Background
This paper is a dissertation on the topic of management approaches. Special attention is given to the need for a radical shift from mechanistic management approaches to human relations approaches. The paper discusses three mechanistic management approaches namely scientific management, bureaucratic and administrative approaches and three human relations approaches namely systems theory, the contingency approach, and the socio-technical approach.
The research which I’m planning to undertake is worth the effort because many organizations have stagnated due to the application of mechanistic approaches in management. It should be noted that the management approach is very critical for the development of organizations because it determines the levels of efficiency, effectiveness and employee motivation. Organizations also exist in dynamic social, political and economic environments and thus the need of making the necessary changes in the management approach so as to make organizations to not only stay relevant but also continue attaining their goals and objectives in an efficient and effective manner (Wreu & Beduau, 2009).
What is an organization?
An organization is a group of people who work together with coordinated efforts to achieve certain objectives or goals. Organizational goals and objectives are of various categories and it is this variation of the goals and objectives which classify organizations into three main categories namely profit-making; service-based and social responsibility based organizations (Murray & Jones, 2006).
What is organization development?
Organization development refers to a systematic and ongoing process of designing and implementing effective organizational change. It is also a scientific field of inquiry in which scholars study how best organizations can be developed (Bradford & Burke, 2005). The underlying principle of organizational development is, therefore, the need to implement change in organizations and manage the change so as to achieve certain predetermined objectives (Cummings & Worley, 2009).
Classical / Mechanistic Approaches to Management
These theories emphasize more on formal organizations and how to increase efficiency in organizations and pay little attention to employee relations and motivation.
The Scientific Management Approach
This theory was developed by Taylor in 1947. The theory focuses on the importance of planning work. The theory may be misused by managers to exploit their employees on the disguise of supervision. It views workers as machines rather than social beings which is very wrong. The theory is also unsuitable in situations where group or teamwork is needed because it only recognizes individuals who are supposed to be specialists in various fields. It can, therefore, make organizations miss the value associated with group or teamwork (Spender & Kijine, 1996).
The theory also leaves no room for employees to be creative and flexible in their operations which may make organizations miss the creativity and initiatives of the employees, some of which may be very important for the progress of the organizations. The theory separates planning, working and functioning. This separation may make organizational departments lack harmony, which may, in turn, interfere or compromise efficiency and effectiveness in organizations thereby reducing organizational productivity and development (Taylor, 2008).
The Bureaucratic Approach
This theoretical approach was formed by Max Weber in 1947. The approach conceptualizes organizations as being guided by hierarchical chains of command, in which decisions are made based on the top-down approach. Those who are at top management positions are responsible for making the decisions while their juniors are responsible for the execution of those decisions. In the hierarchy, each position is composed of specific roles and responsibilities as well as some amount of power to make decisions or to command other employees down the hierarchy (Silber & Kearny, 2010).
With this approach, each position in the hierarchy is held by specialized individuals or bureaucrats who have acquired education and training on that particular position. Specialization is accompanied by some specific powers depending on the position in the hierarchy (Kanigel, 1997).
The approach views organizations as being guided by formal regulations and rules. There are rules governing things like working hours, holidays, offs, the language to be used, communication protocols within the organization based on the hierarchy and the communication channel regarding assignments for specific employees in the hierarchy. These rules and regulations govern the procedures and the processes of the organization so as to give it an identity as well as stability and make it possible to predict the output of the organization because everything is planned in advance and followed to the letter without failure or compromise (FAO Corporate Document Respiratory, 1997).
The approach also views organizations as being guided by rationality. Employees are selected not on the basis of friendship but on merit and their qualifications. The approach does not encourage mixing friendship or family issues with organizational business. All employees are therefore selected in a transparent and competitive process which is free from any bias. The same applies to employee remunerations. Each and every employee is remunerated as per his or her position, qualifications and rank in the organization; meaning that those who are at the top get higher remunerations than those who are at the bottom in the hierarchy (FAO Corporate Document Respiratory, 1997).
The theory is however very rigid and irrational especially on the issue of decision making because it takes a lot of time before the bureaucrats in the chain of command procure a decision, which in turn compromises the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization. The approach tends to build empires within organizations that discourage creativity and innovations of junior employees thereby hindering organizational progress and growth (FAO Corporate Document Respiratory, 1997).
