Introduction
- The need for an effective management tool
- Improved organization of basic operations
- Better control of vital processes
- Ability to generate positive outcomes
- The way for operational excellence
- Lean Six Sigma as the potent tool to achieve desired goals
The increased complexity of modern society impacts the functioning of organizations and the choice of methods to achieve improved outcomes. Today, because of the strict requirements for the healthcare sector and diverse clients’ demands, there is a need for effective management tools that would help to improve basic operations and help to control all processes. At the same time, outcomes depend on operational excellence and the ability to correctly evaluate the situation and introduce the desired change. Under these conditions, Lean Six Sigma becomes one of the possible approaches that can help to address problematic issues and resolve existing problems by engaging in the process of continuous improvement.

Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a combination of two continuous improvement paradigms. Both Lean and Six Sigma methods are known as potent tools to attain operational excellence and provide managers with a clear vision of their missions and how they can be achieved (George et al., 2004). At the same time, there are debates regarding the applicability of these methods and their use in different contexts because of their advantages and weak aspects. The combination of these views results in the formation of a new Lean Six Sigma paradigm that is characterized by the increased attention to details that influence the work of organizations and the opportunity to align a continuous improvement process vital for the achievement of positive outcomes (Rastogi, 2018). The system is also considered an appropriate choice for organizations working in the healthcare sector as it helps to reduce the risk of undesired outcomes and guarantee better results.

Process and Process Improvement
A process can be defined as a specific succession of steps demanded to deliver a particular service or achieve certain outcomes (Rastogi, 2018). The complexity of the modern environment presupposes the appropriate growth in the complexity of processes and the emergence of additional stages needed to attain success and satisfy clients. However, the existence of too many steps might introduce unnecessary sophistication of the whole process, confuse employees, and deteriorate the overall effectiveness of a unit. For this reason, Lean Six Sigma is viewed as a tool for process improvement that helps to evaluate existing successions and their peculiarities with the primary goal to outline current barriers or unnecessary phases (Rastogi, 2018). In such a way, the application of the given system might help to eliminate extra or ineffective elements and create a new, practical approach to process organization and management.

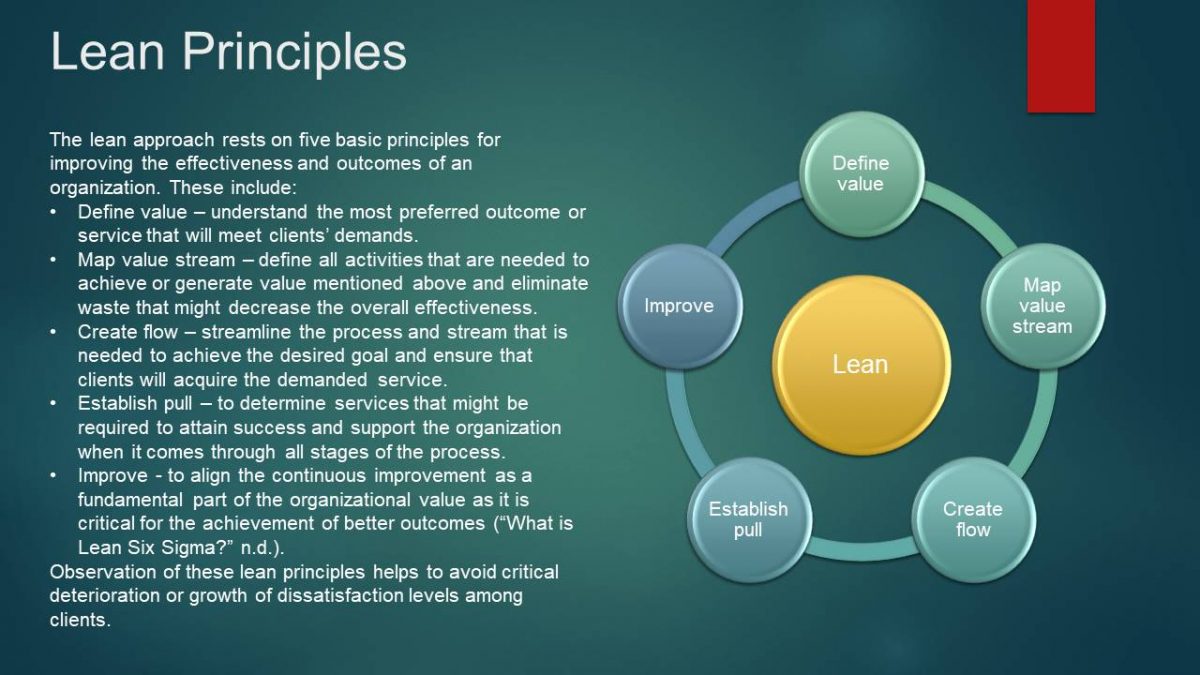
Lean Principles
The lean approach rests on five basic principles for improving the effectiveness and outcomes of an organization. These include:
- Define value – understand the most preferred outcome or service that will meet clients’ demands.
