Introduction
The pandemic caused a significant impact on the global human population mainly because of the consequential economic lockdown and restriction of movement and interactions. A significant percentage of personnel lost their livelihoods due to the scaling down of business operations. One of the key challenges in the U.S is the high cost of medication and the insurance policy. Therefore, the reduced economic activities contributed to the elevated social needs among people, mainly access to quality healthcare services for tests and treatment of the infected during the pandemic.
Background of the Study
In 2020, the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a pandemic, rendering emergency response systems taking over. Researchers establish that a significant percentage of countries have implemented policies enhancing the prevention of the spread of coronavirus (Pokhrel & Chhetri, 2021). The measures included quarantining the infected personnel, restricting interactions and movements, and the economic lockdowns. In this case, the core solution encapsulated limiting the spread while the medical practitioners investigated and focused on developing a vaccine. Despite the preventive measures, the government concentrated on the control mechanism without addressing the influence of medical care policies against the backdrop of COVID-19. It is the responsibility of key stakeholders to coordinate towards the advocacy for sustainable healthcare services among the citizens.
Impact of COVID-19 on Community’s Well-being
The emergence of COVID-19 significantly contributed to identifying key issues in the healthcare service provision system. According to research, the prominent spread of the coronavirus caused the rise in the number of patients admitted to the hospitals (Pokhrel & Chhetri, 2021). The aspect contributed to the necessity of incorporating measures to improve the quality of care and safety among the workers. The main reason for the intensification of protective measures among the frontline workers enshrined the risk of exposing their families to the illness. Therefore, the efficacy in protecting and preventing the adversities engulfed the incorporation of distinctive measures that boosted quality service care provision.
Nurses are mainly the frontline workers in the healthcare sector due to their direct contact with the patients. After the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, a significant percentage of the American population attained the infection. The situation led to the intensification in hospital cases while the nurses face the apt risk of contraction due to the profound encounter with the victims. The researchers collected and analyzed data to determine the various issues affecting the nurses’ welfare (Robinson et al., 2022). In this case, the sample size enshrined 19 respondents, and the data was jointly and separately analyzed to determine the influential core factors. The researchers established four different variables that prominently impact the interdependent relationship. These quotients engulfed overwhelming feelings, role frustration in the care service environment, community, family, leader abandonment, and progressive resilience from perseverance.
Critical infrastructure proficiently empowers medical practitioners and the dynamic frontline workers to complete their assigned tasks efficiently. The participants argued based on the concerns of enhancing the critical infrastructure in the hospitals to boost their performance. Despite the fear of infections, the nurses showed apt concerns about the lack of tools to contribute to the elevation of the performance quotient. It is the responsibility of the nurses to protect and improve the living quotient among the patients. However, the pandemic fostered a proficient increase in admissions and complications among the counterparts. The research depicts that the core aspect of amplifying the living experiences among nurses in rural America involves the relevant stakeholders’ involvement in improving critical infrastructure facilities in the medical care centers, as demonstrated in figure 1.0 (Robinson et al., 2022). The reliability of the study scores high marks mainly because of seeking consent from the respondents and intersecting the primary and secondary literature to affirm the critical objective of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the frontline nurses.
COVID-19 pandemic fostered intensified stress levels among the frontline nurses through the interplay of distinctive issues. The researchers demonstrate that the vital issues enshrine burnout and stress that significantly contribute to the risk and emergence of post-traumatic stress disorders (Yang et al., 2022). The researchers indicate that one of the critical aspects of promoting healthy living among the nurses involves ensuring the flexibility and the involvement of family and community members. During the pandemic, governments initiated economic lockdowns and social isolation among people. The situation caused difficulty in the accessibility of dynamic amenities and the movement of people. The nurses worked extra hours with the concern of exposing the family members to the coronavirus. Overworking leads to burnout among the frontline workers causing the apt risk of poor performance and the development of PTSD. On the one hand, the workers played a crucial role in advocating for patients’ protection. On the other hand, the nurses risk contracting the virus and burnout that affects their physical and mental states.
