Abstract
The story of global expansion of Pepsi smells as sweet as rose who don’t know how difficult job is to get a tremendous success in the global beverage market; therefore, this study has scrutinized the strategy of this brand in the international market and identified that Pepsi has brought its success with a variety of global entry strategies. The purpose of this research paper is to analyze background of Pepsi, provide theoretical framework in the literature review, design a research methodology, and find out the effectiveness of Pepsi’s strategy to overcome the effect of global financial crisis ensure customer value, maintain quality considering customer demand.
Introduction
According to PepsiCo (2012), the company was founded in 1898; Caleb Bradham, a pharmacist and drugstore-owner of North Carolina had discovered it while testing with mixtures of seasonings and fluids trying to create an energizing drink for patrons; however, he achieved a target more than anticipation, as his innovation is now considered one of the best-selling brands around the world.
Pepsi Cola has gradually developed over years in order to gain its current position, for example, in 1902, Caleb introduced the Pepsi-Cola-Company in his pharmacy; moreover, in 1903, it was authoritatively listed in the Patent Office and by 1910, it owned franchises in 24 states around the country; later, in 1964, Diet-Pepsi emerged in the market and gained great success. Next table shows main financial indicators of PepsiCo for years 2009 to 2012.
Table 1: Financial Performance of the PepsiCo. Source: Self-generated from Yahoo finance (2013).
Global strategies of Pepsi
According to the annual report 2011 of PepsiCo, it has strategic plan to expand business worldwide with its wide product lines particularly macro snacks with beverages (Lay’s, Doritos, Cheetos and SunChips); therefore, it is initiating to offer new flavors in tune considering the choice of the consumers of local market and the capability of the company. At the same time, the purpose of the company is to develop strong logistics to reach global consumers and make available in this brand (PepsiCo 2011, p.6).
However, this company focuses on the beverage sector more attentively in order to maximize profits and experience sustainable growth since more than 50% of the total revenues come from this segment. On the other hand, the marketers of this company invests researched on the global market position to assess the perception of the consumers to meet the demand of the local consumers; as a result, the researchers suggest the company to invest more for the development of beverage segment specially Pepsi, 7up, Mirinda (PepsiCo 2011, p.7).
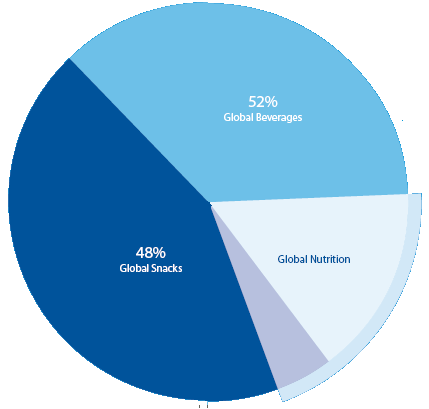
However, the brand expansion plan of Pepsi is not limited for the beverage segment, but it diversifies its business in the nutrition segment with the product line of Quaker, Tropicana and Gatorade; it addition, it has goal to be one of the major players in this segment. As part of the global expansion strategy, Pepsi has already strengthen the position of core brands along with innovation power, focused on shareholder value creation, maintained its strong value shares, and diversified product range for the customers (PepsiCo 2011, p.7). However, the following figure shows the net revenue of Pepsi from different segments –
Literature of Global Expansion Strategy:
Yesilyurt (2012, p.1) pointed out that the global expansion strategies of Multinational Corporations (MNCs) through export entry or investment entry are influenced by several prospect and challenges in the overseas markets while the selection of entry modes are subjective to the factors like market volume, production capacity, environmental hazards, transportation facilities, availability of raw materials, and cost of labor and so on.
Due to high risk of investment entry mode in the foreign market, the MNCs prefer to engage themselves for export entry mode, but the sustainable market response and escalating connection in that markets lead them for merger and acquisition taking into account of further risks and complexities aligned with socioeconomic, political, culture, legislative and accounting system of the target market.
On the other hand, some MNCs prefer to engage with overseas market through the contractual entry mode, which is a long-standing non-equity collaboration among the global companies in the target market by transferring technology and know how through licensing arrangement for a certain period in exchange of royalty and other handsome compensation package those are agreed mutually. Under the post financial crisis, the global economy is still vulnerable and going through a vicious circle of recessionary impact that leads the MNCs to take more cautioned step to in the entry in the overseas market, where they need to ensure elevated positive rate of return for their investment in relation to the pre-crisis period.