- Map value stream – define all activities that are needed to achieve or generate value mentioned above and eliminate waste that might decrease the overall effectiveness.
- Create flow – streamline the process and stream that is needed to achieve the desired goal and ensure that clients will acquire the demanded service.
- Establish pull – to determine services that might be required to attain success and support the organization when it comes through all stages of the process.
- Improve – to align the continuous improvement as a fundamental part of the organizational value as it is critical for the achievement of better outcomes (“What is Lean Six Sigma?” n.d.).
Observation of these lean principles helps to avoid critical deterioration or growth of dissatisfaction levels among clients.
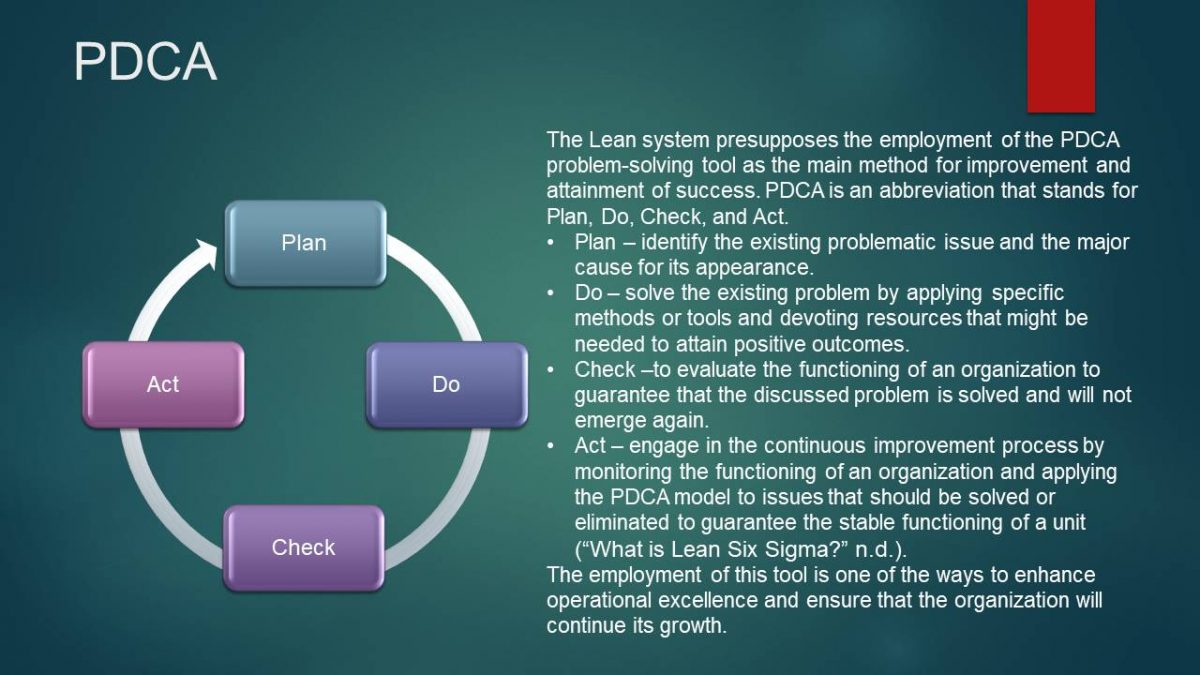
PDCA
The Lean system presupposes the employment of the PDCA problem-solving tool as the main method for improvement and attainment of success. PDCA is an abbreviation that stands for Plan, Do, Check, and Act.
