- Abstract
- Information Value Chain and Business Processes
- 10-step Traditional or Manual
- Improving the Business chain
- Steps to modernise the manual system
- How Professional MIS helps Traditional or Manual makes Business processes faster
- How Professional MIS makes senior management in decision making
- References
Abstract
Information technology has leveraged firms in their core primary and secondary activities in the information value chain and business processes. Manual systems have been shown to have a retrospective effect on the performance of companies, which underpins the need for organisations to shift to the use of the intranets and extranets.
The trend towards adopting information systems to run the core managerial activities for different departments underpins the need for the Nike footwear company to integrate different information systems including decision support system, enterprise resource planning application among other applications to make strategy decisions at different levels of management.
When combined, the applications create a knowledge management system, which provides the senior managers of the company the ability to make various managerial decisions effectively and efficiently.
It has been shown that when the right information is available, it enables the senior managers to make the right decisions, which positively impact on the performance of the lower departments, which include the financial, sales and marketing, production and manufacturing, and the human resource departments.
Information Value Chain and Business Processes
This study focuses on the information value chain between different departments of Nike’s Company, which deals in the production and distribution of footwear in the clothing industry (Arnott & Pervan, 2008).
The concept in question deals with value addition for each of the processes and steps in each of the four departments (human resource, finance, sales and marketing, manufacturing and production) to ensure that the information value chain and business processes are appropriately applied for the competitive advantage of the firm in the market.
Information value chain is important because the activities, which are executed at any department, affect the activities and performance and outcomes in other departments.
The diagram below shows the relationship between the departments and underpins how the manual system which is used to conduct the primary and secondary activities within the departments is related to the performance of each department and the overall business chain performance of the company (Barua, Konana, Whinston & Yin, 2004).
There is a direct relationship between primary and secondary value chain activities and the outcomes from each department. In each department, the primary activities are closely interlinked and any impact caused in one department affects the activities in the other department.
To achieve competitive advantage because of value chain activities, this study will focus on the four major departments and try to analyse the traditional and modern approaches of applying the concept in the four departments, and the influence the primary activities, which include research and development and product design (which belong to the manufacturing and production department), the sales and marketing departments, the human resource department, and the finance department (Lewis, Templeton & Byrd, 2005).
The information value chain and business concept, when implemented within the different departments of the company will provide the company with the strategic advantage over rival firms in the market, in the context of the supplier value chain, firm value chain, distribution value chain, buyer, and disposal value chain activities in the business cycle as shown in the diagram below.
Figure 1
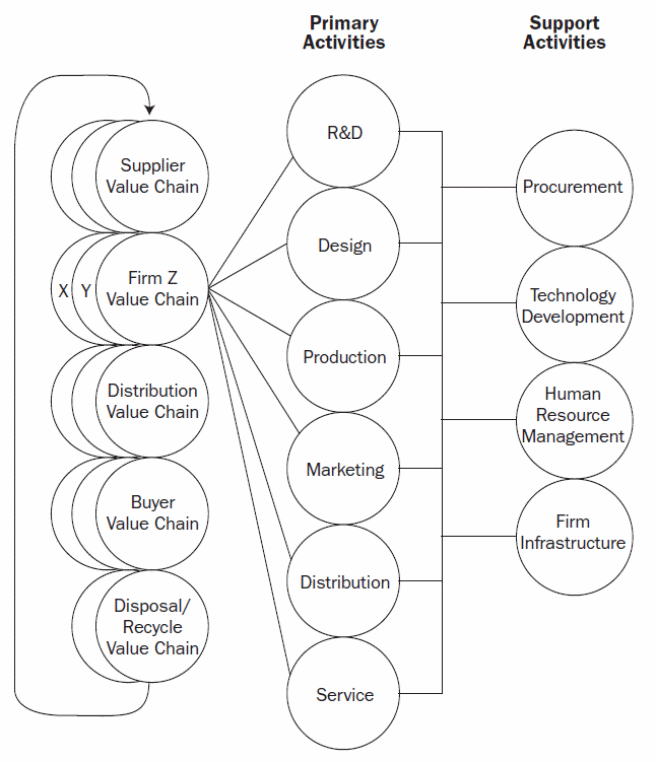
The departments and the relationship between the departments, in terms of the information value chain and business processes are illustrated in figure 2 below.
