Introduction
The tragic death of Trayvon Martin on February 26, 2012, has become a focal point in the ongoing discussions about race and the criminal justice system in the United States. A neighborhood watch volunteer named George Zimmerman shot and killed a black teenager named Trayvon Martin, 17, in what he called self-defense (Blackmon et al. 2019). Protests and demonstrations were scheduled throughout the country when the tragedy in Sanford, Florida, became widely known. The audio and video records of the event have added gasoline to the fire of public outcry. This paper analyzes how various kinds of media, such as newspapers, television, and social networking sites, reported on the Trayvon Martin shooting.
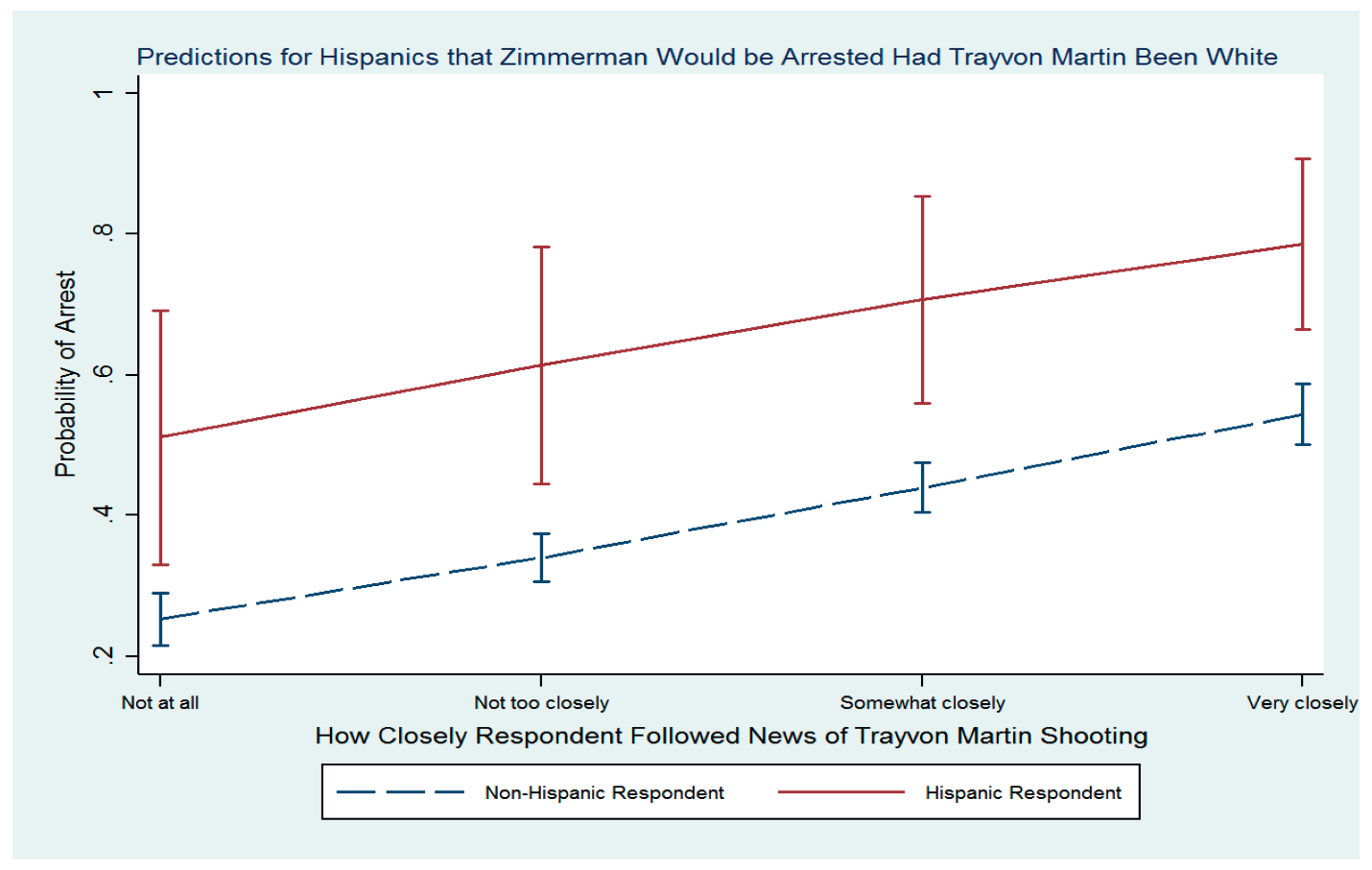
Many questions were raised about the events and motivations leading up to and after the killing of Trayvon Martin. Several individuals claimed that Trayvon Martin was explicitly targeted by police because of his color, raising concerns about racial profiling and discriminatory policing (Lane et al., 2020). Several have argued that George Zimmerman’s use of Florida’s Stand Your Ground legislation as a defense adds fuel to the fire since the law is easily exploited and promotes vigilantism. The killing of Trayvon Martin brought attention to broader sociopolitical concerns, including racism, justice, and police brutality. There was already racial tension in the United States at the time, with the Black Lives Matter movement rising to prominence in reaction to the killings of unarmed black males by police (Jones, 2020; Badaoui, 2020). Many people saw the killing of Trayvon Martin as another proof of the pervasive racism in the American legal system as shown by the different view of individuals in Appendix B, and this only served to stoke the fires of the movement. Overall, the shooting of Trayvon Martin was a divisive and controversial event that generated discussions about race, justice, and law enforcement throughout the country. The tragedy galvanized underserved communities nationwide and highlighted the pervasive problems of racial bias and profiling in the American justice system. There was a lot of coverage of the disaster, but many individuals felt the media was not fair or balanced. The untimely murder of Trayvon Martin will forever serve as a sad reminder of the systemic problems and the need for reform inside the American justice system.