- Plan – identify the existing problematic issue and the major cause for its appearance.
- Do – solve the existing problem by applying specific methods or tools and devoting resources that might be needed to attain positive outcomes.
- Check –to evaluate the functioning of an organization to guarantee that the discussed problem is solved and will not emerge again.
- Act – engage in the continuous improvement process by monitoring the functioning of an organization and applying the PDCA model to issues that should be solved or eliminated to guarantee the stable functioning of a unit (“What is Lean Six Sigma?” n.d.).
The employment of this tool is one of the ways to enhance operational excellence and ensure that the organization will continue its growth.
5S Organization Technique
5S organization technique is another tool that can be used regarding the Lean paradigm. It presupposes the accomplishment of five major tasks, such as sort, set in order, shine, standardize, and sustain, to engage in the continuous improvement and eliminate problematic issues peculiar to a company or organization at the moment (George et al., 2004). The adherence to this model can be beneficial for the healthcare sector as the determination of the current flaws might improve outcomes and ensure the higher satisfaction levels among clients, which is one of the basic determinants of success.

SIX Sigma Basis Principles
- Focus on the achievement of measurable results
- The increased importance of effective management and leadership
- Emphasis on the need for continuous improvement
- All organizational processes should be defined, measured, analyzed, and controlled
- Sustainable evolution of an organization depends on the in-depth understanding
Six Sigma is another tool that can help to align the continuous improvement of an organization and guarantee its improved outcomes. In such a way, it remains similar to the Lean approach as both these paradigms acknowledge the need for cyclic investigation and upgrade (George et al., 2004). However, along with the idea of the measurable character of all organization processes, Six Sigma also states that it is critical to eliminate all defects and reduce variation to align the stable functioning of a unit. Only under these conditions, the desired outcome can be achieved.

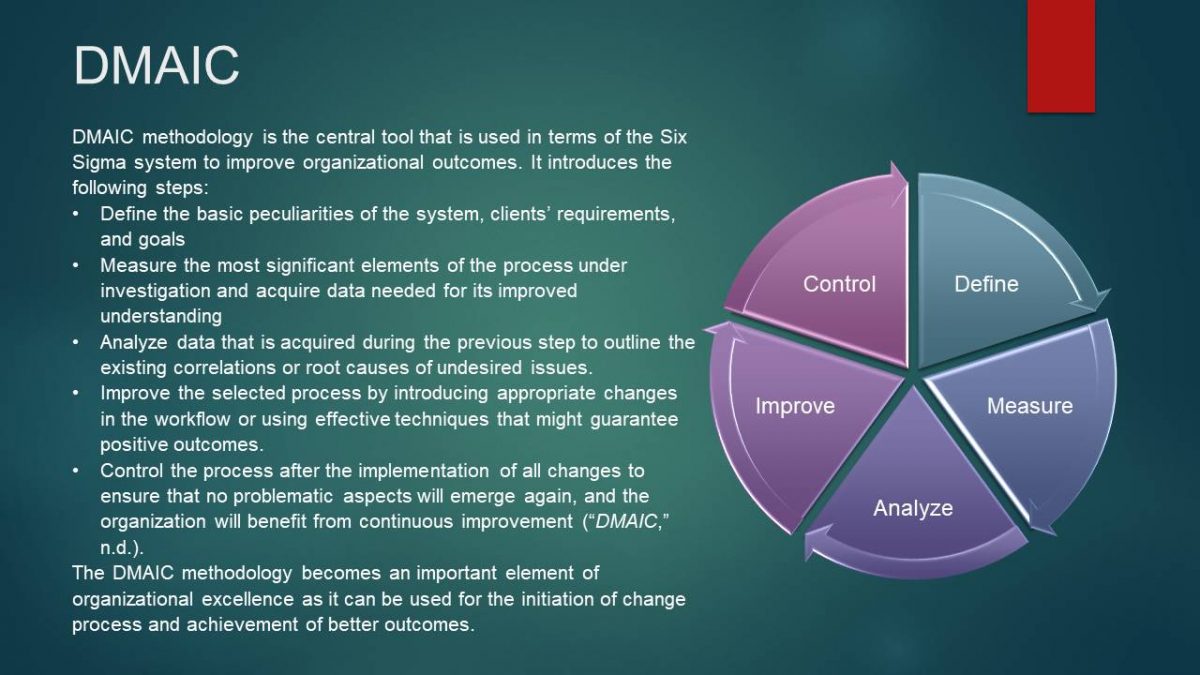
DMAIC
DMAIC methodology is the central tool that is used in terms of the Six Sigma system to improve organizational outcomes. It introduces the following steps:
- Define the basic peculiarities of the system, clients’ requirements, and goals
- Measure the most significant elements of the process under investigation and acquire data needed for its improved understanding
- Analyze data that is acquired during the previous step to outline the existing correlations or root causes of undesired issues.
