Introduction
The opportunity to use network-based learning tools is pleasurable to many practitioners in the engineering teaching stadium, often for varied reasons. This document describes our participation and experience in an operational European collaborative scheme, NETPRO-II, and its aim of mounting network-based solutions to achieve learning aims.
As admission to the Internet and high-speed communication increases for teachers, the possibility for network-based learning and “telecollaboration” characterizes a great prospect for enriching classroom surroundings. While debates and research into network-based dealings in learning have been underway since the mid-1990s with the first free access to the World Wide Web, the rise of the Internet and rising access to ultra-high-bandwidth networks presents an even superior case for such events (Tillinghast 2006). Network-grounded communications can be exclusively between teachers for proficient enhancement, or between classrooms as learning activities including students to varying degrees. Universal to all activities, although, are certain deliberations which must be made to guarantee the achievement of the endeavor.
Network-Based Learning Activity for an Educational Context
Information and message technologies are altering much of what occurs in our schools. We are witnessing a paradigm alter in our schools from educator-centered to beginner-focused ( Morel, R., Domenjoz, J-C., Lachat, C and Rossi, C 2003) so that educators are no longer the sage but the guides(Anderson., J). It is feasible that in the prospect on-line education will cause schools as we now are acquainted with them to turn out to be out of date. It would be likely to do all way of study from the house computer linked to the exterior world using the internet. The realism of this is exposed from side to side to our online route we are participating in here and it is a bold, inspirational and sensible vision of what normal education might be similar to ten or twenty years from now. It is a substance though of the stage of teaching that is the center. For example, though their strength is in the prospect of a virtual classroom it could not be predicted that nursery school children would take delivery of all of the communal and message skills essential to deal efficiently with other populace all through the route of their lives with no the very real communal communication that the classroom surroundings gives (Hunter, B. 2002, 23-34).
Educational Sector Learning
The position of schools as preparation grounds for individual growth in association skills is very significant as is the role schools engage in recreation in the bodily well life form of students by as long as sports commands and physical behavior lessons. At school brood will institute friendships that may last life and they will also be confident to turn out to be members of the team, or contribute in person, generous activities.
Nowadays, since of its possibility and flexibility, all instructive institutions crossways the sphere use computer network-based knowledge for increasing knowledge opportunities and facilitating knowledge behavior to scholars. It can be effective for transports content to students and for teachers to interact with every other by using message tools such as email, bulletin plank, conferencing organization, whiteboards, chat rooms, and still videoconferencing. It can bring inside in multimedia arrangements like a videocassette, audio clips, cartoons, imitation, and movies (Feltovich, P. J., Spiro, 2004).
There is small doubt the employ of ICT in the classroom will change the position of the scholar and will make easy the choices of how they go forward their teaching by requiring less require for contribution or way from a tutor. Students may be clever to straight their study to a better extent, with the educator acting as a director moderator quite than as a manager (Forsyth, 1996: 31) but knowledge alone can not create an effective knowledge procedure and to ensure knowledge quality behavior is a significant factor that all teachers must put together with knowledge. A great instance is the Woolfolk text Educational Psychology that Supplied online links to a variety of web pages for data recovery and also online tests.
Synchronous or Asynchronous
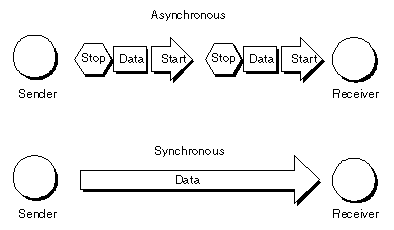
Occurring at usual intervals. The conflicting of synchronous is asynchronous. Most messages between computers and strategy are asynchronous — it can happen at some time and uneven intervals. Communication inside a computer, though, is more often than not synchronous and is governed by the microchip clock. Signals the length of the bus, for instance, can happen only at exact points in the timepiece series (Conklin, J. 2003).
Distributed Network Learning Framework
In our investigation on instructive uses of networks, we have experiential the flow of information across the system, assisted by the lively participation of network peacekeepers (Levin et al., 1987). We have begun to set apart these comments as a Distributed Network Learning Framework (Levin & Jacobson, 1992). In this structure, order and information flow from where they present are to where they are wanted. The center of our labor with this structure has been to look at ways to arrange networks, particularly the peacekeepers so that knowledge can take put most efficiently.
Pedagogical strategy and tool selection
The selection of the pedagogical strategy is the crucial moment of the educational process. The strategy for network-based learning (NBL) should take into account the remoteness of the students, thus, not everyone may be present at the necessary time.
Thus, the strategy should be the following. Tutor needs to use only simple examples, taking into account the difference of the background knowledge of all the learners, as they may be of different ages, different jobs, and appointments.