Administrative Theory
This theory was formed by Henry Fayol in 1949. Just like the bureaucratic approach, the theory advocates for division of labor and specialization of duties as a way of increasing productivity in organizations. The theory also recognizes the importance of authority and responsibilities within organizations. It advocates for the respect of authority within organizations and commitment to one’s responsibilities as per his or her job descriptions (Murphy & Willmott, 2010).
The theory calls for the respect and commitment to the objectives of the organization by employees. It calls for discipline by the workforce and their compliance with the set rules and regulations governing the functioning of the organizations which they serve. It advocates for the unity of command in which each and every employee should get orders and advice from only one person, in this case, the boss or the senior official in the chain of command. The employees are required to be united towards the goals and objectives of the organization guided by its vision. They should also put the interests of the organizations first before their own interests, which imply that there should be high levels of commitment of the employees in the organizational goals and objectives (FAO Corporate Document Respirator, 1997).
The theory advocates for a culture in which every person is treated fairly and equally as well as a culture of cooperation and unity of employees in their operations and duties which leads to more commitment and makes the employees motivated to take any initiative which they think may move the organization forward (Murray & Jones, 2006).
With this approach, division of labor and specialization makes employees bored with their work because they are not allowed to interact and exchange their views and bring in their initiatives to their job, but are instead required to respect authority without questioning, which to some extent interferes with their commitment and devotion to their work.
The theory also does not recognize the importance of motivating employees uniformly but rather focuses on rewarding only those who perform better through bonuses and promotions (Schein, 2010). This may interfere with the motivation and commitment of employees who do not perform better due to some reason or another. The fact that they do not perform better does not mean that they are unable or unwilling. Organizations should therefore not be selective when motivating employees because doing so may create conflicts and feelings of discontentment among some employees especially those who stay for long without being promoted (Thompson, 2003).
Human Relations Approaches to Management
Systems approach
Most of the modern theoretical approaches to organizations are derived from the systems theory founded by Von Bertalanffy in 1951. It conceptualizes organizations as being composed of sub-systems that interact with each other for the common good of organizations. Each sub-system is considered as being important for the success of the whole and therefore organizations need to be guided by mutual trust, harmony and a unity of purpose. Von Bertalanffy argued that each and every employee is unique and thus there is a need of treating them as such without any cultural stereotypes or prejudices (Burns & Flam, 1987).
The systems approach has affected the field of organizational development by making organizations understand that each part of the organization is important for the functioning of the whole. Through the approach, organizations have been able to integrate their various departments to operate in an interdependent manner, a situation which has seen the emergence of what is referred to as line or horizontal management. The harmonization of organizational departments has also led to the emergence of teamwork in many organizations (Jones & Brazzel, 2006).
The contingency approach
According to Burns and Stalker in an article titled “The Management of Innovation”, as quoted in the FAO Corporate Document Respiratory, it is not possible to have a universal approach to all situations. Different situations also require different guidelines and modes of intervention. Organizations do not exist in a vacuum but rather exist in an environment that is characterized by social, cultural, economic, political and technical forces (Donaldson, 2001).
In order for an organization to attain its objectives in an efficient and effective manner, it is good to consider the environments in which it exists and come up with strategies that match those environments, then cultivate an organizational culture that would enable it to thrive in those environments. The contingency approach has affected organizational development in that organizations have become more inclusive in the process of decision making, which has seen employees have the permission to micromanage their work and come up with the best ways of performing their duties. The reason is that management has realized that full control of employees may interfere with their productivity, which in turn negatively affects the productivity of the organizations (Dowling & Welch, 2008).
Socio-technical theory
According to Passmore in an article titled “Designing Effective Organizations”, and as quoted in the FAO Corporate Document Respiratory, each and every organization comprises of the people, the environment and a technical system. The social system is composed of the employees while the technical system is composed of knowledge, tools, and techniques used by the social system (Robbins, 1996).
According to Passmore therefore, there is a need to maintain equilibrium between these subsystems so that organizations may be effective and efficient. The social-technical theory has made organizations to integrate employees’ work with technology with a view of maximizing the available opportunities for attaining organizational goals and objectives (Thompson, 2003).
Justification of the chosen topic for research
From the above review of literature, it is evident that a gap exists between the impact of using mechanistic management approaches and using human relations approaches. Even though previous research work in this area has endeavored to illustrate that the use of mechanistic management approaches may lead to low employee motivation and thus lack of organizational development, no research has been done to compare the effects of using the two management approaches in contemporary organizations. Consequently, this research is justified because it will try to illustrate the effects of using the two management approaches in contemporary organizations and the extent to which mechanistic management approaches can lead to stagnation of organizations in terms of development.