- Improve the selected process by introducing appropriate changes in the workflow or using effective techniques that might guarantee positive outcomes.
- Control the process after the implementation of all changes to ensure that no problematic aspects will emerge again, and the organization will benefit from continuous improvement (“DMAIC,” n.d.).
The DMAIC methodology becomes an important element of organizational excellence as it can be used for the initiation of change process and achievement of better outcomes.
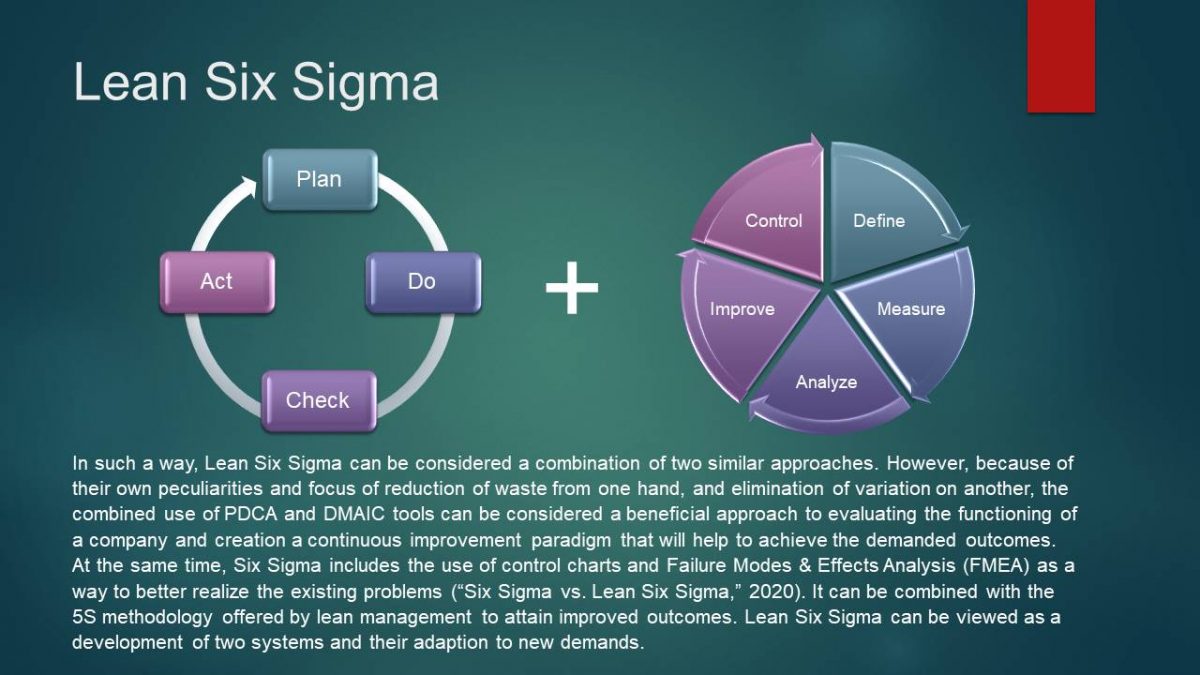
Lean Six Sigma as a Combination of Approaches
In such a way, Lean Six Sigma can be considered a combination of two similar approaches. However, because of their own peculiarities and focus of reduction of waste from one hand, and elimination of variation on another, the combined use of PDCA and DMAIC tools can be considered a beneficial approach to evaluating the functioning of a company and creation a continuous improvement paradigm that will help to achieve the demanded outcomes. At the same time, Six Sigma includes the use of control charts and Failure Modes & Effects Analysis (FMEA) as a way to better realize the existing problems (“Six Sigma vs. Lean Six Sigma,” 2020). It can be combined with the 5S methodology offered by lean management to attain improved outcomes. Lean Six Sigma can be viewed as a development of two systems and their adaption to new demands.
