Abstract
Medical errors have substantial negative implication as they lead to increased hospital stay, diminished quality of life, and increased fatalities. The mistakes that medics do in diagnosis and treatment of patients can be categorized into active, adverse, latent and negligence of the patient. In some cases, the systemic conditions such as a poor organizational culture and communication can be a contributing factor to patient getting the wrong treatment. In the case of Paul, there are many incidences of incompetency that lead to the patient getting the wrong thoracotomy insertion, getting a comma and dying. Notably, all medical errors are preventable by adoption of patient-centered approach to care, organizational safety, and proper teamwork and coordination among the staffs.
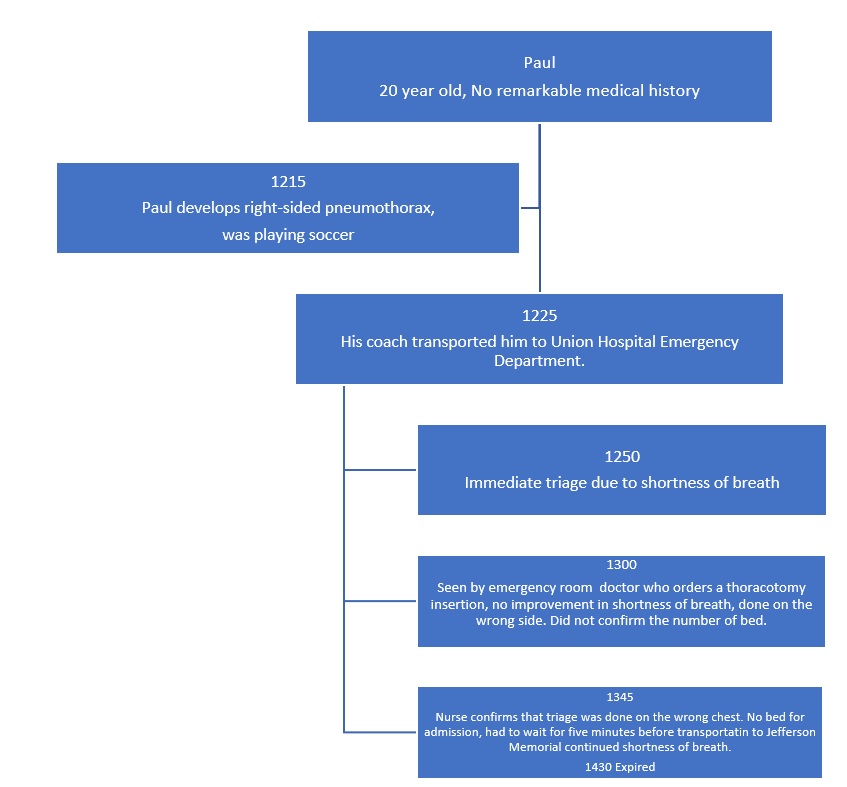
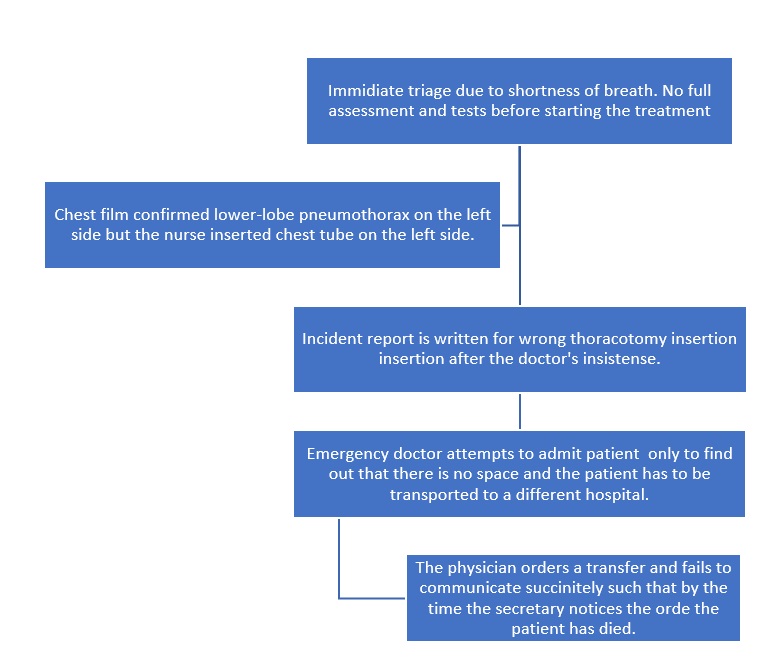
Contributing Factors That Led to The Medical Error
One of the factors that led to the medical error is poor transitions and hand-offs. For instance, the laboratory technician did not tell the nurse about the findings. Next, the miscommunication was present when the nurse did the insertion without waiting for instruction from the physician. Moreover, there was a poor transition when the physician ordered for transfer of the patient. The secretary does not immediately receive the situation such that when he multiple, they should be able to give a shot. The lack of a good transition made the patient waste much time and made guesswork to be the soul receiving.