Description of Representation
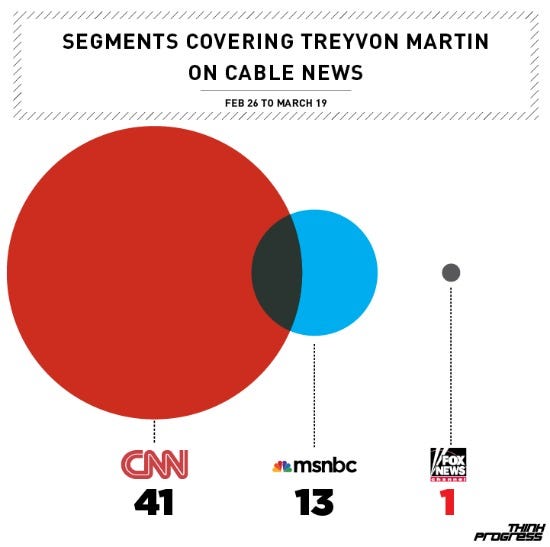
The New York Times, CNN, and Twitter were selected for this research because of their large numbers of viewers and the diversity of presentation formats. The New York Times is a nationally-read daily, and cable news network CNN has a sizable television following (Hannah-Jones, 2020; Brown et al., 2019). On the other hand, Twitter is a social media site where everyone may voice their thoughts and views on the matter (Afolabi and Holder, 2021). The shooting of Trayvon Martin was covered in depth and critically by the New York Times. The newspaper ran several pieces that discussed the case and its broader consequences in detail. For instance, the decision and its debate were discussed in an article titled “What is owed?” (Hannah-Jones, 2020). Racial profiling and gun violence were two broader social concerns addressed in the piece. Broadcast news network CNN reported extensively on the Trayvon Martin shooting as shown in Appendix D, airing live coverage of the trial and providing daily updates. In addition to news and information, the network also included comments and analyses from attorneys, civil rights activists, and other community leaders (Brown et al., 2019). However, many said CNN’s reporting was biased in favor of the trial’s spectacle rather than its substantive concerns. Social media, notably Twitter, heavily influenced the story of the Trayvon Martin shooting. Individuals’ tweets regarding their thoughts and feelings about the issue sparked online discussion and controversy (Afolabi and Holder, 2021). Unfortunately, this also contributed to the proliferation of misleading information and stories. Some users, for instance, disseminated false details about the case’s victim and accused, which shaped public opinion. The Trayvon Martin shooting was a complex and controversial case, and it was reflected in the media’s portrayal of it. CNN’s coverage was criticized for being excessively sensationalized, while the New York Times gave a critical and extensive range. Twitter, in particular, has provided a forum for public discussion and debate but has also facilitated the dissemination of misinformation. The killing of Trayvon Martin served as a powerful example of the media’s potential and limits in influencing public opinion on contentious matters like race, justice, and firearms.