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
- A combined approach to the evaluation of an organization’s work
- Can be employed for all units regardless of their size
- Develops a roadmap to achieve strategic goals
- Improves the work of employees by eliminating barriers for excellence
- Promotes standardization of the work to achieve existing goals
- DMAIC and PDCA frameworks for evaluation.
The central advantage of Lean Six Sigma comes from its nature. It is a combined approach that is used to measure the work of an organization regardless of its size and existing goals. The employment of this combined system helps to generate a roadmap needed to achieve desired goals and avoid failures (George et al., 2004). Moreover, the adherence to the given paradigm cultivates higher standardization of all processes vital for a unit. It contributes to the increased effectiveness of employees and guarantees the attainment of the desired levels of excellence. DMAIC and PDCA approaches can be used concerning the existing problems and elements that should be considered.

Infection Control
- Addresses factors linked to the spread of infections in health units
- HAIs serve as one of the primary causes of the emergence of undesired complications
- Infections critically deteriorate outcomes and clients’ satisfaction
- The need for enhanced infection control to avoid poor results
- Lean Six Sigma can help to achieve the desired goal
The modern healthcare sector is focused on the achievement of positive results and the provision of appropriate care to patients to guarantee their recovery. For this reason, continuous improvement also plays a critical role in this field. Unfortunately, there are multiple healthcare associated infections (HAIs) that might precondition the emergence of undesired complications or deteriorate treatment outcomes (Willemsen & Kluytmans, 2018). There is also a need for practical infection control protocols that might help to reduce accidence and protect patients. In this regard, the application of the Lean Six Sigma approach can be viewed as a promising option for the creation of a sufficient intervention.

Lean Six Sigma and Infection Control: Project Charter
The application of Lean Six Sigma demands a clear definition of the current problem, goals, scope, and boundaries. It means that spread of infections within a healthcare setting should be viewed as a major problem. For this reason, the prior goal is to reduce HAI’s incidence and risks by introducing a new protocol as it will promote better treatment outcomes. The desired term is two months. The scope of the selected issue is evidenced by the fact that the positive change will mean the alteration of the existing approach to infection control and presupposes the involvement of all hospital staff. The given project charter should be used as the basis for the further application of the Six Sigma model.