The other contributing factor is ratio of beds to number of people in the city that are being served. Specifically, the Union Hospital, a level three hospital serving more than 25,000 individuals, has only 150 slots for in-patients. The implication is that Paul did not find a slot after he was admitted for reinsertion. Yet, there were already patients in the emergency section who needed the attention of the doctor.
Moreover, transferring information from one department to the next is inefficient. For instance, the doctor asked for a thoracotomy after the chest film report, and the nurse did not see the imaging results. Yet, she proceeded to do the insertion on the wrong side because she made an assumption. The fact that the patient did not have a remarkable medical history may have contributed because the medics could not understand the health issues that Paul had.
Causal Factor That Led to The Medical Error
The workers do not have time to relax and have their patient’s close vicinity until discharge. For example, the emergency doctor writes the transfer letter for Paul and immediately starts attending to another patient who had a serious accident. The unit secretary was from a late lunch break, and the nurse was attending to other patients after the transfer order had been given. The implication is that when all workers are overworked and exhausted, it is easier to make medical errors. For instance, the emergency doctor could not remember to verify if the nurse had followed through with the order. There is significant time wasted at point of transition.
Evidence-Based Patient Safety Strategies
Improvement in communication flow and teamwork is relevant to enhancing patient safety. Specifically, one of the evidence-based strategies is to carry out training for all staff to improve patient outcomes as it will help the employees understand their mutual roles in providing care to patients (Zheng, 2021). For example, in the case of Paul lack of proper communication between the nurse and the physician-led to wrong treatment. Moreover, it contributed to the negligence of the patient because the secretary did not know in time that there was a need to transfer the client to Jefferson Hospital.
The other evidence-based strategy is to employ more staff such that the ratio of healthcare professionals to that of the patients is proportional. High workload makes it difficult for the employees to take good care of the clients or concentrate on one duty (Zheng, 2021). For example, after attending to Paul and calling the surgeon at Jefferson hospital, the physician had to start working on another severe road accident case. He could not focus on Paul and call to ensure that he had been taken to the standby ambulance ready for transportation. If there were a sufficient number of doctors and nurses in the hospital, it would have been easy even to accompany the patient to the next hospital.
Measurement
Quantitative measurement using the patient records to statistically analyze the percentage and trend in medical errors is effective in determining if there were improvements. For example, if there are improvements, there will be few reports of avoidable mistakes by healthcare professionals. The advantage of such statistical measurements is that they can easily be represented in visual graphs and charts, which are easy to observe and check for trends. Measurements can be done using qualitative measures. For instance, after the training in communication, an interview can be carried out on staff, asking them to give their opinions on the efficiency of care transition after what they have learned. The merit of integrating qualitative measures is that it provides a detailed explanation.
In summary, medical errors are common in clinical practices where healthcare professionals are under-staffed. Lack of proper transition of information from one department to the next contributes to patient negligence. In the case of Paul, his suffering and death could have been avoided if only he received proper care. However, there were constant issues with giving details about his exact diagnosis and treatment. With communication training there will be better teamwork and coordination. Moreover, there is need to employ more staffs to enhance the care of the patients.
Reference
Zheng, F. (2021). Patient safety, an issue of surgical clinics. Elsevier.