Abstract
Israeli-Palestinian conflict has continued for six decades and has caused the deaths of thousands of people. Disputes over territorial borders, ownership of Jerusalem, and water resources are some of the sources of conflict. The type of conflict that is evident is confrontational conflict because the two countries fight to achieve their demands. The conflict does not only cause the deaths of people, but it also threatens international security. The application of the crisis management process is effective in the resolution of conflicts because it offers a systematic process of resolving conflicts. To resolve the conflicts, the recommendations are that Israel and Palestine should cease the attacks, the United Nations should compel signing of peace treaties, the leaders should undertake fruitful negotiations, and the ICC should identify and arrest culprits.
Introduction
The Israeli-Palestinian crisis had continued since the time when Israel gained its independence as a sovereign nation in 1948. Evidently, some of the main causes that initiated the war between Israel and Palestine include border control, ownership of cities such as Jerusalem, and problems related to the displacement of Palestinians. Although Israel and Palestine have signed several peace treaties under the mediation of countries like Egypt and the United States, none of them has honored these treaties. Therefore, the study examines the case study of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and discusses the cause, type of the conflict, effects of the conflict, crisis management process, and offer recommendations.
Case Study
Although the war between Palestine and Israel dates back to the middle part of the 20th century, it became apparent in 1948 when Israel attained its independence. When Israel achieved its independence in 1948, some parts of the Palestinian territory became part of Israel, and thus, some Palestinians retaliated. According to Ross (2004), some Arab countries were not in agreement with the formation of a Jewish state within the borders of Palestine and Jordan. The initial disagreement explains the breakout of war soon after 1948. As a result, the war has continued for the last six decades and has caused thousands of deaths, with Palestinians being the major victims.
Discussion
Major Causes
Some of the major causes of the Palestinian-Israeli war include ownership of Jerusalem city and border control. When Israeli and Palestinian communities were displaced during the Holocaust, the initial borders faded away, and thus, after the Holocaust, Palestinians and Israelis could not trace the initial borders. The absence of initial borders led to war between the two countries, as they compete for resources such as land and water.
Border conflicts date back to the period when Palestinian and Israeli refugees returned to the region (Childress 2011). Furthermore, ownership of Jerusalem stirred war between the Jews, who believe that it is their place of worship since historical times, whereas Palestinian communities want to own Jerusalem, as they believe it is theirs. The intense war in the Gaza Strip is one of the evident border conflicts that Palestinian and Israeli communities have executed.
Type of Conflict
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a confrontational type of crisis, which have smoldered for six decades, because of the nature of war is offensive. Both Israel and Palestine have made demands that they require so that they can cease fighting over Jerusalem, borders, water resources, and security. Palestine does not recognize Israel as a state, it views Israelis as aliens, who arrived and took over their land and formed their state.
In contrast, Israelis view Palestinians as invaders of their sovereign state as they frequently initiate offensive attacks with the view of displacing Israelis like the period of the Holocaust with the view of taking over their territories (Handelman 2011). Since Israel and Palestine have never agreed on the nature of compromises that they have made thus far, they have continued to undertake offensive attacks, which depicts a confrontational type of crisis.
Effects of the Conflict
The direct effects of the Israeli-Palestinian war are the displacement of populations and loss of lives, which constitute crimes against humanity. Although both Israel and Palestine’s experience the displacement of populations and loss of lives, Israeli and Palestinian communities, a majority of reported casualties are usually from the Palestinian regions.
Mothers, children, and young men from regions such as the Gaza Strip regularly die because of the war that has lasted for decades. Since the Israeli-Palestinian conflicts cause disproportionate loss of lives, among the reported deaths, about 20% are Israelis, while about 80% are Palestinians (Ross 2004). Women and children are the main causalities of the war because they are the most vulnerable groups. The number of children’s death is quite alarming because over 90% of deaths are for Palestinians, as depicted in the figure 1 below.
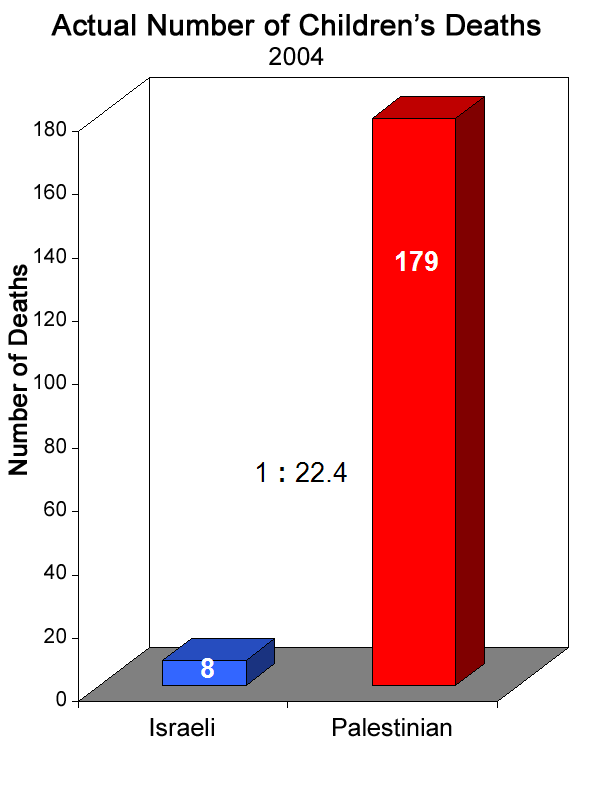
The Israeli-Palestinian crisis has damaging effects on the security at the Middle East and across the world. Although the Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a regional conflict that mainly affect Israelis and Palestinians, the interests of Arab nations and the Western nations has potential of degenerating the conflict into global war.