Critical Analysis
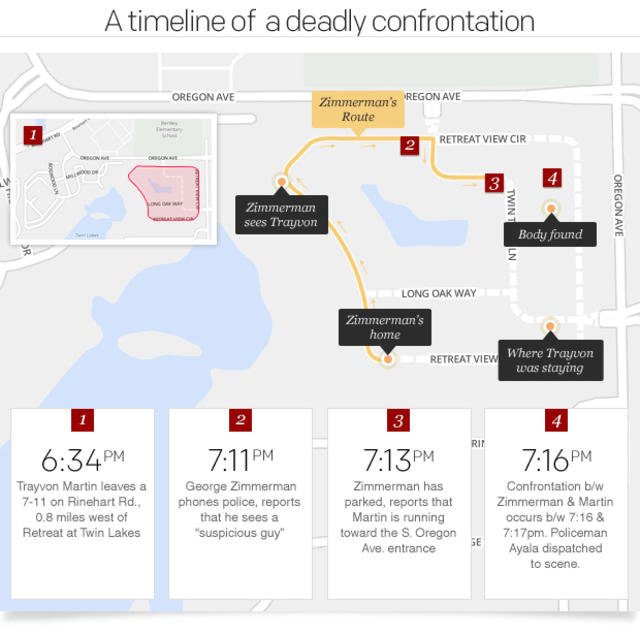
Media outlets’ coverage of the Trayvon Martin case, which has been called one of the most contentious and divisive cases in recent history, varied. The scope of Trayvon Martin’s murder, from a postcolonialist point of view, brings attention to the continuous fight of underprivileged groups against the established order of things (Armstrong and Carlson, 2019). During an altercation in a Florida gated community, as illustrated in Appendix A, neighborhood watch volunteer George Zimmerman shot and killed unarmed black teen Trayvon Martin. The coverage of the incident brought to light the pervasive racism in the culture, where black individuals are disproportionately subject to police harassment and violence. The media’s coverage of the killing of Trayvon Martin mirrored the consumerist values of the United States as a whole. The press immediately and widely covered the incident, with many people using it for their benefit (Kilgo and Mouro, 2019). Similarly, the media and news outlets benefited financially and ratings-wise by sensationalizing the story. The coverage of the killing of Trayvon Martin has also shed light on the problem of American exceptionalism. People of different political persuasions took opposing positions in the national discussion that followed the shooting about gun control and racial profiling (Umamaheswar, 2020). The media’s coverage of the event, which mirrored this sense of patriotism as shown in Appendix C, underlined the need for fair treatment of all people. The multicultural perspective also influenced how the news reported the incident. Race relations, social justice, and civil rights were topics of discussion worldwide after the occurrence (Ostertag, 2019). As a result, people from all walks of life and cultures came together to demand equality and a voice in government. The media’s reaction to the Trayvon Martin shooting indicates the media’s power and the effect it can have on public opinion. The influence of nationalism and diversity on public discourse was examined, as was the continued fight against oppressed people and the capitalist structure of the media. While reporting on controversial subjects, media outlets must remember these things to avoid misrepresenting or exploiting their subjects.
