Identification and Overview of the Instructional Program
- The organization uses Personal Development Instructional Program (PDIP);
- Builds on the skills of individual organizational personnel;
- The acquired personal skills are assets to the organization.
It has been established that the organization applies the personal development instructional program that aims to improve the skills of individual members of the organization. The improvement of skills is expected to have critical implications on the performance of the organization since the capability of organizational members enables them to perform their tasks with proficiency and efficiency.
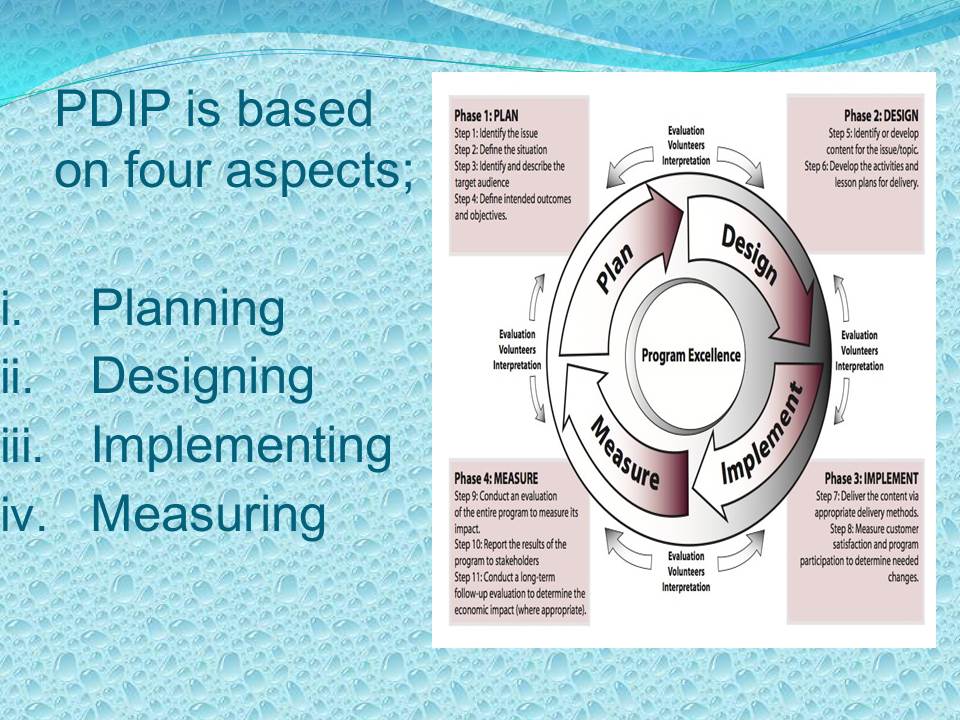
PDIP is based on four aspects:
- Planning;
- Designing;
- Implementing;
- Measuring.
The PDIP is based on four aspects of instructional processes, including planning, designing, implementing and measuring the impact of the program in accordance to the performance of the learners. Planning is associated with the identification of the concepts being learned, definition of context, analysis of the audience and stipulation of the aims of the study. The designing part is meant to come up with the content which enables the achievement of the stipulated objectives. After designing, the content and plan are implemented to instill the skills on the learners. Lastly, the program requires the assessment of the progress in order to determine whether the process is beneficial or not.

Analysis of the Program
Scope of the Program
- Changing Skills;
- Career Development Skills;
- Communication Skills;
- Interpersonal Relationship at work;
- Business Social Skills.
The personal development program for the organization is meant to instill various general skills such as change management, career development, communication skills, interpersonal socialization, and business social skills among others. In this case, it is evident that these skills help the organization to improve the members’ proficiency with regards to how they handle the clients.
- Personal Assessment;
- Decision-Making Skills;
- Stress Management.
Personal assessment skills enable the members to understand the importance of identifying their strengths and weaknesses. In addition, they are equipped with critical skills of decision making in order to facilitate their decision making capabilities. Stress at work is also tackled in this program in order to equip the members with the required skills of managing stress and hence increasing their output.


