Policy Issue
- Nurse ratios are regarded as a factor impacting care quality;
- Enforced nurse ratios are believed to promote patient safety (Heath, 2018);
- The desired staffing levels are different for various departments of healthcare facilities (Heath, 2018);
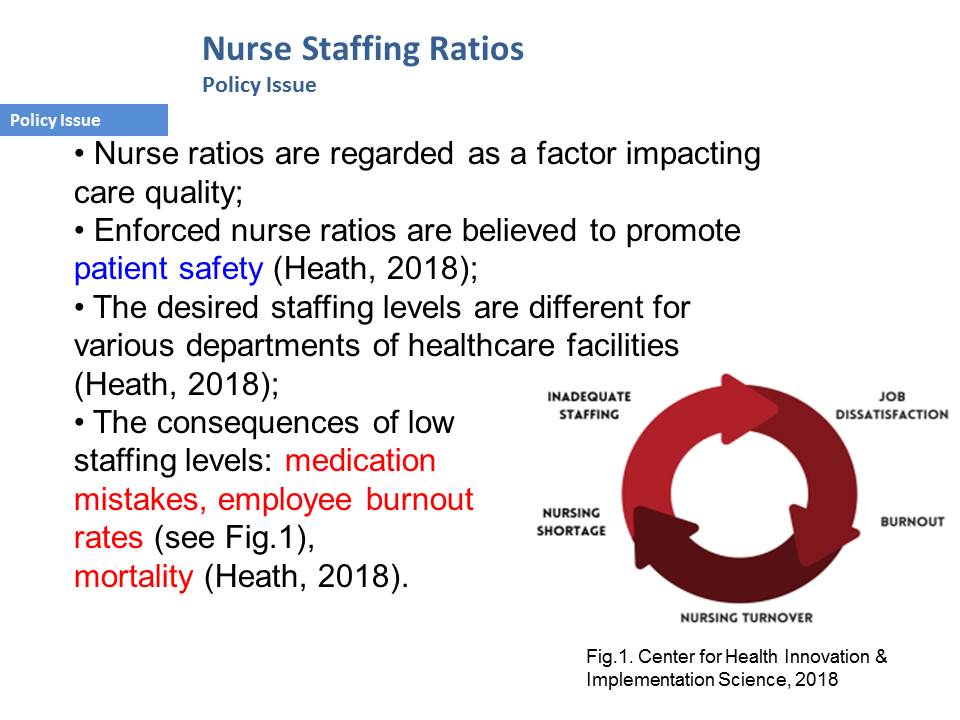
- The consequences of low staffing levels: medication mistakes, employee burnout rates (see Fig.1), mortality (Heath, 2018).
In nursing, the quality of care is believed to be impacted by numerous factors. According to Heath (2018), higher nurse staffing ratios belong to the number of factors that improve health outcomes for patients with both chronic and acute conditions. The proponents of enforced ratios believe that the effects of low staffing levels are detrimental both to patients and nurses, leading to ineffective care and emotional stress.
At first sight, it seems evident that by increasing nurse staffing levels, it is possible to reduce the number of hospital-acquired complications. The problem, however, has not been solved yet due to the contradictory results of research.
Policy Issue: Controversial Findings
- More than 85% of nurses feel pressed in time when providing patient education (Heath, 2018);
- The introduction of enforced staffing ratios can cause negative financial consequences (Heath, 2018);
- The implementation of strict federal staffing standards is criticized (see Fig. 2).
Despite the universal character of the problem, not all specialists see enforced staffing ratios as a good solution. The issue is represented in different aspects of care. The findings of official reports point at the problem; thus, the report of the Parkinson’s Alliance states that more than three-quarters of nurses feel that they would need to devote more time to educating healthcare consumers (Heath, 2018). However, specialists from the Massachusetts Health and Hospital Association prove that enforced ratios can be financially burdensome (Heath, 2018). Given various demographic and financial factors, the introduction of strict federal rules is not widely supported.

Government Response
The proposed ways to reduce the negative consequences of low staffing ratios:
- Oblige all healthcare facilities to create nurse-led staffing committees responsible for planning;
- Implement the state-mandated staffing ratios.
Control the situation through increasing data transparency (American Nurse Association, 2015).
A series of attempts to formalize the desired nurse staffing ratios in legislation has been made since the problematization of the concept. According to the American Nurse Association (2015), the U.S. Government has a few ways of solving the problem: the creation of nurse staffing committees at hospitals and the use of fixed staffing ratios. Additionally, in some states, healthcare facilities may be obliged to publish nurse staffing levels on a regular basis. Nowadays, some of these measures are used in the United States, but their effectiveness is quite difficult to analyze. The model supported by the ANA involves enabling nurses to create and implement staffing plans.
The states that have nurse staffing regulations:
- Nurse-led staffing committees:
- Connecticut, Illinois, Nevada, Ohio,
- Oregon, Texas, Washington;
- Required nurse-patient ratios:
- California (see Fig. 3), Massachusetts;
- Public disclosure of staffing ratios:
- Illinois, New Jersey, New York,
- Rhode Island, Vermont (American Nurse Association, 2015).
Nowadays, nurse staffing rules that represent one of the three previously discussed strategies are in use in more than ten states. The creation of staffing committees, as is clear from the slide, presents the most popular approach to the problem due to its flexibility. Also, the use of public reporting is considered an important option since it promotes honest competition and helps clients make informed choices. The minimum staffing ratios are implemented in California as a key approach to solving the problem. Massachusetts is also going to implement fixed standards for intensive care units – it is planned to use a 1:1 ratio for critical patients and 1:2 ratios for stable patients.


Assessment
The pros of the implemented strategies:
- Nurses’ experience and perceived difficulties are taken into account;
- Nurse-regulated staffing levels make the strategy more flexible (Heath, 2018);
- Public reporting measures can be beneficial both for regulating agencies and patients.
The positive sides of the legislative strategies and initiatives implemented in the United States are numerous and relate to the flexibility of measures and the effects for patients. The establishment of nursing committees that design standards and plans for particular healthcare facilities is extremely helpful. It allows taking into account the factors that would prevent hospitals from meeting federal standards: the situation with employment markets, unexpected epidemics, etc. Also, the use of reporting standards in some states helps increase healthcare consumers’ awareness of potential problems and conduct research based on the retrieved information.
The cons of the implemented strategies:
- The majority of states still have no specific solutions to the problem;
- Both attempts to implement nationwide rules (Senate Bill 1063 and House Resolution 2392) were unsuccessful (Heath, 2018);
- Strict requirements may urge hospitals to hire inexperienced staff.
The key disadvantage of the implemented strategies can be related to their heterogeneity. As a result, it becomes more difficult to compare the situation with care quality in different states. The idea to introduce similar standards for all states is widely criticized, and neither of the two initiatives that refer to universal rules was accepted. An important disadvantage related to the strategy in California relates to some unethical practices that healthcare providers may use to meet the standards. For instance, inexperienced people may be hired, which is detrimental to the safety of patients and incompatible with the law’s initial goals.


References
American Nurse Association. (2015). Nurse staffing ratios [Digital image]. Web.
Center for Health Innovation & Implementation Science. (2018). Nursing turnover [Digital image]. Web.
Heath, S. (2018). How nurse staffing ratios impact patient safety, access to care. PatientEngagementHIT. Web.
National Nurses United. (n.d.a). California ratios [Digital image]. Web.
National Nurses United. (n.d.b). Proposed federal RN-to-patient safe staffing ratios [Digital image]. Web.