Burnout among nurses mediates the relationship between stress levels and the risk of attaining PTSD. Yang et al. (2022) articulate that apart from burnout among the nurses, the longevity of living away from their families significantly contributed to the elevated stress levels. The researchers agree that the core mandate among the counterparts involved providing services to the American population despite the limited resources for care services. Ideally, the pressure prompted the nurses to pose the profound risk of attaining post-traumatic stress order. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure diversity in the work duties and create a sustainable working environment for optimal performance among the nurses. Although it is crucial to promote optimal patient protection, competence in the institution relies on the capacity of the counterparts to coordinate and improve the operational outline. COVID-19 pandemic significantly contributed to the risk of PTSD among frontline workers mainly because of the increased patient population and the essence of contracting the virus.
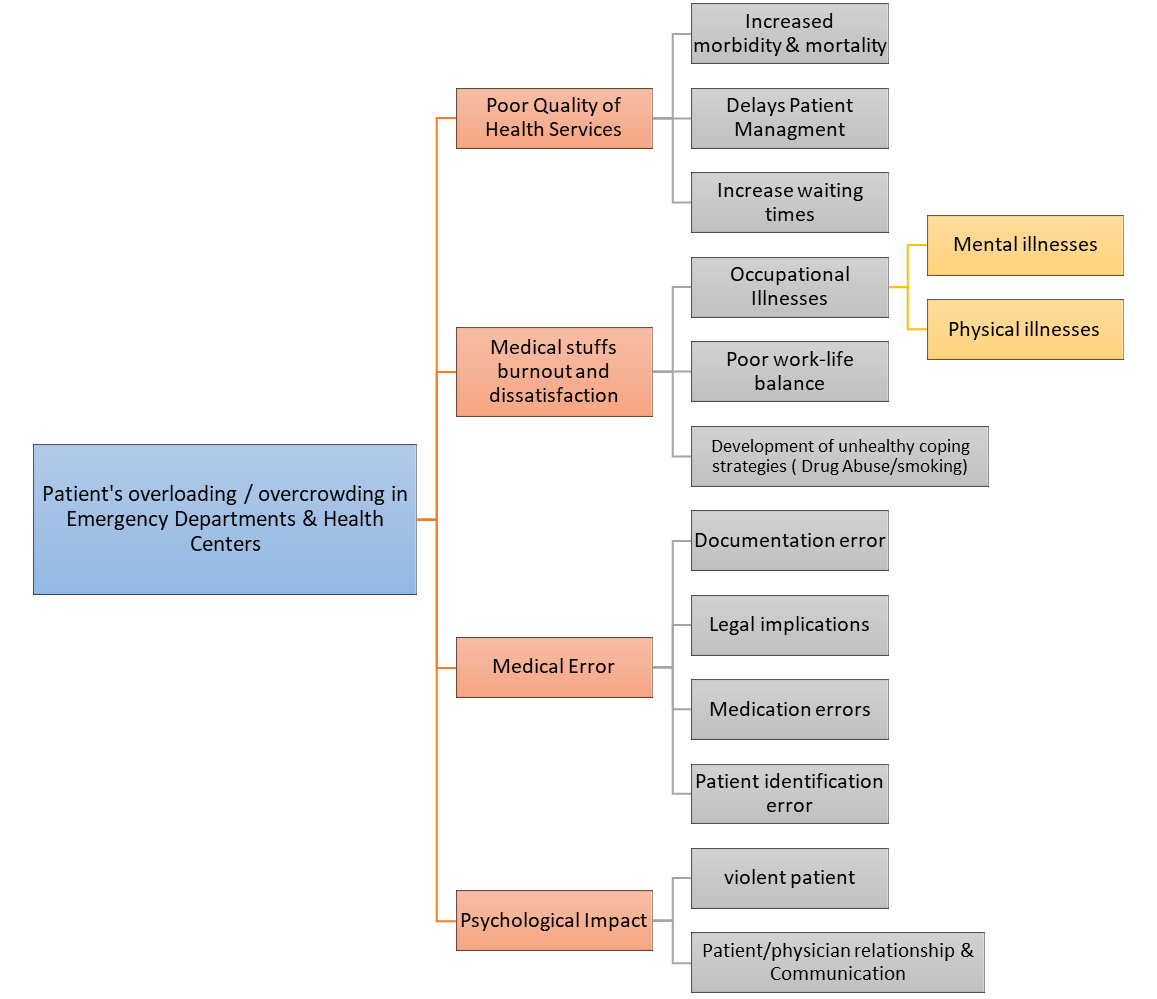
Over the decades, different institutions fostered the development of distinct models of care focusing on the alleviation of the major problem. One of the significant challenges within the Dubai government emergency department encompasses overcrowding. The initiative causes profound adverse effects on the patients and medical practitioners cause of the drawback in the processing timeline among patients that risks poor service delivery system. Research by Kader (2019) indicates that the insufficient supply of equipment and facilities poses a dynamic hindrance to the performance outlier among the nurses and the effective patient treatment. Salim and Rahman (2020) stipulate that the congestion of patients in the Dubai healthcare facilities violates the UAE Vision 2020 pillar on boosting the quality of medical care. In a different spectrum, the lack of adequate studies involving the assessment of the setback of congestion within the healthcare institutions contributes to the prevailing factor within the Dubai territories.