Figure 2
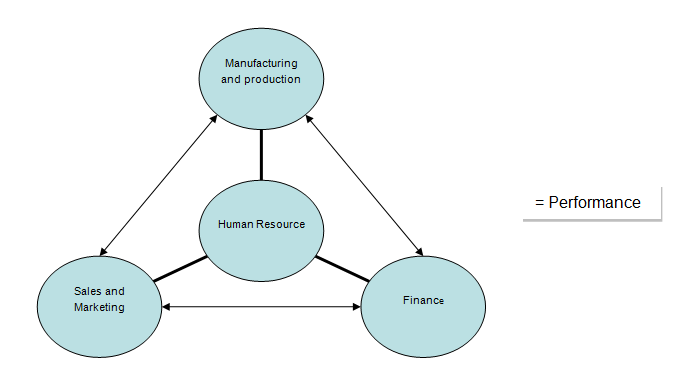
The diagram shows how the performance of each department depends on the primary and secondary value chain activities, and how they affect the output and performance of each of the departments (Evans & Berman, 2001).
It is important to note that the firm has several departments, which play significant roles in the research and development, design, production, and marketing of the final product, by providing the required support activities for the firm in the firms’ operational activities.
Typically, it is possible to see that the activities are divided into primary and secondary or support activities. By focusing on the four departments, it is important to discuss the processes from the traditional point of view, and identify the strategic processes and value addition in the supply chain of footwear in the USA.
10-step Traditional or Manual
The key elements in the ten stage manual system of executing the primary activities include manufacturing and production, accounting activities, which are under the finance department, sales activities in the sales and marketing department, order generation activities, and credit validation and verification.
Once the credit status is accepted, the manual system is required to generate an invoice, and the product is assembled and shipped to the consumer (Evans & Berman, 2001).
Before the company integrated its current information value chain and business into its business functions, it relied on the ten step traditional supply chain system to conduct its business transactions and other processes, which included the primary activities and secondary activities in each of the departments and used the manual system to coordinate the departments.
The primary activities of specialised focus include the research and development, the design, production, the sales and marketing activities. The transactions in four departments had to be conducted manually (March & Hevner, 2007).
In the second step, then Nike Company separated the primary activities as shown in figure one into the above mentioned activities, which belong to the sales and marketing department, the human resource department, the finance department, and the manufacturing and production departments, which can be mapped into Nike’s structure.
Figure 3
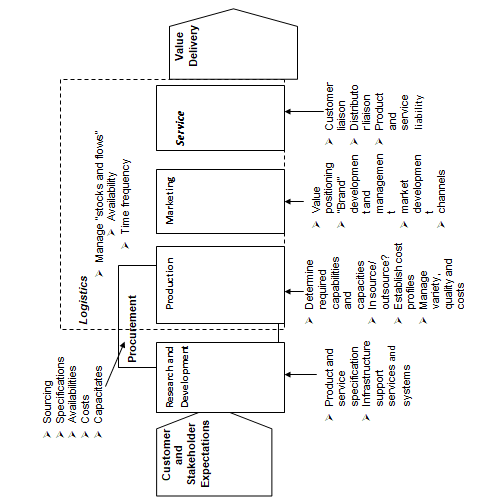
The processes, which map the departmental functions of the Nile Company and the activities at each point of the process, are shown in figure 2 above.
The third step in the manual chain was to establish the products which were required in the market base on the research and development activities (sales and marketing department). Within the research and development primary activities, information was generated by researchers who conducted research by going to the market and collecting data using the manual pen and book system.
In the fourth step, the strategy involved spending a lot of time and resources to capture data from customers in terms of the time to reach the large number of customers and other stakeholders to get to understand what their real needs and expectations were.
In addition to that, the old technologies which used the postal services were also put into use to gather the required data to support the research and development team to achieve their goal.
Based on the information value chain and business activities, it is evident from the above processes how the primary activities of collecting data from the customers by the sales and marketing team (who comprise the research ad development team from Nike company) influence the long term operations of the human resource department, the sales and marketing department, the manufacturing and production department, and the financial department.
The area of specialised focus was the manufacturing and production department and the sales and marketing department.
In the fifth step, the strategy could limit the company from enjoying certain benefits, which include low cost advantage because information was not made available in real time to be acted upon, and when made available, a lot of time was required to anayse the information manually to ensure that the correct information was made available to provide the right and reliable solutions for the accounting activity, which was done manually.
In addition to that, the procedure of collecting, documenting, analyzing information was prone to a lot of errors and sometimes loss of crucial information was experienced.
