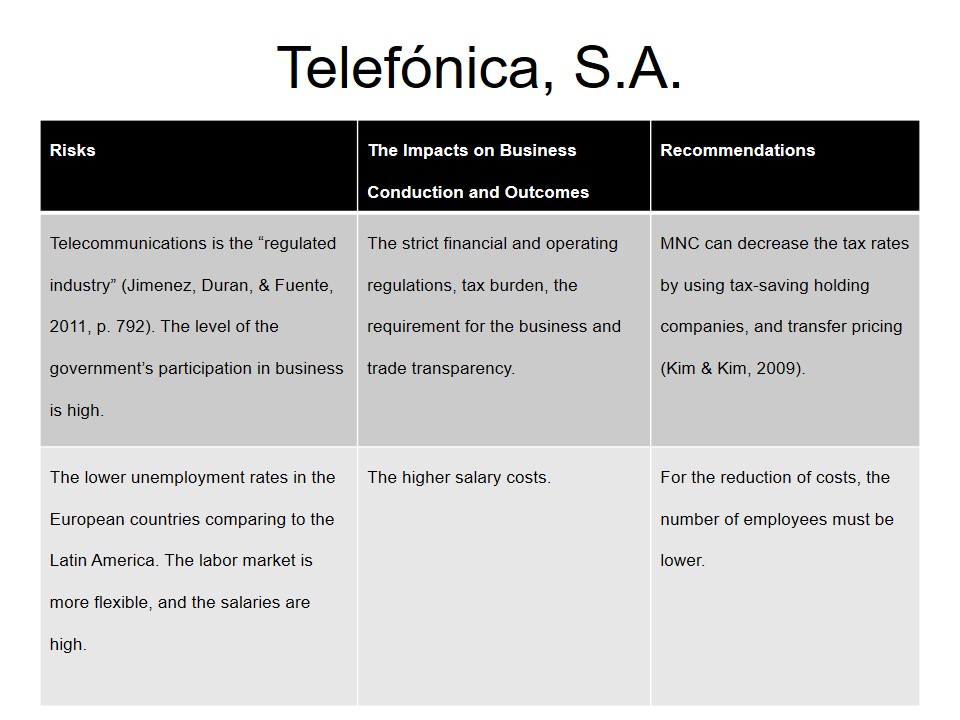
Atento
Iberdrola Generación, S.A.U.: The Political Risks in the US Environment

Conclusion
- The political influence on the markets and economy is extensive. The understanding of the political system’s functioning and consideration of the political risks support the financial sustainability of MNCs.
- “Expectations for a more responsible and reasonable economy and financial business are connected not only with basic foundations of business rationality, but unfortunately also with serious evidence and doubts concerning the negative political impact on the financial market” (Leszek, 2013, p. 46).
- The MNCs’ competitive strategies must include the forecasting and evaluation of the potential impacts of the political changes in the hosting-countries.

References
Butler, K. (2012). Multinational Finance: Evaluating opportunities, costs, and risks of operations. New York, NY: Wiley Finance.
Fitzpatrick, M. (1983). The definition and assessment of political risk in international business: A review of the literature. Academy of Management. The Academy of Management Review, 8, 249-254.
Jimenez, A., Duran, J., & Fuente, J. M. (2011). Political risk as a determinant of investment by Spanish multinational firms in Europe. Applied Economics Letters, 18, 789-793.
Kim, S., & Kim, S. (2009). Global corporate finance: Text and cases. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing.
Krifa-Schneider, H., & Matei, I. (2010). Business climate, political risk and FDI in developing countries: Evidence from Panel Data. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 2(5): 54-65.
Leszek, D. (2013). Political risk on the financial market: The problem of adequate scientific assessment of business operations – the naivety of economists. E-Finance, 9(4), 39-47.