Agarwal & Ramaswami (1992, p.3) added that the literature of international trade has identified the entry mode of the overseas market as a most significant and complex procedure for successful engagement in the target market whether it turned for direct exporting through multi channel, particular licensing, joint venture with a strong counterpart or sole venture with a single company. The most widespread framework for global expansion strategy is the selection of entry mode for that target market composed with three types of predominant factors such as ownership of the company formed in the target market, its location and connectivity, and the extent of globalization in that market for legal barriers of transactions, and accounting standards.
Most of the studies in this area have engaged to identify the problem and prospect either selecting joint venture and sole venture strategy or pointing to the advantage and disadvantage between licensing and foreign direct investment including the rate of return or assessing the impact of merger and acquisition in the target market with the aim to identifying entry strategy.
Upadhyay (2007, p.2) argued that success of global expansion strategy deeply concerned with the engagement of opportunities allow to run free in the emerging markets where the MNCs could achieve enough potential surpluses to comply with their commanding tone to meet the higher degree of market demand of that market raised from the large populations along with growing purchasing power. It is notable that emerging market economies are ever potential than the developing countries with reliable and skilled suppliers and human resources with rising infrastructures and global connectivity that would facilitate the companies to enjoy export market of the surrounding markets through road rail or see with higher positive returns for the investments in the emerging countries.
Samiee (2003, p.9) further stated that the international expansion of Pepsi in the Russian Republic through counter-trade in exchange of Vodka was significantly failure due to the insufficient bottling capacity of the trading partners of that market although Pepsi kept its highest effort to success the deal by a number of price declines. Actually the Russian entry of the Pepsi did not evidenced any success of counter-trade until the PepsiCo acquired Monsieur Henri, the wine and sprit distribution channel of the country and it provided incredible dilemmas are laid behind the counter-trade transactions and demonstrated the washed out of academic interest for counter-trade.
After the fall of Soviet Union in 1991, the post cold war era illustrated that the counter-trade is a backdated means of global expansion for MNCs and the wave of surfacing the market economies explored worldwide all though there are still presence in the public and private sector for very special product or services in the developing and emerging economics.
Schuh (2012, p.3) argued that the global financial crisis originated from the collapse of US mortgage market and thrown the global economy into long-term recessionary impact that the countries couldn’t recover for last six years and the MNCs are anxious with their international expansion while the export market fall down and reducing capital inflows generated pressure on the banking system. The Central and Eastern Europe economy has evidenced rapid wage raise, excessive browning of households, credit squeeze, depreciation on local currencies, and housing market collapse during the crisis while the Asian emerging economy turned backed to the growth path immediately by exploring manufacturing and commodity sector and stabilized the recessionary impacts.
Under such circumstances, the global expansion strategy of the MNCs has significantly curtailed and they most likely shifted their expansion strategy into five major directions formulated by the MNCs management, these are illustrated in the following diagram –
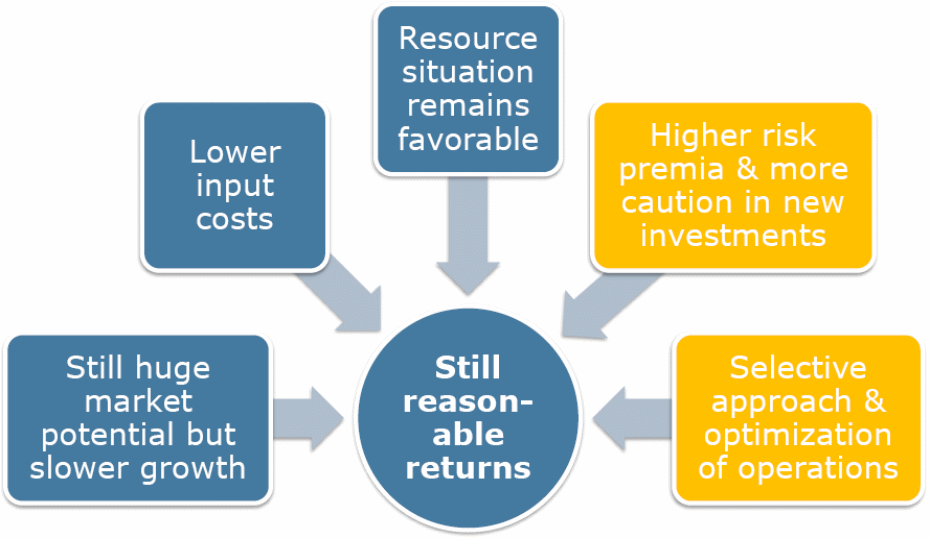
Schuh (2012, p.412) also pointed out that before the global financial crisis the common approach of the MNCs for international operation was to engage decentralized operation and regional offices were independent for their local business decision making, but in the post financial crisis era they have shifted from their wider autonomy of the local operation and engaged central decision making. The headquarters of the MNCs have engaged to establish greater control over the investment decisions, cost saving, liquidity boost and homogeneous accounting system by introducing special cost cutting program and keeping hold of investments with strong cash management that would ultimately assist to encounter with any unfavorable situation of market driven forces.
