Executive Summary
The study of operational management has been around for decades. A general understanding of the nature of operations in management takes businesses to the next level.
Any business has a number of operations divided by their functions, such as the accounting and sales divisions and in any operational unit, work processes exist to smooth operations and eliminate mistakes. All operations of a company are important. They complement and aid each other in the overall operations.
This paper will analyze a historic five-star hotel’s operations. It will focus specifically in its current marketing operation. The marketing division is in focus because of the current setback the hotel is experiencing. The hotel used for this study has special features that provide information adequate for the study.
Common operational management concepts are used to identify and evaluate the current system. Concepts from lectures and other secondary data are also used to describe, supplement, and reference previous research.
Some concepts used are lean manufacturing, benchmarking and business process re-engineering. They were used to identify problems and challenges of the hotel. Potential problems and following recommendations were explored by the end of the paper.
The main concern for the hotel is the decreasing number of customers because of the cheaper and quaint hotels in its vicinity. This information is the reason for selecting the operational unit focused on.
Methodology
The existing data available is provided. There are certain features in the information provided that will allow me to assume a number of things, such as the implications that being a historic hotel will offer.
The concepts used to analyze the data from the hotel and its operations were presented in a lecture during class. They will be discussed on the historic hotel to provide useful information for the improvement of the effectiveness and efficiency of the operations of the hotel. Other secondary data will also be used.
The method of analysis will be as follows. First, the current situation of the hotel and the specific operational unit chosen will be described and analyzed. Then existing problems of the hotel and the operational units will be identified and analyzed.
Next, the paper will provide recommendations for solutions to the current problems identified. Lastly, the paper will provide potential problems, recommendations, and opportunities that the hotel can plan ahead for.
This paper will refer to concepts presented from the class lectures and will aim to improve the overall operations of the hotel by the above method.
Brief Description of Special Features
Special features of the hotel are as follows:
- the hotel is historic,
- it was highly profitable and popular before the past few years,
- it is privately owned,
- it is a five-star hotel,
- it is near hotels which appear economical and quaint,
- it is strategically in the center of an international city that has a high level of tourists, particularly international tourists.
A “historic” hotel means that the hotel was the setting of a historical event, whether it is a cultural or political event. Thus, it would hold a certain ambience prevalent to the culture of the country in that time of history.
The hotel will have retained the architectural style of the period it was built in or at least influenced by it. We can assume that the hotel was popular throughout the years because of this and as suggested by the statement of its high profitability.
That the hotel is privately owned means it is not publicly traded in a securities exchange in the country (Privately owned n.d.). Depending on which type of economy the nation falls into, privately owned enterprises such as this hotel will have a number of implications. If it falls into a traditional economy, operations would be controlled and less dynamic than other systems.
A command economy has strong government control while a free market economy has little government control. Mixed economies which combine elements of command and free market economies are the most common economies used by many countries today because of it provides an enough mix of public and private interventions on economic decisions and resource allocation and distribution. (Schmoop Editorial Team 2008).
Since it was not stated in the problem what the hotel is like in its economic decisions we will assume it is under the most common economy which is a mixed economy.
The historic hotel is described to be a five-star hotel. This means its standard for quality is of the highest ranking. Five-star hotels are expected to offer excellent service and the highest standards of comfort for their guests.
Additional features of five-star hotels include originality in architecture and interior design, high quality construction, and special touches such as fresh flora as decoration. Space, services, and amenities are always sufficient and comfortable (Star rating system hotel requirements for four, five star etc n.d.).
Analysis of Hotel
There are several operational units in this hotel. These would include general management, front office, rooms division, maintenance, food and beverage, purchasing, marketing, human resources, finance, security and safety, and parking (Best practices n.d.). An overall process flow follows.