The rationality for the government intervention is an important factor cause of the emergent issues in healthcare operations. The overcrowding of patients in the emergency departments compromises the standards of engagement between clients and the workers. Improving the quality of services within the medical care sector involves enhancing the accessibility of functional tools and expertise among the nurses (Kader, 2019). The approaches foster the alleviation of the overload and the emergent inherent issues regarding burnout among the healthcare practitioners and customers’ dissatisfaction. Intensifying stress among the laborer risks a higher marginal error among the personnel. Therefore, rendering administrative support surges the system performance in the UAE. The persistence of the issue endangers the reputation of the city’s ability to provide competent care plans to the consumers (Muslim, 2019). The significance of addressing the hindrance engulfs triggering the saving on incurred costs while coordinating the distinct activities.
Policy Options
The effective implementation of policies during the Covid 19 pandemic and project management heavily rely on knowledge’s strategic management. The knowledge theory gears the research mainly because it enhances sustainability in establishing a competitive advantage. The research competence depends on the efficient integration of intellect capital and strategic alliances. In this case, the researcher seeks to utilize secondary and primary information to assess the dependent and independent variables (Pokhrel & Chhetri, 2021). Knowledge management plays a vital role in project management due to establishing information-sharing structures that ensure different stakeholders effectively access the necessary details. On the one hand, strategic management renders the effective completion of the projects. On the other hand, effective knowledge management during a project fosters the optimal derivation of benefits to the relevant stakeholders. In this case, the initiative cultivates a structural development that foresees the sustainable trickle-down effect of accrued benefits.
The spread of coronavirus is an issue that dynamically influenced the American community’s growth and development, mainly because of its pandemic status. The disease rendered the closure of businesses and quarantine of all Americans. In addition to the social media posts about the deaths, the precautionary measures highly affected individuals’ perception of the infection. The utilization of an effective social media campaign significantly contributes to the increase in the prevention of the coronavirus spread across the American community (Pokhrel & Chhetri, 2021). The coronavirus spread’s critical prevention technique is establishing an effective social media campaign that targets all American population dynamics.
Congress focused on implementing a Bill that addresses the frontline workers’ issues mainly during the COVID-19 pandemic. The Bill is founded on the statistics presented by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). According to the CDC statistics, in January 2021, the institution had recorded at least 25,000,000 cases of COVID-19 and 400,000 deaths in the United States (Salud, 2021). The distinctive issues of the spread of the coronavirus in the U.S encompassed a shortage of frontline nurses and limited protective gadgets for the various frontline workers in different sectors. In this case, it was crucial to establish critical measures to improve the performance among the counterparts and their protection from contracting the virus.