During 2011, the MNCs jumped to the survival mode with continued cost saving and investment stops, but geared decentralized operation for local management where reasonable returns and resources are available with lower input cost, large market potentials for steady growth and urged to engage with selective approach taking into account of risk factors for new investment.
PESTEL Analysis of Pepsi
Political Factor
This non- alcoholic drink is controlled by the Food and Drug Administration; as a result, the company upholds the maximum benchmark in its soft drink and complies with all the guidelines specified by Food and Drug Administration; in addition, in diverse global marketplaces, special type of legislation exist – in some cases this guidelines are strict and harsh. The political factors like governmental instability, strikes, or other unrests sometimes pose threat to its business; moreover, the political state of affairs is a huge concern because sometimes owing to social-turmoil and inflation-rates, sells may decrease; more prominently, cross-border circumstances are plainly dissimilar; so Pepsi needs to operate considering every political-policy so that it could adjust to the transformations appropriately.
Economic Factor
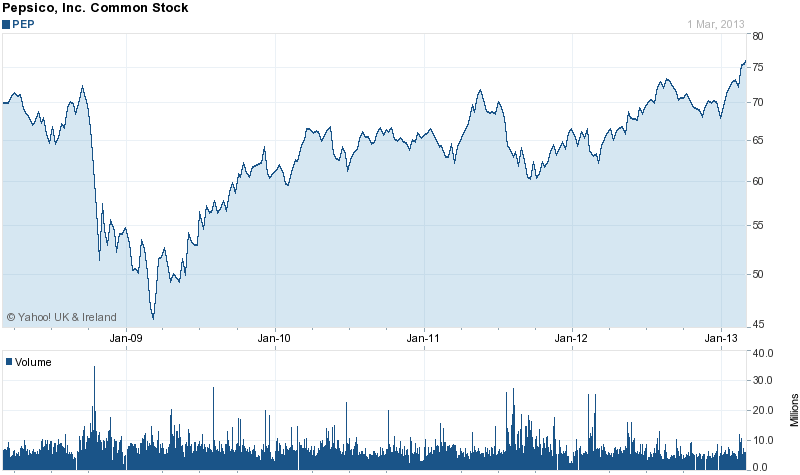
Because of the global financial crisis in the world, several financially strong countries have suffered from feeble market conditions; as a result, many global giants had reorganized the respective departments and advertising agendas largely; in addition, because of decline in turnover, many soft drink companies of the industry have suffered from poor growth throughout the 2009 to 2011 period. Even though there have been widespread troubles in the financial departments of Pepsi, and there has been numerous job cuts and downsizing in the company, still it can be said that the soft drink producer has well recovered from the crisis in recent years.
For example, according to Yahoo Finance (2013), in 2009 this drink manufacturer had faced the worst economic time in its last five years history; however, a gradual improvement in the stock price has occurred in the 2010 and 2011 period. In addition, even though there has been a mild slump in 2012, from the very beginning of 2013, it is showing signs of improvement; the following figure shows this in detail –
Social Factor
Most of the globally recognized cola producers like Coca-Cola or RC Cola needs to act in accordance with the social and cultural issues of the markets in which they operate. In case of Pepsi cola, the same factors operate; as a result, the cola producer conforms to all the social and cultural issues in the markets, which specially have multi- cultural diversity, such as Asian and Middle East markets.