In the sixth stage, it was expensive and difficult to generate the right invoice data, which was collected an acted upon based on the traditional data gathering and processing approach showed a lot of inconsistencies with the data which was collected for use to make some of the most important decisions which could affect the operational efficiency of a firm.
The seventh stage showed how the preceding activities affected other activities in the business value chain. It was critical as the eight stage for the company to develop a strategy to employ a large number of staff to work in the finance department (sales and marketing), which made the company to pay large sums of money in terms of salaries to the staff invoice generation purposes.
The results were a loss of cost advantages in the market, because, the cost of one activity could be translated to the cost of subsequent activities, which could be evident in the cost and shipment of the final product, at the ninth and tenth steps. It is important to note that the system relied on the characteristic behavior of the users of the system because they could introduce their own errors, which were intentional or unintentional.
As opposed to the current system, the manual system was discovered to be time consuming and the cost advantage associated with real time communication and provision of services were not gained by the firm.
Duplication of data entry and lack of accountability and security to ensure that the data was preserved to meet the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of data could not be achieved based on the use of the manual system in the business chain.
Typically, producing the right data and information to use to make the right decisions on the type of products to produce and offer to the customers was a difficult situation for the management of the firm at all levels of management.
Typically, what happened in the manual processes for the company is illustrated in the diagram below.
Figure 4
When it came to the production, marketing and distribution departments, the need to achieve real time information dissemination encountered the same problems associated with the research and development department of the footwear company. However, the challenges in each department were unique to the uniqueness of the departmental functions of the company.
The manufacturing and production department received information and data from the research and development department, which was acted on in the production of the footwear.
However, the time lag and lack of real time information from the market could contribute to the production of products, which made late entry into the market, making the products lack the competitive advantage associated with the earlier entry into the market.
The accounting department, which is the next in the business chain, could not provide real time information in the revenue collected to enable the appropriate departments to forecast and determine the trend of the financial performance of the company besides the usual problems of making errors in balancing the book of accounts.
Such problems were critical because a lot of time was spent in analyzing financial data, which was critical in enabling the firm to determine the right strategies and areas of operation to concentrate in (Jasperson, Carter & Zmud, 2005).
The sales element of the manual system presented a number of problems and challenges associated with the dissemination of the right information about the products to the market in the business chain.
It is of much importance for the business chain to provide the required information about the market in terms of demographic trends, the consumer characteristics, buying behavior, income levels, and market trends to help the marketing department to make the marketing department to create the right marketing strategies for their products (Jasperson, Carter & Zmud, 2005).
A critical analysis of the manual system shows that the firm was at a loss in getting the right information at the right time and in most cases because the right information was not made available at the right time, the customer could miss out on the products they had placed an order for or they arrived late, when they were not required.
In addition to that, it is critically clear that the marketing department performs a number of functions which have to be fulfilled to make position the footwear in the market. Typically, the marketing functions become effective when there is real time communication of information about the market needs and trend in real time.
The manual systems could not enable the marketing department, as one of the elements in the business chain to disseminate information into the market in real time (Goldschmidt, 2005).
The next element in the business chain is to generate the order given by the customer. It is critical to note that once the order has been generated, the manual system does not add the required value in terms of enhancing the rate at which the order is generated. It is possible to make mistakes at each level of department.
The research and development department might not have the requisite specification on new changes on the order, and the production department might not be able to link in real time with other departments on new changes to product specifications, leading to a waste of resources in terms of money and products.
Other processes involved in the business chain, which occurs between the departments include submitting the order, check credit, approve credit, generate invoice, assemble, and ship the product.
Improving the Business chain
The two areas of interest of the manual system, which can be acted on include the sales and marketing and the manufacturing and production departments.
The underlying reasons are that the manual system suffers a significant number of setbacks when integrated and used within the research and development, production, design, and marketing departments of the Nike footwear company to execute the core functions in the business chain (Goldschmidt, 2005).
The problems and challenges associated with the use of the manual system underpin the need for company to integrate the Information value chain” and “business processes into the core business processes of the two departmental areas already identified in the study.
Here, a number of solutions come in handy to provide the company with the competitive advantage required for the operations and the solutions to be integrated into the functional departments of the company (Goldschmidt, 2005).
