Trek is a worldwide company which was established in 1979. When Trek was established, it had a simple mission, that is, to build the best bikes in the world (Trek Bicycle Corporation, 2012).
Portfolio Analysis
Product Life Cycle (PLC)
Trek products have undergone four stages in their life cycle namely introduction, growth, maturity and decline. Under the introduction stage, Trek’s products were first sold in US before the company expanded its market to England (Johnson, 2008). Under the growth stage, Trek expanded its market such that in 2005, Trek bikes were available in over 90 countries via 10 subsidiaries and around 70 distributors (Johnson, 2008).
During this stage, the company moved from producing only mountain bikes to producing a variety of products like road bikes as well as town bikes. In the maturity stage, Trek products have become available worldwide even through the internet. In this stage, Trek products have become customer oriented through the Project One custom build program (Johnson, 2008). This enables customers to select their own features to be applied in making their bikes. Trek products are yet to undergo the decline stage and are still under maturity.
BCG Matrix
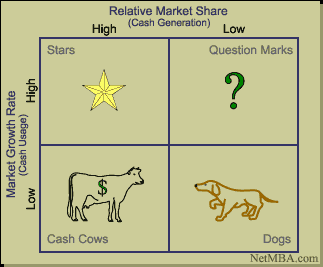
Under the BCG matrix, there are four sections which include; stars, cash cows, dogs and question marks. This section shows different combinations of both market growth rate and relative market share. Trek’s products in the BSG matrix, fall in different sections. The mountain bikes fall under the star section as they have both high market growth rate and high relative market share.
The road bikes fall under the cash cows section with low growth rate but relative market share. Collections which include women’s bikes fall under the BSG dogs section as they have both low market growth rate and low relative market share. The town bikes fall under the section of question marks because of their high market growth rate and low relative market share. This portfolio analysis shows how different Trek’s products are faring in the market.
SWOT Analysis
Trek has established itself in producing high quality products which is one of its strengths (Griffin, 2011). The company has other strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This company’s SWOT analysis is summarized in a grid format below.
Competitors
With Trek operating worldwide, it faces great competition from other companies in the bike industry. The greatest competitors include; Giant Manufacturing, Specialized Bicycle Components, Electra Bicycle and Schwinn Bicycle Company (Johnson, 2008).
Giant Manufacturing has established good marketing of their products all over the world. This has been possible through advertising mostly through promotions and tournaments. This has created a big name with brand recognition in the world. The company has a variety of products to suit different needs of different categories of their consumers. The company enhances its distribution through use of bike dealers and local retailers.
Specialized Bicycle Components has developed from producing only mountain bikes to also producing road bikes. The company has established itself with the introduction of Stumpjumper in both mountain and road bikes. The company has established a strong market hold through its production of cutting-edge bicycle products. The company has intensified its distribution through use of sporting good stores and discount retailers as a way of reaching new customers (Jobber, 2010).
Electra Bicycle is another Trek’s big competitor with its bikes guaranteed to be creative ones. The company’s success has greatly been influenced by production of cruiser bicycles which were America’s standard bike in early 1930’s. The company has applied innovation in combining modern bike styles with that of cruisers. This use of old school looks with contemporary technology to produce cruiser bikes has led to the company’s significant growth.
On the other hand, Schwinn Bicycle Company has remained successful as a cheap entry-level bike as its brand has been around longer as compared to other competing companies. The company was associated with production of quality bikes but this has changed. The company has been unable to produce quality bikes but still have an upper-level lineup.
With the idea of poor quality products among consumers, the company’s market share has decreased significantly. The company still has the opportunity to capture some of the lost market share through use of the new line of bikes it has introduced. This will only be possible if the company markets them correctly (Svend, 2006).
Though Trek is a faced with high competition from its competitors it is still faring well worldwide due to its competitive advantage. Through its production of quality and innovative products which are customer oriented, Trek has become the best not only to bikers but even to non-bikers. This has been as a result of its constant quest for innovation in the maturity stage and across regions (Kolter, and Armstrong, 2010).
Four key issues
One of the key issues the company should address is how to maintain and increase the market share of current products. This is because the company has a weakness of forecasting and reacting to demand. This is because this weakness under Ansoff Growth matrix calls for market penetration. Another issue which Trek should consider is how to come up with new products through product development to solve its weakness of lack of a variety of products (Cooper, and Lane, 1997).
Another issue to consider should be which technology to be applied in order to ensure production of products which compete with those from Japan and which promote Green Movement. The fourth issue which the company should consider is how to restructure a mature market through driving out competitors (Kumar, 2010). This according to Ansoff Growth matrix will enable market penetration.
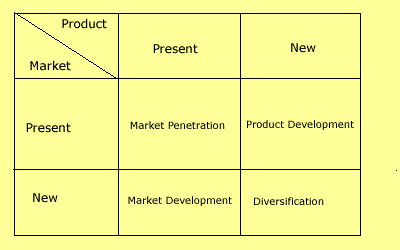
According to Ansoff‘s Growth matrix, the company should undertake market product development as its growth strategy (Bachmeier, 2009). This is because under the PLC analysis the company is under the maturity stage. Under this stage, though the company has introduced new products like road bikes and town bikes, more innovative products are required under collections.
In the BCG matrix the collections are under the question mark section as they have high market growth but low market relative share. This means that the company needs to come up with new innovative and technologically advanced products under collections as a way of product development (Doyle and Stern, 2006).
References
Bachmeier, K., 2009. Analysis of Marketing Strategies Used by PepsiCo Based on Ansoff’s Theory. Norderstedt: GRIN Verlag.
Cooper, J., & Lane, P., 1997. Practical Marketing Planning. Athens: Macmillan.
Doyle, P., & Stern, P., 2006. Marketing management and strategy. New York: Financial Times Prentice Hall. Griffin, R., 2011. Fundamentals of Management. New York: Cengage Learning.
Jobber, D., 2010. Principles and Practice of Marketing. New York: McGraw-Hill Education.
Johnson, S., 2008. Trek Bicycle Corporation: Situation Analysis. Web.
Kolter, P., & Armstrong, G., 2010. Principles of Marketing. New York: Pearson.
Kumar, D., 2010. Enterprise Growth Strategy: Vision, Planning and Execution. Farnham: Gower Publishing, Ltd.
Svend, H., 2006. Marketing planning: a global perspective. New York: McGraw-Hill Education.
Trek Bicycle Corporation, 2012. We believe in a better world. Web.