The annual report of the company suggests that it currently operates on around 200 markets; it is notable that different countries have different set of socio-cultural background, ethnic origins, historical contexts, diverse ideologies, and traditions or customs. As a result, this global brand requires to afford a great amount of effort in adapting to those cultural contexts in its business areas and finally to operate in those markets with considerable success.
Technological Factor
Because of the introduction of innovative features and branches in technological arenas, businesses have wholly incorporated their operations with all the up to date alterations, which took place so far; there has been a marked drift among global giants to adopt this technological advancements, but more significantly, a strong tendency is seen towards a drive to social media for advertisements.
In this context, Pepsi cola has also engaged itself in campaigns and promotions over social networks for attracting mass internet users at the same time; apart from this, use of technology is also present from marketing to production to financial departments; for example, without proper use of technical equipments, it would be nearly impossible for company to produce good-quality Pepsi.
Legal Factor
The legal issues always remain a major concern for all beverage producers in the industry; this is because there are strict laws for governing the players in the industry; Pepsi, however, closely observes all the regulations of the different markets in order to avoid legal dilemmas or lawsuits and operate peacefully. However, irrespective of such cautious operations, Pepsi sometimes unwillingly suffers from damages to reputation because of legal dilemmas in certain markets, such as India.
Environmental Factor
It is notable that when the soft drink producers dispose off the industrial-wastes in rivers, water gets contaminated- this may result in not only damages to marine creatures but also in harm to human health; in addition, ecological experts have argued that the intricate chemical properties of certain drinks could harm tiny creatures and aggravate its impacts on global ecosystems. On the other hand, because of Pepsi’s environmental sustainability programs, these impacts can be reduced to certain degree through comprehensive examinations on ecological safeguard; moreover, the sustainability report of the company shows that it has taken other impressive steps to lower carbon footprint or contribution to global warming.
Research Methodology
This paper has organized by taking data from secondary data sources, as Pepsi global strategy is very common area of research to the researcher and they have already provided many useful information in this regard, such as, brand expansion strategy of Pepsi and comparison the position of this brand with Coca cola. However, this report based on descriptive research approach and it used many articles from internet sources, such as, international counter-trade, effective business strategies of multinational corporations, international expansion strategies; in addition, it addressed annual report 2011 of Pepsi, Pepsi’s strategy in the carbonated soft drinks market, company website and so on.
Sample Size
The questionnaire has prepared with intent to get response regarding Pepsi Strategy from the target population (Management and employees of PepsiCo); however, this questionnaire has distributed to eighty staff and forty managers of Pepsi, but not all the respondents provide their views; here, subsequent table provides information about the interviewees –
Table 5: – Selected Respondents in order to interview.
Finding and Result
The purpose of this chapter is to appraise and evaluate the global strategies of Pepsi by questioning the management and employees of the company about the fitness of its global expansion strategy, strategy for ensuring value for money, product qualities, customer loyalties, and strategy to overcome the global financial crisis. Therefore, the researcher has conducted a resourceful survey among 100 respondents to find out the real picture of the strategic success of Pepsi Cola.