Steps to modernise the manual system
The first step to take to modernise the operations of the two areas of the sales and marketing operations and the manufacturing, which is also revered to as the production area is to assess the type of transactions taking place within the departments to, which could provide appropriate information on best strategy and applications to use to address the needs of the departments (Goldschmidt, 2005).
The first department to consider is the sales and marketing department.
The department core functions include gathering statistical data on the behavior of the market, current market trends, income demographics, real time access to the market, market segmentation, product segmentation, market intelligence reports, competitors, new threats, existing threats, market penetration strategies, and other elements (Luftman, Kempaiah & Nash, 2006).
The manual information processing system falls short of providing real time information to the sales and marketing department in real time to perform the core functions in time.
The solution for the scenario is to use a web-base management information system, which is then integrated into the management information system of the company to leverage the performance of core services at all level of the sales and marketing strategy (Luftman, Kempaiah & Nash, 2006).
The management information system integrated with the web based information systems module could provide the sales and marketing department a competitive advantage over the manual system because it brings services closer to the people by using the internet as a platform to communicate.
The following diagram provides an overview of how the internet is a tool that has contributes to the operational efficiency of the departments of the company in supporting and offering a real time platform to execute the primary activities and other support or secondary activities.
Figure 5
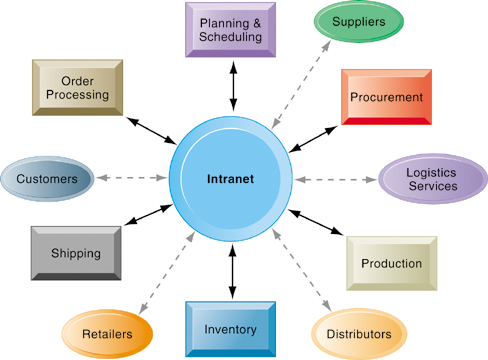
It is critical to note that at the center of the diagram, we have an intranet, and other sections or components connected to the intranet.
Observations show that the value chain activities of the business can have an overall impact on the market, including the retailing activities, inventory management, product distribution , production, shipping, order processing, suppliers, procurement, and the planning and scheduling functions (Marakas, 2003).
Each activity in each department depends on the flexibility and use of the intranet, which is a network that is used within the organisation, making the intranet a web based application by integrating its functions with the internet could provide a competitive advantage to the business organisation.
The system could provide the organisation with leverage over its primary and secondary activities by enabling the sales and marketing department to perform the activities of gathering and creating data besides information generation and application, and the use of the information to generate the required knowledge to perform the cores sales and marketing activities with efficiency and effectiveness (Dennis, Wixom & Tegarden, 2005).
The hardware requirements vary from one platform to the other, especially when different users access the site through the internet. It is therefore possible for the web based application to run on different devices including mobile phones, lap tops, and desk top computers and electronic devices, which have a processor and access point to the internet.
Another area of concern is the hardware requirements to host the management information system which has a web based module integrated to the information system (Dennis, Wixom & Tegarden, 2005). The hardware requirements include high processing powers, which are based on MPC8548E, MPC8547E specifications for high speed processing of data and which provide high speed interconnectivity for networking.
The MPC8548E, MPC8547E processors have a dual speed of 4.0 GHz and a RAM of 5 GB. The processors fall into the family of the most modern QorIQ communications processors, which are used for network communication services.
In addition to that, the hardware supports both the 64 bit and the 32 bit operating systems and is compatible with different operating systems, which include Microsoft windows based operating systems, and the Linux based operating systems.
The software requirements include a 64 bit or a 32 bit network operating system, a web module, which can be made available through open source acquisition process. The recommended management information system which can be easily integrated with the web based applications is CRM from Microsoft.
The critical advantages with the software are that it can be used to generate business reports, which are suitable for different levels of management of the company (March & Hevner, 2007). The software can be used to generate data, and can perform the forecasting function of trade sales and marketing data and information, which is critical for decision making.
Other functions, which can be performed in the system, include real time access and gathering of data and information from the customers, which leads to an increase in sales, increase in the size or quantity of product orders, higher accuracy in forecasting, and increase in sales and marketing productivity. The software provides real tie services for small, medium, and large sized companies (March & Hevner, 2007).
Another area of sepcialised focus for the application of the information value chain and business processes concept is the research, design, and product manufacturing department.
The need to integrate the web based information system is to allow the marketing department, which when working in tandem with the sales and marketing department, will enable real time sharing of information on the dynamic needs of the customers in the market, the type of products on demand, and other innovations, which can be made on existing products, to meet the ever changing market needs.