Application of DMAIC Tool to the Problem
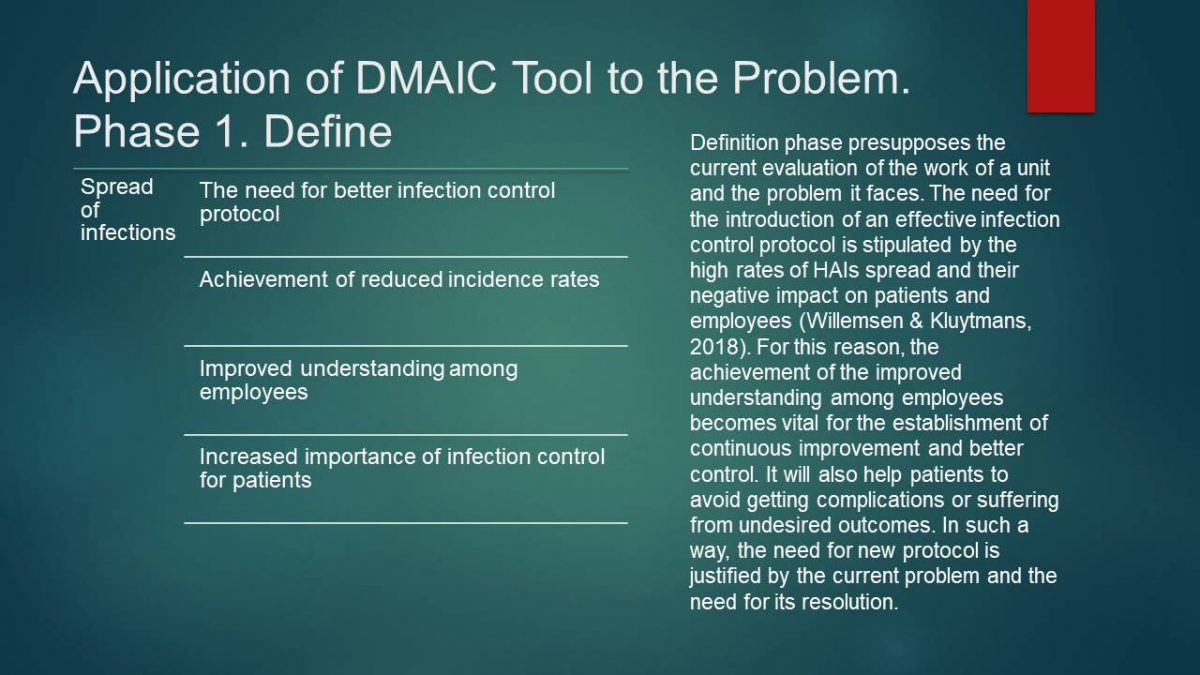
Phase 1. Define
Definition phase presupposes the current evaluation of the work of a unit and the problem it faces. The need for the introduction of an effective infection control protocol is stipulated by the high rates of HAIs spread and their negative impact on patients and employees (Willemsen & Kluytmans, 2018). For this reason, the achievement of the improved understanding among employees becomes vital for the establishment of continuous improvement and better control. It will also help patients to avoid getting complications or suffering from undesired outcomes. In such a way, the need for new protocol is justified by the current problem and the need for its resolution.
Phase 2. Measure
During the measurement phase, the results of observations regarding the primary causes for the emergence of undesired problems and its impact on the work of the unit should be collected. This information is vital for a new protocol as it helps to introduce steps to avoid undesired outcomes. The use of surveys, interviews, and monitoring tools shows that staff members might forget to perform all hygiene actions or disregard existing recommendations (CDC, 2016). The existing research proves that the application of electronic control approaches might be helpful to solve this problem (CDC, 2016). That is why the planned intervention presupposing the change in protocol might have a positive influence on outcomes.
Phase 3. Analyze
The analysis of the problem and evaluation of the current employees’ performance helps to reveal the root causes of the problem. These include a lack of awareness, forgetfulness, and ineffective monitoring tools (Willemsen & Kluytmans, 2018). For this reason, during this phase, the main interventions aimed at the elimination of these barriers should be included in the protocol. The given stage is also vital for the creation of the improved vision of the would-be change and how new guidelines will contribute to the establishment of a healthier environment. The analysis also shows that the elimination of these issues can help to improve outcomes as HAIs serve as one of the prior causes for poor results among clients.