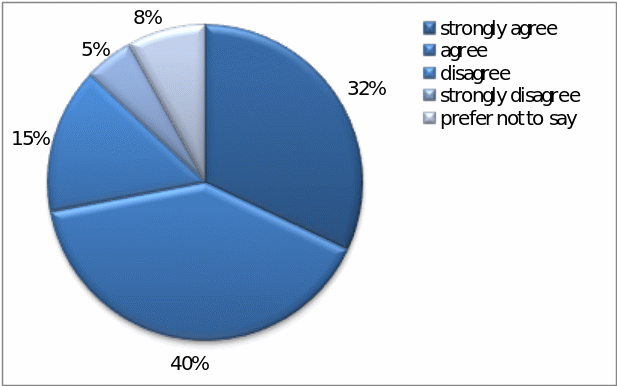
Question – 1: – To what extent the respondents agree that global expansion strategy of Pepsi is fit for the purpose –
In answering this question, 32% respondents strongly agreed that global expansion strategy of Pepsi is fit for the purpose, 40% respondents agreed to this, 15% respondents disagreed to this, 5% strongly disagreed, where as 8% respondents preferred not to say anything regarding this matter; however, the result illustrates that the global expansion strategy is quite impressive –
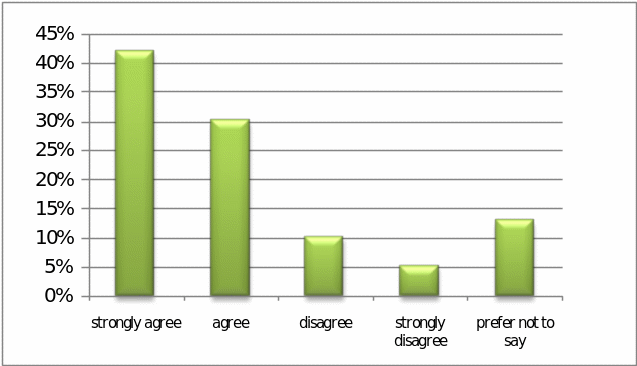
Question – 2: – To what extent the respondents agree that Pepsi’s strategy is ensuring customer’s Value for Money –
It is notable that 42% respondents strongly agreed to this point, 30% respondents agreed to this, 10% respondents disagreed, 5% strongly disagreed, whereas 13% respondents have not commented anything on this issue; so, it is clear that Pepsi’s strategy is ensuring customer’s value for money:
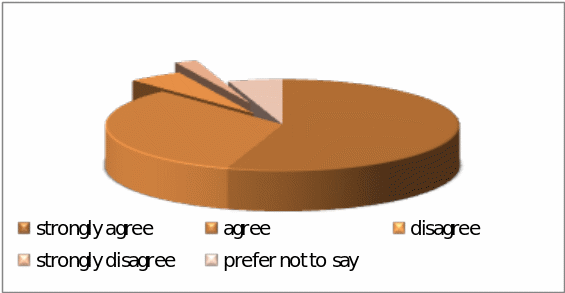
Question – 3: – To what extent the respondents agree that Pepsi manufactures quality products considering customer demand –
Here, 55% respondents strongly agreed to the proposed question, 33% agreed with it, 5% disagreed, 2% strongly disagreed, whilst 5% people selected the prefer not to say option; however, the result reflects that Pepsi in fact manufactures quality products considering customers’ demand.
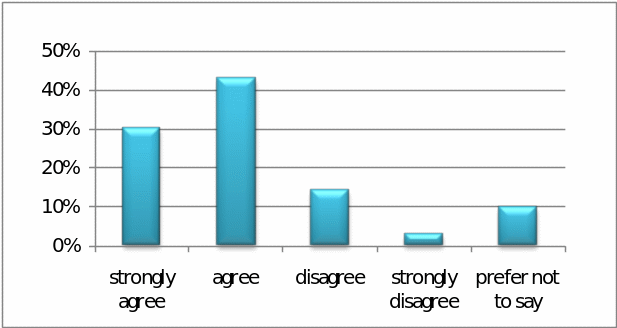
Question – 4: – To what extent the respondents agree that Pepsi has large volume of loyal customers –
It is important to state that 30% respondents strongly agreed to this question, 43% people agreed, 14% people disagreed, 3% people strongly disagreed, whilst 10% people have not commented anything on this matter; therefore, it can be concluded that Pepsi’s loyal customer base is quite strong; the following figure shows this in detail –
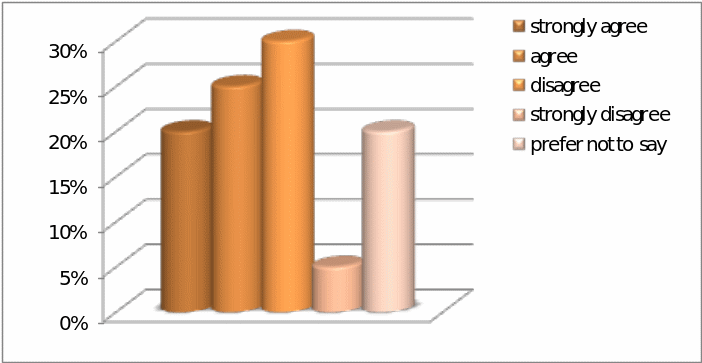
Question – 5: – To what extent the respondents agree that Pepsi needs to change strategy to overcome the effect of global financial crisis –
It is notable that in answering this question, 20% respondents had strongly agreed, 25% respondents had agreed, 30% had disagreed, 5% had strongly disagreed, whereas 20% had selected the prefer not to say option. This factor is illustrated in the graph below, which indicates that there are mixed opinions among the management and employees of the company regarding this issue.