The first measure of the Bill encapsulated Congress honoring and enhancing contribution to improving critical infrastructure for the personnel. Another measure enshrined Congress’s reaffirmation to implement approaches enhancing the protection among the elderly and frontline workers by providing protective and safety equipment. The Bill was referred to the subcommittee on health and the House Committee on Energy and Commerce (Salud, 2021). The implementation of the regulation fosters the prominent commitment of the House of Representatives toward investing optimal resources in advancing the quality of care in the U.S. The engagement demonstrates the profound importance and relevance of the issue concerning the interdependent quotients. The Bill is one of the foundational aspects of intensifying the role of government in improving medical care provision across the American population.
Recommendations
A social media campaign is a guiding tool for the communities on well-being mainly because healthcare professionals share crucial medical-based information across the different platforms. Yousuf et al. (2020) stipulate that a social media campaign is an empowerment tool for the American community since it fosters the effective sharing of crucial information about coronavirus and the infection. The spread of healthcare information about coronavirus through social media platforms asserts the communities regarding the appropriate steps to carry out infections. It is a contrasting technique that eliminates mythologies’ influence that instills fear among individuals.
Social media campaign engulfs the provision of updated information regarding the progress of coronavirus prevention. On the one hand, it is crucial to provide guidelines to the community about the best prevention and treatment approaches. On the other hand, it is vital to provide updated information frequently. It is an initiative that the campaign attains credibility and reliance from the patients. In a research study, Ali et al. (2020) establish that the healthcare practitioners’ responsibility is to maximize the online presence and update the followers about the curve of coronavirus and the emerging issues such as the essence of the mutating forms. Therefore, the social media campaign’s credibility and reliability depend on the frequent provision of updated information.
Sustainable use of social media campaigns is an initiative that involves the utilization of moral and ethical hashtags and titles of discussion forums. The American population is dynamic based on moral and ethical perspectives on religious practices. In this case, it is essential to utilize a common language that attracts all American citizens to the discussion forum, contribute, and learn about coronavirus prevention (Dong et al., 2020). The social media campaign engulfs a dynamic number of stakeholders. The social media campaign’s relevant stakeholders comprise medical experts, government representatives, and the American community. The optimal participation of all stakeholders in the social media campaign on the prevention of coronavirus poses a significant impact on the curve’s flattening.
One of the critical challenges that social media campaigns encounter entails information literacy across the American community. However, the social media campaign will significantly benefit Washington Heights mainly because of addressing the main issues the population encounters during the prevention and treatment process. According to researchers, social media platforms empower Americans to access adequate information and independently interpret it for personal consumption. Although it is beneficial for all Americans to access the information, there is a high risk of misinterpretation from the illiterate (Graffigna et al., 2020). In this case, the social media campaigners must present information for the lay audience to profoundly understand and comprehend. Social media platforms accommodate all population demographics. However, incorporating effective strategies in providing coronavirus information integrates the core values of literacy and illiteracy dynamism.
The planning and designing of a functional and effective social media campaign is a multifaceted phenomenon mainly because of the intersection of stakeholders’ roles. The major stakeholders participating in the social media campaign include the task force and community elders in the neighborhood. According to researchers, social media campaigns contribute to disseminating information (Graffigna et al., 2020). Therefore, the strategic management of the process encompasses the ability to interpret the features of information. In this case, the first step engulfs defining the traits of the data. The disseminated information is characterized by layman’s language for more straightforward interpretation and common English language to eliminate some Americans’ marginalization effect. The second step is defining the key stakeholders positively affected by the social media campaign. In developing a social media campaign, the key stakeholders include government representatives, medical experts, and the American community.
The effectiveness of social media campaigns enshrines the ability to amplify the experts’ contributions to various forums. The social media campaign is a multidimensional phenomenon that significantly influences the development of dynamic online engagements among Americans. Therefore, it is essential to optimally engage the experts in the discussion forums to eradicate the spread of misinformation (Graffigna et al., 2020). The integration of celebrities in campaigning about coronavirus prevention with the medical experts’ support is an initiative that profoundly impacts the American community.