It provides real time information in the areas where value will be added in the product manufacturing process to ensure they are compatible with the needs of the need of the customer, the products are processed faster and efficiently, and the cost of production is low.
How Professional MIS helps Traditional or Manual makes Business processes faster
The management information system (MIS) to carry out the day to day business transactions and generate reports, which are crucial for the successful, execution of the core business operations in the Nike’s business operations (March & Hevner, 2007).
A number of applications can be used to provide the business value required for successful implementation and execution of the business transactions and include the enterprise resource planning (ERP) management information system.
The RRP is a suite of applications or modules which provide different services and a common repository of information known as the database (Shim, Warkentin, Courtney, Power, Sharda & Carlsson, 2002).
Typically, the ERP provides the flexibility of collecting information, which can be accessed by other modules once the information has been entered into the system and stored in the database. The enterprise software is defined by different modules, which include the human resource, the manufacturing and production, and the sales and marketing department.
The next application of worth to be integrated into the management information system is the transaction processing information system. An analytical examination of the system shows that it provides the necessary facility to conduct the day to day transactions necessary to conduct business between the customer and the company.
The transaction processing system provides the capability for the sales and marketing department to effectively conduct the primary activities of capturing data and information. The TPS allows the sales and marketing department to capture and analyse large amounts of data, which is accepted into the system as input data.
The TPs is able to process, store, organise, and share the processed data for business decision making. The system is able to generate reports on the processed data an present the information in a manner that enables the operational level management to make strategic decisions for the operational efficiency of the departments.
Another management information system that could be of critical value is the decisions support system (DSS). The DSS provides managers with the required information to make non-routine decisions. The information system relies on the use of different mathematical models to provide management solutions (Shim, Warkentin, Courtney, Power, Sharda & Carlsson, 2002).
On the other hand, since the management information system was integrated into the core operations of the company, by removing the manual operations in the company, which made the company to realize a number of core advantages, which include an increase in the core business values based on an increase in the operational efficiency of all the departments of the company (Luftman, Kempaiah & Nash, 2006).
The manual system reduced the operational efficiency of the firm because it incurred a number of weaknesses, which include data loss, inaccuracies, unreliability, and it is prone to accidental modifications. However, with the use of the MIS, it is now possible for the sales and marketing department to collect market data, which can be made available for other departments to use.
Such data can be used to support organisation wide decision making. Nike is a company, which majorly focuses on footwear and the information available from the sales and marketing department can be used to make the right decision on research and development and the type of footwear to produce, based on the current market tastes (Luftman, Kempaiah & Nash, 2006).
Typically, real time information provides the management, and particularly the sales and marketing debarment to collect an anayse data in real time to provide rapid response to the customers and their requests for certain products and services in real time.
The system consists of modules which have analytical tools for processing and analyzing data and information, which has been posted or collected from the people to make real time decisions (Marakas, 2003).
How Professional MIS makes senior management in decision making
It has been shown that management information system which integrates different the core modules of the transaction processing system, the decision support system, the management information system, executive support system, and the enterprise resource planning, when integrated into a single application referred to as the management information system can provide strategic advantages in decision making, by enabling the senior managers to make short and long term strategic decision by re aligning them to the vision and mission statements of the organisation (Shim, Warkentin, Courtney, Power, Sharda & Carlsson, 2002).
Typically, the application can be integrated into as single application known as the Knowledge Management Systems (KMS) helps management to make strategic decisions, at the human resource level and the operational level of the human resource department, by enabling the department to access appropriate information about current employees with expertise in certain areas, and who have the potential to make significant contributions to the performance of the organisation.
The company is able to identify the weaknesses and strengths of the personnel and to determine the quality and quantity of work and employee contributions to the performance of the company (Tallon, Kraemer & Gurbaxani, 2001).
Another area is the sales and marketing department. It has been established that the application helps senior managers to plan for effective resource allocation for the sales and marketing activities.