SWOT Analysis of Pepsi
Strengths
Brand name of Pepsi is the main strength point because the people all over the world have aware about this brand and they like to purchase this brand with highest reliability. At the same time, this brand is offering exceptional quality products since the manufacturing process includes newest machinery to manufacture hygienic products for the local and international market; in addition, the franchisees are also use similar tools to control distribution networks with outstanding quality drinks.
On the other hand, the employees of this company are highly skilled, motivated, and dedicated to serve the specific purposes; moreover, it enjoys brand loyalty (PepsiCo 2011). According to the annual report 2011 of this company, market share, and position of Pepsi Cola in the global market is another strength point for this brand.
Moreover, the marketers of this brand use many useful promotional tools in order to carry on the business with glorious success and develop the strong business network in new place, for instance, it has different adverting policies to attract different target customers. However, integrated marketing campaign, supply chain management, latest equipment, and variation in the packaging for different locations help this brand to increase loyal customer base in the international market.
Weaknesses
According to the report of Angelkov, Black & Green (2003), it has problem to distribute its products in the rural area where the competitors like Coca cola has strong presence. On the other hand, it has to face some dilemmas to apply marketing strategies in the Muslim countries where people treat this brand as Jewish brand, which indicates the marketers failed to apply proper strategy to tackle the cultural issues; at the same time, customers can get similar products at lower price.
This brand has faced some complain related with labor exploitation and political interference in the developing countries; however, it needs to spend relatively a large amount of money for advertisement and other promotional events to promote this brand, but it lost few market due to lack of innovative advertising ideas.
On the other hand, this brand has not addressed properly the obesity related problems in the society since the market share of the sweetened and diet soft drinks deceased significantly due to lack of nutritive value though the purchasers think about children’s weight and activity level.
Opportunities
It has scope to develop brand image in the rural areas by increasing production capacity and restructuring distribution channels considering the demand of the new locations. At the same time, Pepsi has the capability to lead the noncarbonated drinks market as a market leader while it has already captured 8% market share in this segment where the nearest competitor holds 7% share in this segment. According to the annual report 2011 of PepsiCo, sponsors of different cricket teams, football teams and other games can be increased market demand of this brand.
Threats
According to the annual report 2011, this brand has experienced excessive competition from the market leader in the beverage industry known as Coca Cola since it is global brand, which has long product lines. On the other hand, rules, and regulation of different countries, frequent change of demand of the consumers, match
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis:
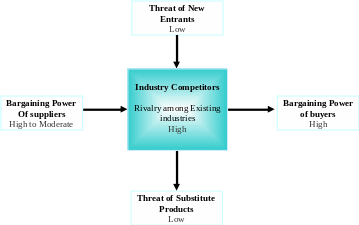
New Entrants
Roche (2012) focused on the historical perspective of the soft drinks industry and pointed out that threat of new entrants is low because Pepsi is one of the most prominent brands in the whole economy in terms of size, sales volume, distribution networks, and strength; therefore, it would be very difficult to enter into this industry. At the same time, Roche (2012) stated that it is essential to have strong financial support and customer acceptance to experience high profitability and return on investment; however, the company like Costco has the opportunity to enter the market with similar product range, which can crate extreme threat for Pepsi.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Suppliers’ position can change time to time considering global economic position, external and internal environment of the buyers and so on; however, suppliers are most crucial factors to Pepsi because this brand is committed to maintain quality of the products, offer attractive packaging, avoid legal actions, and control commodity prices to decrease costs.
Bargaining Power of Customers
Roche (2012, p.7) closely observed that the customers have plenty of options due to available of soft drinks at lower price in the beverage industry though the quality of the products are not same. In this context, this power is high while the consumers have plenty of options to choose other name brand and generic soft drinks; so, the marketers of this brand need to offer different package to sustain the market with strong position considering high bargaining power of the consumers.