One of the media’s most divisive and frequently debated topics was the coverage of the Trayvon Martin shooting. A neighborhood watch volunteer named George Zimmerman was responsible for shooting and killing an unarmed black teenager, which sparked a national discourse about race, gun control, and the judicial system. Several outlets, from newspapers and television to news websites and social media, gave substantial coverage to the issue. Examining the theoretical foundation of the analysis is crucial to comprehending the scope of the Trayvon Martin incident. Media framing is a useful theoretical lens in this respect. The term “media framing” is used to describe the method by which news items are presented, including the material that is chosen, emphasized, and interpreted (Afolabi and Holder, 2021). How the media frames an issue, a story, or a person may significantly affect how the general public views such things. The way Trayvon Martin’s killing was framed significantly influenced public opinion and the national race, justice, and security dialogue. There was a lot of coverage of the Trayvon Martin shooting, which was complicated since various outlets told the event from different perspectives. Newspapers, television networks, and internet news outlets reported on the tragedy, although their coverage took different angles and highlighted additional details. The fact that Trayvon Martin was an unarmed black teenager shot by a white Hispanic man, George Zimmerman, was stressed by several media sources to underline the racial component of the event (Dunivin et al., 2022; Smiley, 2019). Other media sources also discussed the legality of Zimmerman’s conduct and the significance of Florida’s Stand Your Ground statute.
However, popular opinion and discussion about the Trayvon Martin shooting were heavily influenced by social media. People could organize demonstrations, spread information, and voice their concerns using social media (Kilgo and Mouro, 2019). For some who felt that Martin’s killing was unfair and racially motivated, the hashtag #JusticeforTrayvon became a rallying cry. There is no better example of the influence of media framing on public opinion and debate than the coverage of the Trayvon Martin killing. The media’s selection, emphasis, and interpretation of information may shape the public’s perception of events, problems, and persons (Umamaheswar, 2020). The role of social media in sparking public debate and organizing protests is another point driven home by the Trayvon Martin killing. Media portrayals of the Trayvon Martin shooting and its effects on public conversation and opinion constitute a fascinating case study. People may get insight into the decision-making process behind news coverage by considering theoretical viewpoints like media framing. The death of Trayvon Martin is further evidence of the enormous role that social media has played in shaping public opinion and sparking demonstrations. To avoid being influenced by it, media outlets must be aware of the effect that media framing has on public debate and opinion.
Several news outlets, including CNN, Fox News, and NBC, as illustrated in Appendix E, portrayed the shooting as a heartbreaking tragedy with undertones of racism. The event itself, the legal proceedings, and the general public’s reactions were all subjected to wide attention in the media (Hannah-Jones, 2020). Additionally, these more traditional news channels devoted equal emphasis to the accusations made by both the prosecution and the defense (Hurtado, 2020). On the other hand, Twitter was a crucial player in both the mobilization of the people and the dissemination of news about the death of Trayvon Martin. Hashtags, including #TrayvonMartin, #BlackLivesMatter, and #JusticeForTrayvon, circulated on social media as people vented their anger and fury over the incident (Jones, 2020; Badaoui, 2020). Users could voice their concerns and find others who shared them, resulting in a movement calling for justice for Trayvon Martin to be served. Independent blogs, podcasts, and other non-mainstream media outlets provided a more critical and often radical interpretation of the Trayvon Martin killing. Many accounts emphasized the role that institutional racism and socioeconomic inequality had in the incident, as well as the discriminatory treatment of black persons in the court system (Ruffin, 2021; Lane et al., 2020). They spoke on the shooting’s broader implications, such as the increase in vigilante justice and the necessity for grassroots efforts to eradicate prejudice. The media widely covered the shooting of Trayvon Martin, yet each outlet presented a somewhat different angle on the story. One thing was evident across the board: the shooting of Trayvon Martin had serious repercussions (Kilgo and Mouro, 2019). The media attention sparked a national dialogue on issues of racism and social justice that continues today.
