Definition
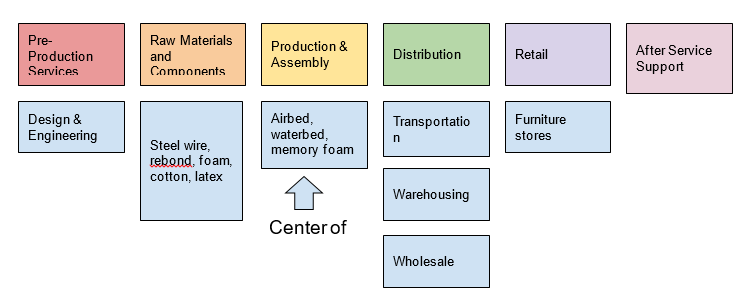
An industry value chain (IVC) is a representation of a process required for producing goods and services, starting from devising the initial idea and ending with providing the customer with the end product. As seen from Graph 1, the industry value chain for the mattress industry consists of five essential elements: pre-production and services, raw materials and components, production assembly, distribution, retail, and after-service support. At the pre-production stage, companies decide on design and engineering solutions that would appease the customer. For instance, Honest Mattress Reviews (2019) and Grand View Research (2019) describe the mattress market in the US and Canada to be dynamic and characterized by changing tendencies.
The first stage
The first emerging trend described by the researchers is the need for customized goods: customers become more vocal when it comes to firmness and layering options. Interestingly enough, some vendors go as far as to offer opportunities for couples where each side is adjusted to a respective person’s needs. The awareness of the harmful effects of chemicals and synthetic compounds used for mattresses explains the growing interest in eco-friendly materials. Lastly, customers have started to put a value on multi-functionalism. Given the rapid urbanism rates and property prices, people want to utilize every square foot of space available and make it as useful as possible.
Companies might want to hire in-house product designers and engineers or outsource these tasks. The former option presents its own set of benefits: the hiring company has more control over overtime allocation and availability. Besides, an in-house designer or engineer is familiar with the organization: they know its values, mission, and vision. Outsourcing might be riskier if the hiring company does not know exactly what to expect, but on the other hand, it might make more financial sense.
The second stage
The second stage encompasses business decisions regarding raw materials and components: steel wire, rebond, foam, cotton, latex, and others. Given the variety of materials needed to manufacture mattresses, companies will have to start relationships with suppliers of respective goods. While it might be an economically sound decision, it requires extra planning and management. Besides, relying on external suppliers might pose a certain risk: a mattress company will have less control over quality and safety, which might lead to a diminished inspection.
The third stage
During the production and assembly stage, most companies subcontract the production of innerspring coils to other firms that specialize in manufacturing springs. Later, cushioning is added, which defines the level of comfort that a given mattress can provide. Lastly, decorative, outer parts are added to fit the bottom and the top of the mattress; side panels are often cut from the same composite. Product and assembly constitute the industry’s center of gravity: they include the core activities necessary for launching products of desired quality and quantity. However, locating the exact center of gravity for the mattress industry is not easy: each of the stages described so far contributes to the quality of the end-product.
The fourth and the fifth stages
The fourth stage encompasses the various operations that a mattress company needs to conduct to distribute its goods: transportation, warehousing, and wholesale. For shipping, companies need to settle on a strategy that would be multi-dimensional and reflective of factors such as customers’ needs, segments, and mode selection (Mangan & Lalwani, 2016). Warehousing is essential to maintain as it allows to house buffer stock and keep customers happy (Ivanov, 2018).
Apart from that, proper storage accounts for the better longevity of the goods. Mattresses can survive for up to ten years when appropriately handled: covered in a protective wrap, kept flat, and aired regularly. As for the fifth stage, companies’ goods appear in retail stores, whether they are sold separately or as part of the furniture. This is when customers come into contact with the product and give feedback through sales and reviews.
After-sales support
The input is typically processed during the last stage: after service support (Zamora, 2016). The importance of after-sales support in the mattress industry cannot be underestimated. Choosing the right mattress improves customers’ quality of sleep and, therefore, their quality of life. When the stakes are that high, customers do want to know that the company that they have singled out is reliable and trustworthy. Sufficient support after the purchase is made proves that the company does not solely pursue profit: it is also interested in customers’ long-term satisfaction.
Conclusion
As a result, the company builds trusting relationships with buyers and increases their loyalty. Complaints and suggestions may be later used for new design and engineering solutions, which completes the cycle.
References
Grand View Research. (2019). Mattress market size, share & trends analysis report by product (innerspring, latex, memory foam), by application (domestic & commercial), by region, and segment forecasts, 2019 – 2025. Web.
Honest Mattress Reviews. (2019). Top 3 emerging trends impacting the global mattress market from 2017-2021. Web.
Ivanov, D. (2018). Structural dynamics and resilience in supply chain risk management (Vol. 265). Berlin: Springer International Publishing.
Mangan, J., & Lalwani, C. L. (2016). Global logistics and supply chain management. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Zamora, E. A. (2016). Value chain analysis: A brief review. Asian Journal of Innovation and Policy, 5(2), 116-128.