Threat of Substitutes
The researchers like Roche (2012, p.7) and Puravankara (2007) have already addressed substitute products are the long-term threat to the entire beverage industry because the customers have even shown the propensity to choose different products of the competitors, such as, brands of soda and juices grocery store.
Competitive Rivalry
According to the annual report 2011 and Yahoo Finance 2013, Pepsi generated more than 65 billion sales revenue and 6.17 billion net profits on 2011; however, 52% revenue has earned from the beverage segment where Coca cola is the prominent competitor of Pepsi while it has strong presence in the global market; however, the following figure shows the competitive position –
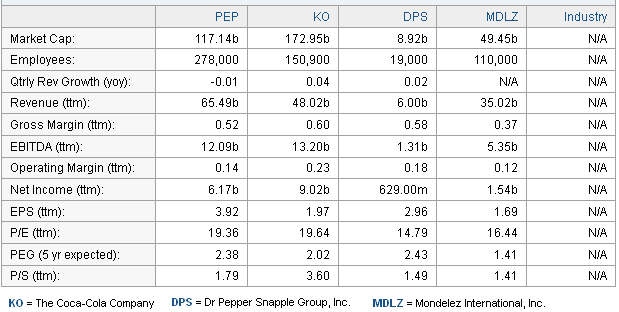
Pepsi diversified the product line of beverage segment in order to compete with Coca cola as Pepsi has strong position in the Middle East where Coke failed to create market for controversy, but Cock is popular brand in the US, Mexico, German and Brazilian. However, CPM Analysis demonstrates the competitive position of Pepsi –
Table 2: CPM Analysis.
Pricing Strategy of Pepsi
Scribd (2009, p.39) reported that the main objective of this brand is to offer the best quality products at the lowest possible pricing price to increase sales volume along with market share; thus, it uses inexpensive and recyclable plastic bottles as the purchasing power of the customers in the Middle East and other Asian countries are not too high. At the same time, Scribd (2009, p.39) expressed that the marketers of this brand need to consider tax (government tax, sales tax, license fees, and other duty) of the particular area to fix prices of its products; in addition, price of the raw materials is also key variables to set prices; however, the following figure gives more details:
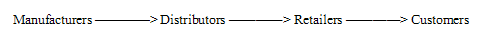
Here, it is important to mention that the difference between manufacturing costs and retail price is too high, for which the customers are bound to expend additional fund, for example, if production costs Rs.9 then the customer has to purchase with Rs. 22 in India as selling price includes transportation and distribution costs.
Place
The annual report of Pepsi suggested that the process of placing the colas to the shelves of the customers after the production procedure is a quite complex method. In some cases, the drinks go to the wholesaler from the manufacturer, and from the wholesaler to the retailer; however, in other situations, it goes from the manufacturer to the company warehouse and from the company warehouse to the retailer. As delivery or placement is vital feature for gaining better performance in the market, the players require strong supply chain so that the placement activity is carried out fruitfully.
Moreover, in this pace of globalization and quickly budding market of colas, it is essential for businesses like Pepsi cola to look forward to have superior bottlers. This means that with better bottlers, the cola producer will be able to maintain its powerful position in terms of well- built distribution channel throughout the 200 countries in which it operates. As a result, creating relation with bottlers by joint ventures together with better preservation of present bottler-relationship must remain the key concern for Pepsi’s global marketing; yet, it is notable that in comparison to Coca- Cola, Pepsi always seems to ignore the bottlers, which in turn make the distribution channel of Pepsi weaker then Coke for the most part.
Promotional Strategy
In order to conduct all its promotional activities successfully, the manufacturer of the Pepsi cola greatly concentrates on a number of mass media options together with some outdoor advertising methods. Because of the fact that a great amount of fund is required to advertise the cola through large media like TV every year, there is a drive in the companies like Pepsi to choose online advertising mediums to build the image of the product through the integrated campaign and develop public awareness in a relatively less expensive method. Such online campaigns sometimes consist of internet marketing, for example, search engine optimization, Pepsi’s own website creation, impressive and compelling writings in the blogs, electronic mails, and more essentially, campaigns through social networking places.