Since the war between Israelis and Palestinians have smoldered for a period of about six decades, it is likely to trigger global war given that the Western countries like the United States and the United Kingdom support Israel, while the Middle Eastern countries like Iraq, Syria, Iran, and Pakistan advocates for the extermination of Israeli state (Rabinovich & Reinharz 2008). Hence, the precarious nature of the Israeli-Palestinian crisis could easily degenerate into global war if appropriate interventions are not in place to manage the crisis.
Crisis Management Process
The crisis management process provides systemic process of addressing diverse form of crises. Coombs (2011) states that pre-crisis, crisis response, and post-crisis are the three phases that are applicable in the management of crises. The pre-crisis phase entails preparation of effective interventions to manage crisis effectively, while the crisis response phase focuses on the actual process of managing the crisis.
The post-crisis phase reviews the activities undertaken during the phase of crisis response with a view of improving the process of managing a crisis effectively. Therefore, in the case of Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the application of crisis management process is essential to effectively manage the conflict and avert further occurrence or deterioration.
In the pre-crisis phase, the activities should focus on reducing the risks that cause the conflict. Coombs (2011) identifies crisis management team, crisis management plan, and spokesperson as requirements of pre-crisis phase. The crisis management team comprising Israeli and Palestinian leaders, international community, the media, and military leaders should deliberate on the crisis.
The management team should formulate crisis management plan, which outline very tasks that they should perform so that they can settle the conflict fairly. Since the media play a significant role in influencing the course of the conflict, the crisis management team should have spokesperson with capacity to create public relations without indicating any form of biases.
The crisis response phase is critical in the resolution of conflicts because it reflects the nature of interventions undertaken. Coombs (2011) states that the crisis response phase commences with the initial crisis response, which must be rapid, accurate, and consistent to enhance successful management of crisis. In this view, the crisis management team must focus on resolving contentious issues such as recognize ownership of Jerusalem, define territorial borders, cease offensive attacks, and specify share resources.
The second aspect of the crisis response is reputation repair, which entails creating public relations, communicating effectively, and maintaining appealing image. Regarding the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the reputation repair aspect should focus on taking appropriate actions such as identifying the culprits, justifying the occurrence of crisis, apportioning blame, and compensating victims.
The reputation repair continues and becomes part of the post-crisis phase, where a review of the interventions occurs. In the post-crisis phase, the management team can review their progress and provide appropriate recommendations. According to Coombs (2011), the best practices for post-crisis are delivering information to stakeholders, updating stakeholders, and analyzing the progress of the crisis. Hence, since Palestine, Israel, and international community are major stakeholders, the management team should update them with interventions undertaken and update them with the progress of the conflict.
Recommendations
- The Israel and Palestine should cease the offensive attacks and concentrate on building their relationships for mutual benefits.
- The international community and the United Nations should pressure Israel and Palestine to sign peace treaties and stop the use of weapons against each other.
- The Israeli and Palestinian leaders should negotiate and settle disputes of border, resources, and Jerusalem.
- The International Criminal Court (ICC) should intervene by identifying culprits and prosecuting them for crimes against humanity.
Conclusion
The crisis between Israel and Palestine has existed for six decades and has caused the deaths of thousands of people. Border conflicts, ownership of Jerusalem, and settlement of displaced individuals are some of the causes of the crisis. As a confrontational and smoldering conflict, the crisis requires the application of crisis management process to resolve. Cease-fire, treaties, negotiations, and prosecution of culprits are some of the solutions that are appropriate in resolving the crisis.
References
Childress, D 2011, A Hitchhiker’s Guide to Armageddon, SCB Distributors, New York.
Coombs, T 2011, Crisis management and communications. Web.
Handelman, S 2011, Conflict and Peacemaking in Israel-Palestine: Theory and Application, Routledge, London.
Rabinovich, I., & Reinharz, J 2008, Israel in the Middle East: Documents and Readings on Society, Politics, and Foreign Relations, Pre-1948 to the Present, UPNE, Lebanon.
Ross, S 2004, Causes and Consequences of the Arab-Israeli Conflict, Evans Brothers, Lagos.