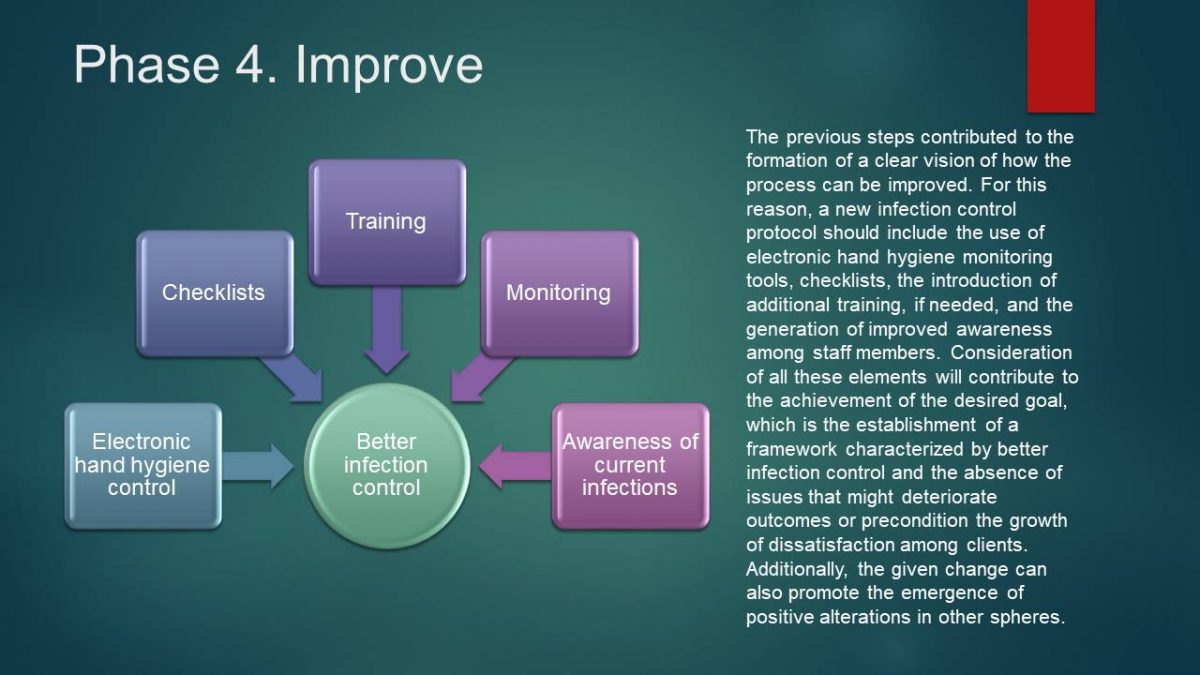
Phase 4. Improve
The previous steps contributed to the formation of a clear vision of how the process can be improved. For this reason, a new infection control protocol should include the use of electronic hand hygiene monitoring tools, checklists, the introduction of additional training, if needed, and the generation of improved awareness among staff members. Consideration of all these elements will contribute to the achievement of the desired goal, which is the establishment of a framework characterized by better infection control and the absence of issues that might deteriorate outcomes or precondition the growth of dissatisfaction among clients. Additionally, the given change can also promote the emergence of positive alterations in other spheres.
Phase 5. Control
- Offer the final protocol
- Ensure that the plan is observed
- Monitor outcomes to avoid failures
- Implement improvements to other spheres
- Establish the continuous improvement paradigm
The finalizing state of the analysis by using Lean Six Sigma presupposes consideration of all aspects mentioned above and the formation of a new and more effective infection control protocol that will rest on the factors outlined during the analysis. Additionally, the implementation of guidelines should be followed by monitoring activities as in the majority of cases, the change process preconditions the emergence of multiple misunderstandings and resistance. For this reason, to establish a continuous improvement paradigm, it is critical to ensure that all staff members realize the importance of the offered protocol and are ready to observe it to avoid failures or critical issues in their work.



Lean Six Sigma Results
- The major problem is the high risk of infection spread
- The primary causes include disregard of existing hygiene norms and absence of monitoring tools
- Hospital staff should be considered the main stakeholders
- Improved paradigm will help to reduce the incidence
- Continuous improvement can be established by reviewing the current situation
In such a way, the application of the Lean Six Sigma system helps to outline the basic problems and areas that should be affected by the change. The new protocol should consider the causes revealed by the analysis and offer effective tools that can contribute to the achievement of desired outcomes. Additionally, the nature of the problem presupposes the hospital staff should be considered the main stakeholders provided with specific attention to guarantee that they realize the existing situation and are ready to improve it. These results will serve as the basis for the formulation of a new infection control protocol that is vital for continuous improvement.