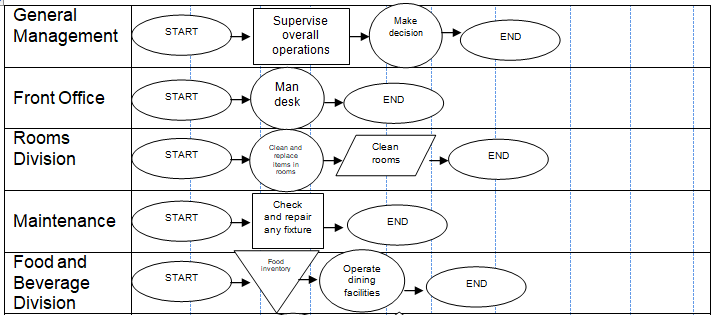
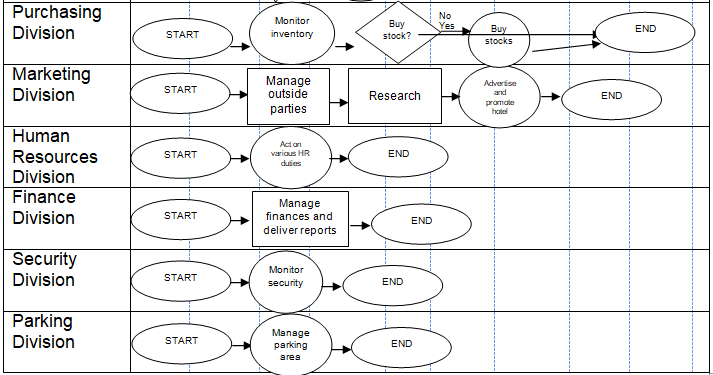
The hotel’s processes are service types. They are considered service shops, which are characterized by medium levels of volume of customers, medium or mixed levels of customer contact, medium or mixed levels of customization, and medium or mixed levels of staff discretion (Slack, Chambers & Johnston 2010). These characteristics put the operations between the extremes of professional and mass services.
The implications provided by the description of the hotel are that the hotel’s design is not contemporary and the accommodations are pricey.
The main problem of the hotel is in marketing their products and services to tourists amidst cheaper hotels in the area. The hotel is in an area where competition is high because it is located in an international city and in a tourist spot. It is essential that a new marketing strategy is applied to save the hotel from lesser profitability in the near future and possible bankruptcy in the long-run.
Although not on the same level, competition with the cheaper hotels is challenging and needs to be addressed immediately. The hotel’s marketing division, since this is the main concern, is the focus of the paper.
Analysis of Marketing Operation
I chose the marketing division as the operational unit to focus on because it pertains to the mentioned problem of the hotel, which is the decrease of customers.
The marketing team is responsible in providing leadership on serving guests better. They provide insight on how to serve the hotel’s customers better by developing pricing, conducting customer surveys, contributing insights on product and service development, and examining competition.
The team also supports other divisions in their operations. They support the general management and the purchasing division. Marketing is responsible for advertising and promoting the establishment. Different media are used to do so.
Finally, the marketing team is responsible for managing relationships, whether with suppliers, competitors, or customers (4 core marketing strategies n.d.). Below is a process flowchart of the marketing division.
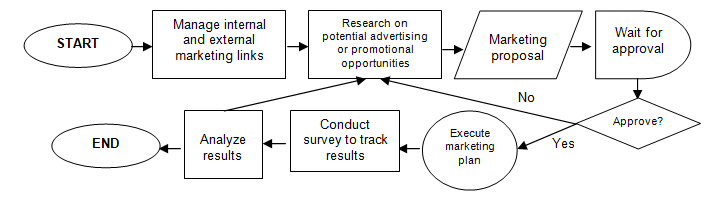
The hotel is said to have lesser customers due to the existence of cheaper quaint hotels around its vicinity. It is located in the middle of an international city and is a tourist spot. Tourists choose other hotels because of the price and charm of neighboring hotels over our hotel.
This is not unexpected since tourists do generally vacation on a budget. Affordability is a major factor taken into account by most tourists (Tourists seek cheaper travel options 2012). It is, however, not the only reason as we will discuss later.