Industry Background
Management is about planning, coordinating and controlling organizational resources so as to facilitate the achievement of organizational goals and objectives in an efficient and effective manner. The nature of management therefore only allows for the top leadership of an organization to act as the drivers of the organization in a way that facilitates the organization to achieve its goals and objectives, including the management of organizational change (Melkman & Trotman, 2005).
This research aims at investigating how the application of human relations approaches to management can lead to organizational development. The research is being done during the era of globalization which comes with cultural diversity (Scholte, 2005). It is also being done during the era of advancement in information and communication technology, which obliges organizations to be flexible in their management approaches so as to attain efficiency and effectiveness.
The case of Service Adhesives
Based on a case study on Service Adhesives done by Dr. Ran Bahmra who is a lecturer at the Loughborough University, a shift from a traditional mechanistic approach to organizational structure and management to a team-based management approach saw Service Adhesives get transformed from a loss-making organization to a rapidly growing organization (Bahmra, 2013).
Research questions
- Does a good relationship between employees and management lead to increased efficiency and effectiveness?
- What makes employees more comfortable at their workplace?
Hypotheses
- Rigidity in management leads to decreased efficiency and effectiveness thus inhibiting organizational growth.
- The human relations approach to management is better placed to enhance organizational development than mechanistic management approaches.
Objectives
- To investigate whether the good relationship between employees and management leads to increased efficiency and effectiveness.
- To investigate what makes employees more comfortable at their workplace
- To understand what factors influence organizational growth and development.
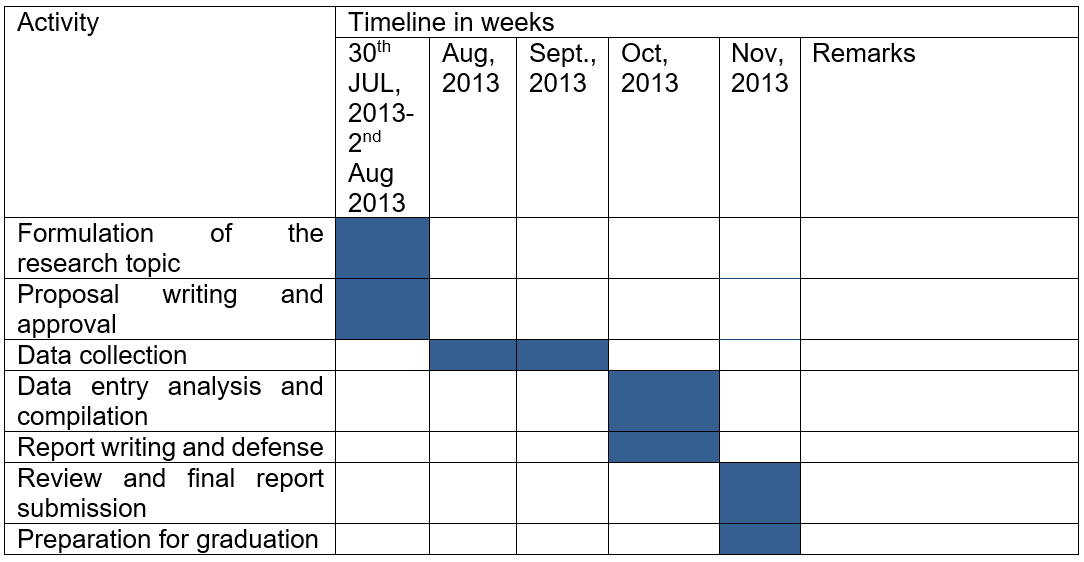
Research Methodology
This chapter mainly presents an overview of the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis. It also provides an outline of the study area and target population. Research involves the collection of data, facts, and information for various social, political and economic purposes. In the collection of data, various research designs are utilized. The qualitative method uses samples of the population to represent the whole. Data collected is non-numerical and descriptive in nature. The quantitative research method, on the other hand, is concerned with the quantification of social phenomena and usually deals with large or whole populations. Data is collected in statistical or numerical form. Qualitative and quantitative research designs are sometimes used as a continuum in that they complement each other (Newman and Benz, 1998).
In this research, the methodology to be used is that of interviewing. This will involve the mailing of questionnaires to the targeted respondents through their email addresses. The questions will be designed so as to get the views of the respondents in regard to the issue of management approaches and organizational development.