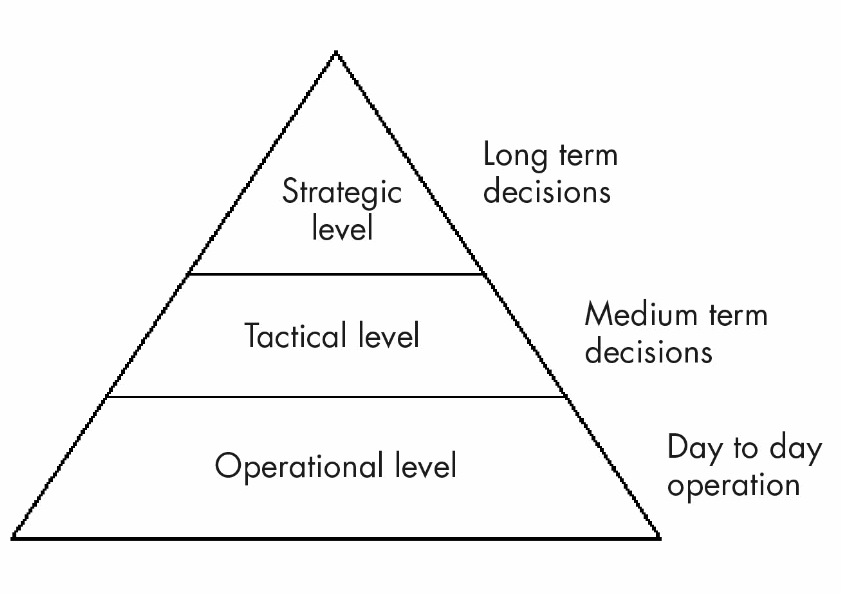
The success of planning properly depends on already processed customer data, which is accessed, stored, processed, and generated in real time to ensure that effective decision making. It is important to note that the decisions made by senior management affect the operations of lower level managers, who include the tactical and operational level managers.
Senior managers are able to make decisions which affect the reputation of the firm. In the business value which have short and long term implication on the performance of the company (Turban, Aronson & Liang, 2005).
Figure 6
According to Luftman, Kempaiah and Nash (2006) and Lee and Yang (2000), the KMS provides supports the processes to acquire, store, process, and apply available knowledge to organise information in an appropriate forms for effective decision making.
KMS is a professional application which allows other applications to collect both internal and external information and interlinks both sources of information to make strategic decisions (Melville, 2010). Typically, the applications consist of a repository of information about expertise employees who have specialised skills to benefit the organisation in decision making.
References
Arnott, D., & Pervan, G. (2008). Eight key issues for the decision support systems discipline. Decision Support Systems, 44(3), 657-672.
Barua, A., Konana, P., Whinston, A. B., & Yin, F. (2004). An empirical investigation of net-enabled business value. Mis Quarterly, 28(4), 585-620.
Dennis, A., Wixom, B. H., & Tegarden, D. (2005). Systems analysis and design with UML version 2.0. Wiley.
Evans, J. R., & Berman, B. (2001). Conceptualizing and operationalizing the business- to-business value chain. Industrial Marketing Management, 30(2), 135-148.
Goldschmidt, P. G. (2005). HIT and MIS: implications of health information technology and medical information systems. Communications of the ACM, 48(10), 68-74.
Jasperson, J. S., Carter, P. E., & Zmud, R. W. (2005). A comprehensive conceptualization of post-adoptive behaviors associated with information technology enabled work systems. Mis Quarterly, 29(3), 525-557.
Lee, C. C., & Yang, J. (2000). Knowledge value chain. Journal of management development, 19(9), 783-794.
Lewis, B. R., Templeton, G. F., & Byrd, T. A. (2005). A methodology for construct development in MIS research. European Journal of Information Systems, 14(4), 388-400.
Luftman, J., Kempaiah, R., & Nash, E. (2006). Key issues for IT executives 2005. MIS Quarterly Executive, 5(2).
Marakas, G. M. (2003). Decision support systems in the 21st century (Vol. 134). ^ eNew Jersey New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
March, S. T., & Hevner, A. R. (2007). Integrated decision support systems: A data warehousing perspective. Decision Support Systems, 43(3), 1031-1043.
Melville, N. P. (2010). Information systems innovation for environmental sustainability. MIS Quarterly, 34(1), 1-21.
Shim, J. P., Warkentin, M., Courtney, J. F., Power, D. J., Sharda, R., & Carlsson, C. (2002). Past, present, and future of decision support technology. Decision support systems, 33(2), 111-126.
Tallon, P., Kraemer, K. L., & Gurbaxani, V. (2001). Executives’ perceptions of the business value of information technology: a process-oriented approach.
Turban, E., Aronson, J., & Liang, T. P. (2005). Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems 7”‘Edition. Pearson Prentice Hall.