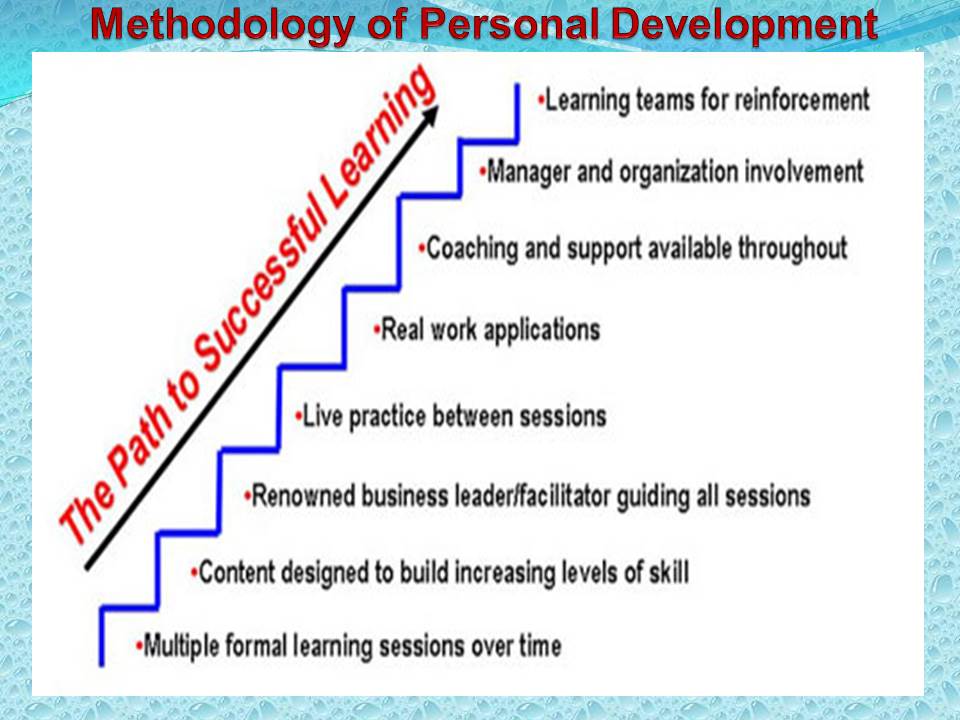
Methodology of Personal Development
The program is based on a ladder-like process of learning. This ladder includes various undertaking such as multiple lessons to ensure continuity, designing content in a manner that enables the increment of skills, and practical application of theoretical knowledge. In addition, the process recommends the involvement of managers in the learning process in order to provide role modeling. This is reinforced by the creation of learning teams in order to facilitate sharing of ideas.
Theories Underpinning PDIP
- Experiential Learning Theory;
- Observational Learning;
- Constructivist Theory;
- Environmentalist Theory of Learning;
- Maturationist Theory of Learning and Skills Acquisition.
Having analyzed the instructional program applied by the organization, it is evident that experiential observational, constructivist, environmentalists, and maturationist theories have been applied in the organizational learning processes. As such, these theories have been integrated in various ways as shown in the next several slides.