Discussion and Conclusions
One of the most contentious and highly documented occurrences of recent times was the shooting of Trayvon Martin. Protests and discussions occurred all around the country after the 2012 killing of Trayvon Martin, an African-American adolescent, in Sanford, Florida, by George Zimmerman, a white neighborhood watch volunteer. Traditional news channels, social media, and even some non-mainstream media took notice of the occurrence. The public’s reactions to the incident were as diverse as the coverage it received in the various media outlets. Television stations aired biased and sensationalized accounts of Trayvon Martin’s murder. The media’s coverage of the case focused on the racial tensions surrounding it rather than the underlying legal issues. Racism flared out when the case was reported as a white guy shooting an unarmed Black youngster. Instead of reporting the facts, the media emphasized the drama and excitement surrounding the case. In addition, the news programs tended to focus on analytical commentary rather than hard facts, which may have contributed to skewed reporting. Twitter, in particular, was essential in spreading the news about the Trayvon Martin killing. Several individuals used Twitter to voice their opinions on the Trayvon Martin case, causing the hashtag #JusticeForTrayvon to trend. Yet, there are caveats to using social media; for example, they might facilitate the spread of misinformation and conspiracy theories. Social media had a significant part in magnifying the skewed coverage of the Trayvon Martin case.
The Trayvon Martin case was covered more objectively in the print media than on television or social media. Newspapers and magazines covered all sides of the argument and further detailed the law surrounding the issue. However, not all print media sources delivered objective reporting; some emphasized analysis based on the authors’ opinions rather than factual evidence. The media’s skewed reporting of the killing of Trayvon Martin has broader implications, including the possibility of deepening racial tensions in the United States. The media’s skewed portrayal of the Trayvon Martin case may serve as a template for how similar racial tension and violent situations will be portrayed. This has the potential to deepen national divisions, making it more challenging to attain social justice for everyone. Representations of the Trayvon Martin shooting were crucial in molding public opinion about the tragedy. While all major types of media, mainstream media, social media, and alternative news sources contributed to making the story public, each had a unique viewpoint. The media’s portrayal of the Trayvon Martin shooting was one-sided, sensationalized, and unbalanced. The media’s slanted reporting on the Trayvon Martin case has the potential to influence how similar incidents involving race and violence are reported in the future, deepening the country’s racial divide. Journalists should present all sides of an issue fairly and accurately to enlighten the public and promote equality. However, it is inevitable that the shooting woke many people up and sparked a national discussion on issues of race, justice, and equality. People can only expect to live in a society free of tragedies like the Trayvon Martin shooting if they keep talking and taking action.
Reference List
Afolabi, O. and Holder, R. (2021). ‘Social media and racism in 21 st Century America: a case study of Twitter’, Merriam-Webster. (nd). Xenophobia vs. racism: Explaining the difference. Merriam-Webster. Web.
Armstrong, M. and Carlson, J. (2019). ‘Speaking of trauma: the race talk, the gun violence talk, and the racialization of gun trauma’, Palgrave Communications, 5(1).
Badaoui, S. (2020). ‘Black lives matter: a new perspective from Twitter data mining’, Policy Center for the New South, pp. 2021-01. Web.
Blackmon, S.K.M., Neville, H.A. and Jones Thomas, A. (2019). ‘Ideology matters: college students’ emotional reactions to the killing of Trayvon Martin’, The Counseling Psychologist, 47(6), pp. 909-937. Web.
Brown, D.K., Mourao, R.R. and Sylvie, G. (2019). ‘Martin to Brown: how time and platform impact coverage of the Black Lives Matter movement’, Journalism Practice, 13(4), pp. 413-430.
Dunivin, Z.O. et al. (2022). ‘Black Lives Matter protests shift public discourse’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 119(10), p. e2117320119.
Hannah-Jones, N. (2020). ‘What is owed’, New York Times Magazine, 24. Web.