Data collection
There are many ways of collecting data to answer survey questions. The ideal situation would be to collect data from more than one source and or to collect more than one type of information. The selection of a method of collecting information must balance several concerns including resources available, credibility, analysis and reporting resources and the skill of the interviewer or evaluator.
This study will employ both primary and secondary data collection methods though it seeks to utilize majorly data from primary sources. The primary data collection tools that this study seeks to utilize are self-administered questionnaires which will be sent directly to individual respondents. The respondents will be expected to fill the questionnaires without the assistance of the interviewer. This will help in ensuring that all questionnaires are filled well and submitted on time for analysis. The questionnaire that this study will use has well-structured questions both closed and open-ended to ensure that all required data, views and opinions are captured.
Resources
This survey will employ both desk reviews of relevant publications and the internet as secondary data collection tools. Published and unpublished information materials containing relevant information will be reviewed to extract data and other information concerning this survey. Other information relevant to this survey will be obtained through internet searches. Internet provides a means of obtaining information that may not be obtainable through interviews and review of existing publications.
Target respondents
The research will target respondents from three London based organizations namely British Petroleum (BP), Barclays bank plc and Tesco. These organizations are drawn from different industries with BP representing the oil industry, Barclay’s bank representing the banking industry and Tesco representing the general merchandise industry. The respondents will comprise thirty employees (ten from each organization) who are either current or former employees of the three organizations. Their names and contacts will be obtained from the organizations’ employee’s database or from the organizations’ regional offices in London. After getting the names and their contacts, they will be requested to participate in the interview at their will. Questions will be asked with an overall objective of verifying which management approach is better for employee motivation and hence for organizational development.
They will be explained about the purpose of the interview and be assured that the information which they give will remain confidential and will not be used to accord or deny them any privileges as employees or former employees of the organizations. They will also be guaranteed anonymity in the analysis of the information which they will give. This will be done so as to ensure that they participate in the interview without any form of biases.
Why I have chosen the methodology
The methodology is the best for answering the research questions because it is possible to prepare the questions in a manner that will make it possible to extract the information from the participants. Since the research questions which emerged from the literature review are whether the good relationship between employees and management leads to increased efficiency and effectiveness and the factors which make employees more comfortable in their workplace, the methodology is believed to maximize the chances of getting the answers to these questions more than using any other methodology.
This particular method will also be used because it is the most viable to get the information required for the research. Since it will not involve any face to face interaction, it will ensure that the interviewees will participate in the interview at their own pace and thus they will not be rushed to answer the questions. This will maximize the response rate as opposed to if the interview was to involve face to face interaction with the interviewer.
The method will also be used because of its high levels of confidentiality. This is because the respondents will give the information through their personal email addresses and therefore, they will not be exposed to the public and this will enhance their participation in the research. The method is also preferred because of its low costs. This is because it will just involve the salutations and greetings and then attaching the questionnaire, then entering the email addresses for all the participants and sending it to them. This will take a relatively short time.
Research design
A logical structure of inquiry will be employed to ensure that the evidence obtained will be able to answer the research questions as unambiguously as possible. This study will take on a survey design as well as a descriptive design. Survey research design will help collect data to determine the relationship between management style and organizational development in the two organizations namely BP and Service Adhesives which have different management approaches.
The descriptive research design will employ correlational techniques in collecting data that will seek to answer questions to establish how management approaches affect organizational effectiveness and efficiency, which are prerequisites for organizational development.
Appropriateness of triangulation in the research
Triangulation is the use of more than one data source to confirm a certain proposition. It is done to enhance the validity and reliability of the research findings on a certain topic of research. In this particular research, triangulation will be achieved by comparing the information provided on the websites of the companies and what the respondents will be saying.
Validity and reliability
To ensure that the information collected is relevant to the purpose of the study, a review of variables has been done. To augment the same, the research instruments will be formulated in a manner to ensure clarity and precision in capturing the required data. A pilot study will be crucial to test the suitability and effectiveness of the instruments before the actual study is conducted.
Test reliability (consistency) is an essential requirement for test validity. Consistency of the results or scores obtained is paramount in this study as in any other research work. In this sense, split-half reliability will be a useful measure of the reliability of the research instrument used in this survey. This is an evaluation of the internal consistency of a test by splitting test items randomly into two halves and comparing participants’ performance on the two halves. The two scores should correlate highly if the test is internally reliable (Cohen & Swerdlik, 2002).
The researcher will ensure a proper understanding of the research instruments among the respondents by making the questions as simple and clear as possible. Moreover, the interviews will be self-administered and this will allow the respondents to fill the questionnaires at their own pace without being rushed through.