What the hotel needs to do is ‘think outside the box’ and innovate their services to attract tourists to stay at their hotel regardless of the price. Although the hotel can be said to offer exceptional services as evidence of its five-star status, it needs to think outside the box and market what it can offer to customers that other hotels cannot.
Tourists on a budget trip do not mind cheaper hotels’ lack of quality service and the competition in the area is the main challenge the hotel faces. What the hotel needs to do is to “think outside the box.” Jones (2001, p.82) says that consumers are increasingly looking for “solutions”, where product, service, advice and expertise are seamlessly integrated. Innovation is important in any industry.
It is important for the hotel we are looking at. Innovation with products and services will give the business a competitive edge against competitors in the vicinity.
It will give value and uniqueness to the product and services offered and it is up to the managers of the hotel to think of “solutions” for the customers. Once consumers needs are determined and agreed, then can the innovators work out precisely what to deliver to the consumers and when.
It is sensible to learn from past mistakes. A lesson learned from automakers from the past is this – while western automakers focused on ‘adding luxury’ to their vehicles, Japanese automakers focused on ‘adding quality to everything’ (Tennant 2001, p. 4).
It is a feature of any five-star establishment to be luxurious but the lesson the hotel can draw from this is to re-focus efforts not on adding luxury to the products offered but to the quality of existing products and services of the hotel.
Continuing from this line of thought, the hotel can also do this – focus on quality – by adapting ‘lean’ principles in its operations. Lean principles state that expenditures of resources, if not seen by consumers as value-adding or worthy, should be eradicated (Holweg 2007).
This practice reduces unnecessary costs and staffing requirements. For the management of a luxury hotel though, it can be hard to decide if the luxuries offered are reasonable. There is a fine line for five-star establishments between luxuries and those extras that should be eradicated because in definition, luxuries are extra indulgences conductive to pleasure and comfort (Luxury n.d.).
The hotel can also do to benchmark. Benchmarking is identifying, analyzing, evaluating, and adapting the industry’s best practices for the advantage of the hotel (Boxwell 1994). The hotel has function rooms that can be used for all kinds of events, from weddings to conferences.
Von Starck (2004, para. 3), a general manager of a five-star restaurant and a consultant on hotel marketing issues, particularly on food and beverage issues, says that the design and furniture of function rooms gives an establishment a big advantage.
Socialites and brides, in particular, are heavily attracted to the appearance. Food and beverage is also important in drawing good reviews. Food, he says, should be imaginative, with good presentation. The service provided is also important. The quality of service will keep customers coming back developing good relations to clients.
Von Starck (2004, para. 6), also said that hotels could really boost sales by working on their menus. By customizing the style, pictures, and look of the design, menus could target different audiences, separately and discretely.
Another good marketing strategy practiced by hotels is to bring a personal touch to their websites. Von Starck (2004, para. 1) claims it a fact that the most visited websites are those that include stories and bios about employees of the establishment. The reasoning behind this is that people want to know about the people behind the business.
In addition to what the business offers to its customers and what the staff is like, people want to know how these will reflect on them. They want to know if the business will coincide with their personality and lifestyles. They want to know if the business is worth paying and they base these off the websites. The internet is the most convenient and economically friendly media both for businesses and consumers (Negi 2011).
The hotel’s website is a helpful tool in marketing if used wisely. Studies showed that people are increasingly using the internet to book reservations (Crick n.d.). There may come a time when it will become the only media for information gathering that people will use.
The hotel having problems with its marketing implies that the current marketing operation is not effective or efficient anymore. Another concept that might help the business in the long run is the concept of business process re-engineering.
Business process re-engineering or BPR means that process or work flow of marketing operation will be scrutinized, analyzed and changed if its performance is not effective or efficient for the hotel anymore (Business process re-engineering 2001).
The steps in BPR requires the analyst to first identify the processes in the work flow, review and analyze the data and information gathered, design a new work flow, test the new work flow, and after adjustments, implement it. Implementation of BPR is said to be difficult.