Hurtado, A. (2020). ‘Justice forged on the bodies of children of color: lessons of compassion from the Trayvon Martin case’, Journal of Humanistic Psychology, 60(6), pp. 792-806. Web.
Jones, L.K. (2020). ‘# BlackLivesMatter: an analysis of the movement as social drama’, Humanity & Society, 44(1), pp. 92-110. Web.
Kilgo, D. and Mourão, R.R. (2019). ‘Media effects and marginalized ideas: relationships among media consumption and support for Black Lives Matter’, International Journal of Communication, 13, p.19. Web.
Lane, K. et al. (2020). ‘The framing of race: Trayvon Martin and the Black Lives Matter movement’, Journal of Black Studies, 51(8), pp. 790-812.
Ostertag, S.F. (2019). ‘Antiracism movements and the US Civil Sphere’, Breaching the Civil Order: Radicalism and the Civil Sphere, p.70. Web.
Ruffin, H.G. (2021). ‘Working together to survive and thrive: the struggle for Black lives past and present’, Leadership, 17(1), pp. 32-46. Web.
Smiley, C. (2019). ‘Release in the era of BLM: the nexus of black lives matter and prisoner reentry’, The Prison Journal, 99(4), pp. 396-419. Web.
Umamaheswar, J. (2020). ‘Policing and racial (in) justice in the media: newspaper portrayals of the “Black Lives Matter” movement’, Civic Sociology, 1(1).
Appendices
Appendix A
Appendix B
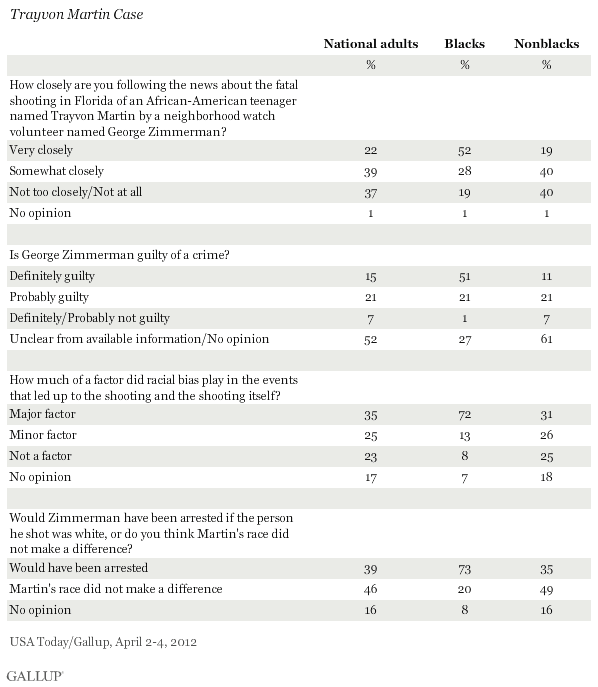
Different views of Martin case between Blacks and Non-blacks
Appendix C
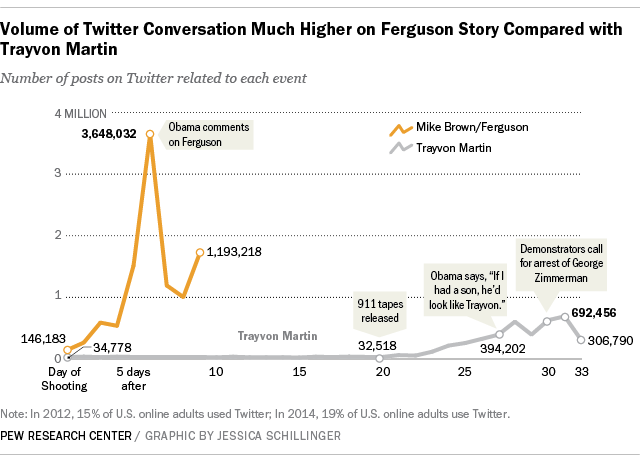
How people on Twitter reacted to Trayvon Martin and Ferguson Case
Appendix D
Appendix E