The key value of the resilience factor in enacting and enforcing regulatory policies on disaster management entails promoting sustainable growth and development. Nowag (2020) argues that understanding the significance and application in the governance system poses optimal effectiveness in the trickle-down of accrued benefits. The researcher recommends governments integrate resilience with the competition law mainly because of the outcome. Current regulations focus on protectionism against the essence of resilience. In this case, the administrations implement initiatives dealing with the crisis while posing minimal effect in the emergency spectrum. An excellent example is the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic. The declaration of coronavirus as a global pandemic rendered economic closure and lockdowns, thus prominently affecting livelihoods among people. France’s government incorporates the self-sufficiency policy framework involving the residents’ reliance on local produce (Nowag, 2020). The initiative elevated the resilience against the negative effect of internationally restricted movement of goods and services. Notably, resilience is a conceptual aspect that promotes the comprehension of distinctive aspects promoting the management of socio-cultural and economic welfare within a particular setting.
Conclusion
The pandemic-drive policies in the healthcare sector offer a profound insight into the significance of stakeholders’ engagement. COVID-19 pandemic steered the intensification of individuals’ hospitalization, leading to overworking among medical practitioners. The issue further intensified based on the central concept of the established measures. One of the policies introduced by the U.S congress encompassed boosting the funding of healthcare facilities and the construction of critical infrastructure. The ideology emanated from the perception concerning the safety of the frontline workers. The employees encountered optimal risks of contamination. Therefore, the government focused on enhancing their protection by providing protective gadgets. The main reason enshrined the determination of core practices that prevented the spread of coronavirus to the vast American community. Different countries used dynamic perspectives and practices to ensure the safety of the residents. As a result, it is important to ensure the apt resilience of the policies implemented to prevent the emergence of distinctive controversies.
References
Ali, S. H., Foreman, J., Capasso, A., Jones, A. M., Tozan, Y., & DiClemente, R. J. (2020). Social media as a recruitment platform for a nationwide online survey of COVID-19 knowledge, beliefs, and practices in the United States: Methodology and feasibility analysis. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 20(1), pp. 1-11.
Dong, E., Du, H., & Gardner, L. (2020). An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real-time. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 20(5), pp. 533-534.
Graffigna, G., Bosio, C., Savarese, M., Barello, M., & Barello, S. (2020). “# I-Am-Engaged”: conceptualization and first implementation of a multi-actor participatory, co-designed social media campaign to raise Italian citizens’ engagement in preventing the spread of COVID-19 virus. Frontiers in Psychology.
Kader, B. A. (2019). New steps to reduce crowding at emergency units in Abu Dhabi. Health – Gulf News. Web.
Muslim, N. (2019). Public hospitals to charge only after patient stabilises. Health – Gulf News. Web.
Pokhrel, S., & Chhetri, R. (2021). A literature review on impact of COVID-19 pandemic on teaching and learning. Higher Education for the Future, 8(1), pp. 133-141.
Robinson, K. R., Jensen, G. A., Gierach, M., McClellan, C., Wolles, B., Bartelt, S., & Hodge, J. (2022). The lived experience of frontline nurses: COVID‐19 in rural America. In Nursing Forum.
Salim, F. M., & Rahman, M. H. (2017). The impact of joint commission international healthcare accreditation on infection control performance: A study in Dubai hospital. GATR Global Journal of Business Social Sciences Review, 5(1), pp. 37–45.
Salud, C. (2021). H.Res.86 – Expressing support for frontline workers of the COVID-19 pandemic. Congress.Gov. Web.
Yang, B. J., Yen, C. W., Lin, S. J., Huang, C. H., Wu, J. L., Cheng, Y. R., Hsieh, C.C., & Hsiao, F. H. (2022). Emergency nurses’ burnout levels as the mediator of the relationship between stress and post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms during COVID‐19 pandemic. Journal of Advanced Nursing.
Yousuf, H., Corbin, J., Sweep, G., Hofstra, M., Scherder, E., van Gorp, E., Zwetsloot, P.P., Zhao, J., van Rossum, B., Jiang, T., Lindemans, J.W., Narula, J., & Hofstra, L. (2020). Association of a public health campaign about coronavirus disease 2019 promoted by news media and a social influencer with self-reported personal hygiene and physical distancing in the Netherlands. JAMA Network Open, 3(7), pp. 1-12.