The rate of failure of BPR is over fifty percent (Revenaugh 1994). The process of changing the work flow takes time and persistence because it requires participation and cooperation of everyone involved.
Possible Difficulties and Recommendations
It is daunting to face major challenges, especially in the large-scale. Innovation always comes with risk. Implementation of new strategies requires careful planning and attention. There should always a contingency plan or a backup for when going through with a new radical idea.
When implementing new strategies, there will be risks of failure. There is a potential that the business would lose more money than they would have gained. When benchmarking and adapting new practices, there is the potential that the best practices do not go well with the particular establishment.
Working on smaller projects for the hotel might be more difficult. When working on menus and websites, it is noteworthy to be meticulous.
A potential problem for the management when looking to eliminate products or services that add no value is the risk of opposite results. When implementing a new work process, problems such as resistance or difficulty in transition of persons involved is expected (Allen & Fifield 1999).
Careful planning is important when acting on new strategies. To avoid losing money and other set-backs, management should take the time to test products before buying them in bulk and be certain that new services offered will perform to standard before applying them to customers.
Management should have contingency plans and emergency procedures for retaliating on defects and errors to stop problems at the earliest time. Maintenance and constant monitoring is necessary to avoid accidents. Opinions and suggestions should be welcomed and taken into account. Resources should be used wisely to avoid loses (Lean manufacturing techniques 2011).
Summary of Key Findings
By analyzing the given business using several concepts in operational management, this paper was able to discuss and evaluate the hotel.
To start, the hotel needs to think outside the box and implement a new marketing strategy to increase profitability – a demand from any establishment when competition is high in its area. To do this, management needs to add value to their products and services to meet consumers’ ever evolving wants and needs.
Instead of focusing on adding luxury to the products and services, management should look at the current quality offered by the hotel and work on improving that. The lean practice of operational management suggests that the establishment eliminates products and/or services with no value to the customers, therefore reducing costs and unnecessary actions.
The hotel can benefit greatly by benchmarking. Learning from the best in the industry and adapting practices that suit the establishment will allow the hotel to grow and be competitive amidst heavy competition. Improving the establishment’s tools is helpful.
Paying attention to menus and websites will subtly improve the hotel’s marketing. Adding personality gives the hotel uniqueness and advantage. Finally, the business process re-engineering method would be helpful in the long-run but be prepared for the difficulties it would ensue.
Reference List
4 core marketing strategies. Web.
Allen, D. & Fifield, N. 1999, ‘Re-engineering change in higher education’, Information Research, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 104-110.
Best practices. Web.
Boxwell, R. 1994, Benchmarking for competitive advantage, McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing, London, UK.
Business process re-engineering (BPR) 2001. Web.
Crick, C., Travel opinions – key influences on tourist decision making. Web.
Holweg, M. 2007, ‘The genealogy of lean production’, Journal of Operations Management, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 420-437.
Jones, D. 2001, ‘Thinking outside the box’, ECR Journal, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 81-89.
Lean manufacturing techniques for identifying waste 2011. Web.
Luxury. Web.
Negi, S. 2011, E-publishing: the most convenient, eco-friendly and 24×4 accessible online media. Web.
Privately owned. Web.
Revenaugh, D. 1994, ‘Implementing major organizational change: can we really do it?’, The TQM Magazine, vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 38-48.
Shmoop Editiorial Team 2008, Types of economic systems. Web.
Slack, N., Chambers, S. & Johnston, R. 2010, Operations Management, 2nd edn, Pearson Education Limited, England.
Star rating system hotel requirements for four, five star etc. Web.
Von Starck, E. 2004, Food and beverage: how caterers can cream hotels and what to do to get the business back. Web.
Von Starck, E. 2004, Menus that work as a sales tool. Web.
Von Starck, E. 2004, Personality on your web site and why. Web.
Tennant, G. 2001, Six sigma SPC and TQM in manufacturing and services, Gower Publishing Company, England.
Tourists seek cheaper travel options 2012. Web.