Data analysis
When selecting a data analysis technique, a researcher should make sure that the assumptions related to the technique are satisfied (i.e., normal distribution, independence among observations, linearity, and lack of multi-collinearity between independent variables, e.t.c.
Quantitative data from this survey will be subjected to cross-tabulation (the process of creating a contingency table from the multi-variant frequency distribution of statistical variables. A contingency table is a matrix display of the categories of two nominal scaled variables, containing frequency counts of a number of subjects in each bivariate category. For example, showing how both genders are endowed in terms of opportunities and resources.
This survey will also employ the chi-square test which is a statistical test commonly used to compare observed data with data we would expect to obtain according to a specific hypothesis. It helps us know about the “goodness to fit” between the observed and expected. As per the hypotheses, this study assumes that rigidity in management leads to decreased efficiency and effectiveness thus inhibiting organizational growth. It also assumes that the human relations approach to management is better placed to enhance organizational development than mechanistic management approaches. This test will help establish whether these are the true causes of the situation. Correlation analysis will also be used to establish the relationships between independent variables (rigidity in management and the dependent variable (organizational development and efficiency).
Qualitative information obtained from individual respondents will be transcribed and analyzed along the study themes to supplement and back up the survey data. Secondary information captured during the survey will be utilized to augment and confirm the conjectural viewpoint and conclusions drawn along the study themes.
Ethical issues
This research will be done in a way that is in compliance with the United Kingdom’s data protection Act. It will also treat the information given with the utmost confidentiality. As already mentioned, the respondents will be guaranteed that the information they will give will not be used in any way to accord or deny them any privileges but their views will only be used for the purposes of the research.
Reference List
Bahmra, R 2013, Service adhesive tries again. Web.
Bradford, D. L & Burke, W. W (Eds.) 2005, Reinventing organization development: New approaches to change in organizations, Wiley, San Francisco, CA.
Burns, T.R & Flam, H 1987, The shaping of social organization : social rule system theory with applications, Sage Publishers, London.
Cohen, R.J & Swerdlik, M.E 2002, Psychological testing and measurement: An introduction to tests and measurement, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Cummings, T. G & Worley, C. G 2009, Organization development and change, 9th ed, Cengage Learning, Mason: OH.
Donaldson, L 2001, The contingency theory of organizations, Sage Publishers, Thousand Oaks, Calif.
Dowling, P & Welch, D 2008, International Human Resources Management: Managing People in a Multinational Context, 5th edn, Thomas Learning, London.
FAO Corporate Document Respiratory 1997, Management of Agricultural Research: A Training Manual. Module 3: Organizational Principles and Design. Web.
Jones, B. B & Brazzel, M (Eds) 2006, The NTL handbook of organization development and change: Principles, practices, and perspectives, Pfeiffer, San Francisco, CA.
Kanigel, R 1997, ‘Taylor-made’, ‘19th-century efficiency expert Frederick Taylor’, v37 i3 18(1).
Melkman, A & Trotman, J 2005,Training international managers : designing, deploying and delivering effective training for multi-cultural groups, GOWER, Burlington, VT.
Murphy, D.J & Willmott, H 2010, Organization Theory and Design, Cengage Learning EMEA, Andover SP10 5BE.
Murray, P & Jones, G 2006, Contemporary issues in Management and Organizational Behaviour, Cengage Learning, Farmington Hills, MI.
Newman, I & Benz, R 1998, Qualitative-quantitative research methodology: exploring the interactive continuum, SIU Press, Wien.
Robbins, S 1996, Organizational behaviour: concepts, controversies, applications, 7th edn, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Schein , E 2010, Organizational culture and leadership, 4th edn, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, Calif.
Scholte, J. A 2005, Globalisation: A Critical Introduction, 2nd edn, Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke.
Silber, K & Kearny, L 2010, Organizational intelligence: a guide to understanding the business of your organization for HR, training, and performance consulting, Pfeiffer, San Francisco, CA.
Spender J.C & Kijine, H 1996, Scientific Management (Taylorism). Web.
Taylor, F.D 2008, The Principles of Scientific Management, Digireads.com Publishing, Philadelphia, PA.
Thompson, J.D 2003, Organizations in action: social science bases of administrative theory, Transaction Publishers, New Brunswick, NJ.
Wreu D & Beduau A 2009, The evolution of management thought, 6th edn, John Wiley and Sons, New York.