Theoretical Integration
Experiential Learning
- The organization members acquire skills by engaging in tasks.
- Repetition of skills lead to improvement.
- Members work together to acquire inter-professional skills.
In the organization , it is evident that the members learn a lot of skills by engaging in the performance of various tasks actively. Essentially, it is noted that members acquire skills progressively as they continue being exposed to the tasks. In fact, it is critical to notice that according to experiential learning, the learners become more proficient and effective with increase in experience (Reynolds, 2009).
Observational Learning Theory
- Junior members are allowed to work with seniors to observe.
- Their skills increase with increased exposure.
- Behaviors in decision making change as they continue interacting their colleagues.
Observational learning is a first-hand method of learning in which learners are expected to make observation and use them as the basis of approaching future tasks (Elen & Kariv, 2010). This is applied when teaching learners about decision making and business social skills. By observing the managers when making decisions, the learners obtain a general insight on how decision should be made or how to interact with people in business sociology.
Constructivist Theory
- It is based on preparedness.
- Members are allowed to interact with organizational processes.
- The members are active participants in most of the undertakings.
- Builds on members understanding about the organization.
The constructivist theory is based on the fact learners acquire skills once they interact with the environment (Marinkovic, 2011). In that regard, the organization has committed to involve members in undertaking critical activities. For example, they are involved in decision making in order to train them on how they should make basic decisions in their working station.
Environmentalist Theory of Learning
- The organization uses it environment to facilitate learning.
- It has set rules and regulation.
- Members respond to those regulations and hence understands the ideologies of the organization.
The learning program has been built on set of rules and regulation which is one of the aspects of a learning environment (Case, 2012). In that regard, the learners are bound to respond the regulations in order to achieve the set objectives. With the mentioned responses, the learners can acquire skills through conditioning. As such, it is evident that the environmentalist theory of learning has been implemented.
Maturationist Theory of Learning
- The program classifies members according to their years of service to the organization.
- The classification is in compliance with maturationist theory.
- The theory is based on the fact that people acquire skills naturally as the time of exposure increases (Jerome, 2009).
In this regard, it was established that the members have been ranked according to their skills and the number of years they have served in the organization. The classification based on years of service is in line with the maturationist theory of learning. In essence, this theory indicates that people acquire skills naturally as the time of exposure and involvement increases.





Recommendation of Theories
Cognitive Load Theory
- The organization needs to apply this theory in their PDIP.
- It instills skills in accordance to brain architecture (Kirschner, 2009).
- As such, different people should be exposed to different skills according to their cognitive capability and orientation.
This theory will be of great help to the organization due to various reasons. First, it recommends the organization to train members according to their cognitive capability. If some members are oriented towards technological interests, they should be exposed to tasks that enable them to acquire more technological skills.
Operant Learning
- The organization should facilitate learning by consequence.
- Positive consequence is better in this case.
- Awards should be provided to members of extemporary performance.
This theory should be integrated in the program to facilitate the appreciation of good performance and correspondent reaction to reluctance. As such, learners who register good performance should be awarded promotion or increase in salaries in order to motivate all members to acquire more skills. As such, it facilitates competition that enables the employees to acquire more skills and help the company to become more efficient in the long run (Whitney, 2009).
Inter-professional Learning Theory
- The organization should allow different members to interact and share ideas.
- Development of new ideas and strategies will arise.
- It is the basis of innovation.
This theory advocates for the multi-professional learning and training of learners such that the members will enjoy the opportunity of sharing ideas in order to improve the organizational processes. Multi-Professional learning has been proven as one of the determinants of innovation and creativity.



Conclusion
- The organization applied the Personal Development Instructional Program.
- They apply the Experiential learning, observational and constructivist theory among others.
- However, they should integrate the cognitive, operant and inter-professional theories.
- Innovation, objectivity and motivation.

References
Case, R. (2012). Theories Of Learning And Theories Of Development. Educational Psychologist,17(9), 219-233.
Elen, H., & Kariv, S. (2010). An experimental test of observational learning under imperfect information. Economic Theory,18(6), 677- 699.
Jerome, L. (2009). Ways of learning: Learning theories and learning styles in the classroom. European Journal of Teacher Education,15(8), 219-221.
Kirschner, P. (2009). Cognitive load theory: Implications of cognitive load theory on the design of learning. Learning and Instruction,7(2), 1-10.
Marinkovic, D. (2011). Sociology and constructivist perspective: Sociological theory and constructivist meta-theory. Developmental Psychology and Learning,13(6), 109-124.
Reynolds, M. (2009). Wild Frontiers Reflections on Experiential Learning. Management Learning,9(6), 387-392.
Whitney, L. (2009). Operant Learning Theory. Nursing Research,7(3), 234-229.