Such networking-websites are marvelous for raising consumer relationships; furthermore, it is moderately straightforward to hook-up with patrons at social websites; it encompasses generating accounts at accepted social-sites, accruing community/customers, endowing supportive facts about beverages, and renovating information recurrently; equally, patrons would like unification in community as an arena to share their understanding and unearth information concerning what to purchase.
National-daily is one of the most decisive medium to come into observation of mass population, consequently, Pepsi maintains paid circular promotions with attention-grabbing snaps; additionally, Pepsi also comes up with press kits, brochures, and posters; it also promotes itself by radio-broadcasts – this better covers lively citizens who, for instance, listen to radio whilst driving cars or whilst cooking food. Moreover, even those people who enjoys a free time more often sticks to the radio; in addition, radio advertising also enlarges the potential-outcomes for integrated marketing campaign with sense of limberness and can have a superior-capture over audiences with help of good maxims; all these features makes this medium an attractive form for Pepsi to advertise itself in certain markets.
In addition, outdoor integrated-marketing-campaign remains a very imperative tool to address mass people; this could be a gigantic type of advertising to put vast contributions to conquer the aim of campaign; this often includes setting Pepsi-billboards at active streets beside colleges, universities, offices, shopping-centers, bus-terminals, or airport roads to draw an increasing number of inhabitants to buy Pepsi cola. On the other hand, Pepsi often undertakes public relation activities that can create huge customer involvement; in addition, it also focuses on undertaking other forms of campaigns, such as promoting through magazines, or concentrating on special promotions; in certain situations, this cola also sponsors different important events, such as concerts, football, or soccer matches.
Pepsi cola is always more interested for advertising itself over TV; this is because it is the superior method to pull inhabitant of all ethnic backgrounds, middle-aged men and women, working people, young generation aging from twenty to thirty- five, as well as the teenagers, or people of diverse cultures or religions – indeed, this promotional tool is very engaging. However, it is notable that Pepsi cola always come up with suitable forms of TV advertising targeted at different set of target population, so that people of different cultures or religions can adapt with those.
Ansoff Matrix for Pepsi
Table 3: Ansoff’s model for Pepsi.
Recommendations
The consumption of carbonated soft drinks has decreased significantly due to increase health consciousness, so, this company should concentrate more on the non- carbonated drinks segment to order to increase market share in the beverage sector while it generated 52% of the total revenue. In addition, the parents all over the world are now trying to provide to their children healthy products to consume for which they would not like to purchase drinks; as a result, Pepsi should introduce innovative products considering health issues, such as, teeth damage.
On the other hand, Pepsi should take more initiatives as part of its corporate social responsibility program though it can reduce loyal customer base; therefore, it should aware people over consumption of Pepsi could create health problem, such as, mental and physical problem (obesity level).
Conclusion
There are some problems related with financial crisis, strategy, competitive forces, labor exploitation, distribution network, and political interference; however, Pepsi strongly maintains local legislation and global code of conduct, controls quality of the products, offers special packages to expand the business in the international market and increase market share as well.
Reference List
Agarwal, S. & Ramaswami, S. N. (1992). Choice of Foreign Market Entry Mode: Impact of Ownership, Location and Internalization Factors. Journal of International Business Studies, 23(1), 1-27. Web.
Angelkov, V. Black, T. & Green, A. (2003). Pepsi’s Strategy in the Carbonated Soft Drinks Market. Web.
PepsiCo. (2011). Annual report 2011 of PepsiCo. Web.
PepsiCo. (2012). Our History. Web.
Puravankara, D. (2007). Strategic Analysis of the Coca-Cola Company. Web.
Roche, P. 2012. Beverages (Soft Drinks). Web.
Samiee, S. (2003). International Counter-trade: A Reverse Marketing Perspective. Advances in International Marketing, 14(1), 9–33. Web.
Schuh, A. (2012). Strategic Responses to the Global Financial and Economic Crisis in Central and Eastern Europe – The Foreign Multinational Company Perspective. Progress in International Business Research, 7(1), 393–419. Web.
Upadhyay, S. (2007). Effective Business Strategies of Multinational Corporations in an Emerging Market Economy. Journal of Practical Consulting, 2(1), 3-8. Web.
Yahoo Finance. (2013). Competitors of the PepsiCo. Web.
Yesilyurt, O. (2012). International Expansion Strategies: Are Cross-Border Mergers & Acquisitions Successful? Web.