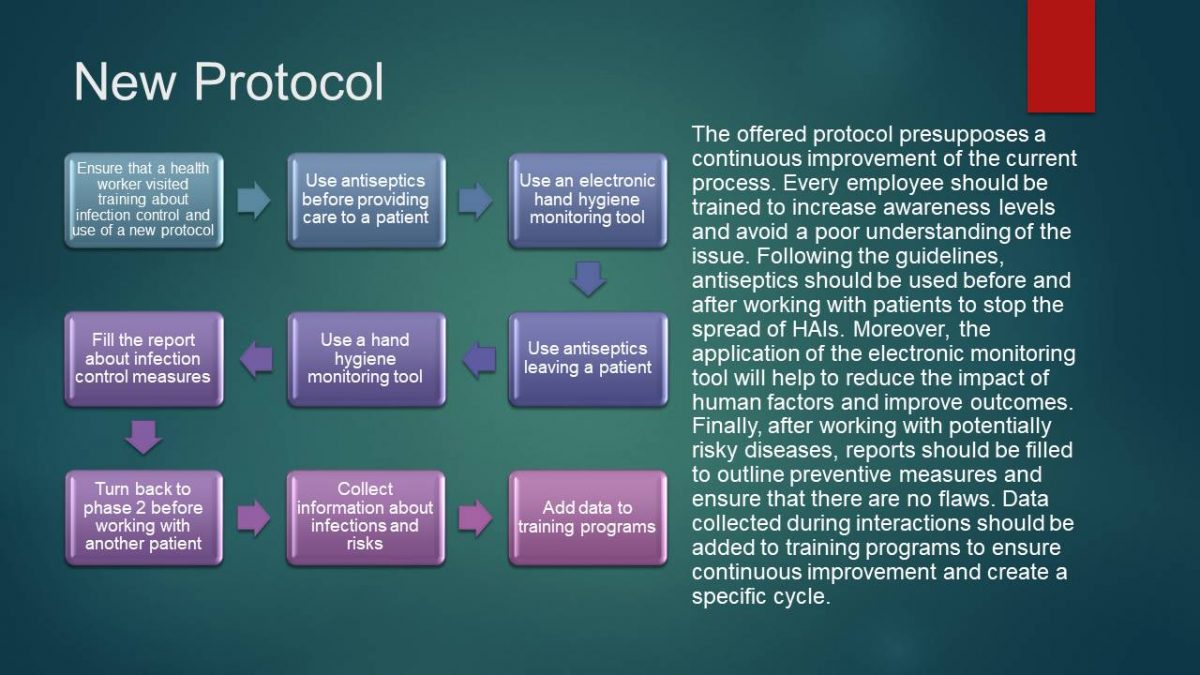
New Protocol
The offered protocol presupposes a continuous improvement of the current process. Every employee should be trained to increase awareness levels and avoid a poor understanding of the issue. Following the guidelines, antiseptics should be used before and after working with patients to stop the spread of HAIs. Moreover, the application of the electronic monitoring tool will help to reduce the impact of human factors and improve outcomes. Finally, after working with potentially risky diseases, reports should be filled to outline preventive measures and ensure that there are no flaws. Data collected during interactions should be added to training programs to ensure continuous improvement and create a specific cycle.
Conclusion
- Lean Six Sigma is a potent analysis and improvement tool
- The system has a high practical value
- Can be applied to different systems
- Useful in healthcare settings and infection control
Altogether, it is possible to conclude that Lean Six Sigma is an extremely powerful system that has a high practical value. It can be applied to different organizations and environments to reveal existing problems and create solutions that will promote positive change. For the healthcare setting, Lean Six Sigma can be applied to design a new infection control protocol that is critical regarding the spread of infections within a healthcare setting.

References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2016). Infection control basics. Web.
DMAIC – The 5 pases of Lean Six Sigma. (n.d.). Web.
George, M., Maxey, J., Rowlands, D., & Price, M. (2004). The Lean Six Sigma pocket toolbook. New York, NY: McGraw Hill.
Rastogi, A. (2018). A brief introduction to lean, six sigma and lean six sigma. Web.
Six Sigma vs. Lean Six Sigma. (2020). Web.
What is Lean Six Sigma?(n.d.). Web.
Willemsen, I., & Kluytmans, J. (2018). The infection risk scan (IRIS): standardization and transparency in infection control and antimicrobial use. Antimicrobial resistance & Infection Control, 7, 38. Web.