- If some experiments should be explained or viewed, it is better to provide the video, or the necessary data in order the students were able either repeat it or create the sequence of the steps in their minds. A brief overview of the experiment will be not only harmful but may complicate further studies.
- The organization of the course should follow the elementary principles.
- Be divided into at least three parts (introduction, the main topic, knowledge control).
- Provide all the prerequisites for the successful study (materials, plans, outlines, tables, and graphs).
- The study should include boxes and other visual materials (as has been pointed above), as such an approach simplifies the perception of the facts.
An example of creating a curriculum on physics may be the following
The Elaboration of the NBL Plan
The current chapter is claimed to elaborate on the network-based learning activity, focusing on the theoretical approaches of network learning and training. It is necessary to emphasize, that the principles of learning stay the same despite the sphere of studying, as the methodology of teaching never changes.
As it has been defined above, network-based learning is often arranged with the assessment of the World Wide Web services and offers either synchronous or asynchronous. Synchronous may last for a few hours (one or two hours – this is the time during which an average adult may concentrate the attention on some particular object/ subject). The approximate plan for the process of tutoring may be the following:
- Definition of the main aim of the course (subject, basis, and the topics that must be revealed)
- The elaboration of the methodology (the type of teaching, the form of giving the material, the timetable of the lessons, and the type of checking the knowledge)
- The proceeding of the necessary literature (both: methodological and relating to the main subject of the studies)
- Creating the suitable graphical interface of the course, in the order it attracted the attention, and in no way irritated the eyes and distracted the learner
- Creation of the preview of the course, or explaining its necessity, if the study is obligatory for the workers of some particular company.
- Providing the materials of the network-based study
- On-line lecture with the explanations of the backgrounds, bases, and, obviously, the prehistory of the study
It would be necessary to mention, that this plan may be used for both Synchronous and Asynchronous studies, with the several distinctions:
- The plan for Asynchronous studies should be elaborated taking into account the possibility of non-electronic mail sending of the materials, which expands the possibilities of the volumes of the learners.
- The online consultations may take place only in a non-real-time regime. This factor has both advantages and disadvantages. On the one hand, it breaks the educational process, but on the other hand, it gives the tutor a possibility to work through the necessary materials, and give the deeply grounded reply, or even base another lesson.
The pre-activity tasks of network-based learning play a rather significant role in the process of education, as these tasks usually define the base knowledge of the learners, help to construct the future curriculum.
The significance of the graphics in the NBL
The beginning of World Wide Web authoring has led to an overabundance of explicitly rich web pages. Moreover, to placing promotion information of the Network-Based Learning the power of the graphics lies in its litheness to link to business catalogs and processes running in a multiplicity of data systems, both web, and non-web servers. Commissions such as creating operational systems for studying, creating graphical user interfaces for the systems of education, require the web designer to take into account more than HTML systems and image maps. The inheritance of interactive design for network-based solutions has helped interface designers realize how to relate their craft to create effective network-based solutions in general, and learning in particular.
Conclusion
The use of network-based interactive activities in learning offers benefits to learners and teachers, either as a substitute or addition to conventional classroom-based tutoring. Deliberate propose and planning in five universal topics will augment the activity’s usefulness and chances for triumph. Understanding the role of construction, Process, Mediation, Community Building, and Institutional Support in the design of network-based contacts will better update both users and workers of these developments and improve the general user experience.
Reference
Beeman, W. O., Anderson, K. T., Bader, G., Larkin, J., McClard, A. P., McQuillan, P. J., & Shields, M. (2002). Intermedia: A case study of innovation in higher education (Final report to the Annenberg/CPB Project). Providence, RI: Brown University, Office of Program Analysis, Institute for Research in Information and Scholarship.
Bruce, B. C., & Peyton, J. K. (2002). A situated evaluation of computer networking to teach writing (Technical Report No. 565). Urbana: University of Illinois, Center for the Study of Reading.
Conklin, J. (2003). Hypertext: An introduction and survey. IEEE Computer, 20(9), 17-41.
Feltovich, P. J., Spiro, R. J., & Coulson, R. L. (2004). The nature of conceptual understanding in biomedicine: The deep structure of complex ideas and the development of misconceptions. In D. Evans & V. Patel (Eds.), The cognitive sciences in medicine (pp. 113-172). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press (Bradford Books).
Hunter, B. (2002). Linking for learning: Computer-and-communications network support for nationwide innovation in education. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 1(1), 23-34.
Jacobson, M. J., & Spiro, R. J. (2003). Hypertext learning environments, cognitive flexibility, and the transfer of complex knowledge: An empirical investigation. Paper submitted for publication.
Jonassen, D. H., & Wang, S. (2003). Acquiring structural knowledge from semantically structured hypertext. Journal of Computer-Based Instruction, 20(1), 1-8.
Tillinghast, J. (2006). Uses of Internet2 Connectivity in the K-12 Music Classroom. Web.