Introduction
The Greiners growth phases model which he developed in 1972 gives a description of six phases of development most businesses go through. It shows one why some managerial techniques, coordination mechanisms may be able to bring results at some particular stages of an business organizations growth and not do the same in others.
Critically analyzing the situation of PLG, we come to the conclusion that it has gone past the phase of growth through coordination and monitoring and is now at the red tape crisis as it crosses over into the fifth phase of growth through collaboration.
At this stage the company is faced with various problems which include: Reduced efficiency, the company incurs very high costs in its operations and these may be expounded by the red tape crisis or the level of bureaucracy which has been implemented in the company. For the company to be able to overcome these hurdles and continue with its growth course, there are a number of techniques which can be explored.
Main body
The company should start seeking solutions to its problems by setting up with cross functional teams to deal with the problems. Even though the company has set up its headquarters, the authority should be decentralized by having the various branches and their workers have some level of autonomy. This would give the various managers some sense of responsibility and morale to put in more effort.
The control mechanisms which are there should be simplified further but without compromising the reliability. This will make it easier for more people to understand its functioning. The information management systems on the other hand should be enhanced to make it more advanced to handle the increasing size of the business operations. The staff teams should be exposed more to team behavior enlightment procedures, they should also be given rewards. As it goes beyond this, the company comes to the extra organizational solutions where it will be handling collaborations with other companies.
Continuous Research and development. This would help the company in getting to know exactly which markets are untapped and how they can utilizes the potential demand for their services. Also they will be able to know in which areas they may be lagging behind in comparison to other multinational companies in the developed countries. Formation of subsidiaries which can specialize in the different areas of logistics. This can be in terms of rail transport. Road transport, sea transport, air freight, international logistics, local logistics and express delivery.
The company should control expansion or diversification into other areas if at all there are any problems the company may be facing at the moment but it has not yet fully found a solution for. This will ensure that no new complex problems arise. Branching out, i.e. increasing the number of branches and widen its network in order to establish its market presence in the logistics industry.
Their services should be more customer oriented and more vigorous marketing techniques with constant improvements in service delivery to ensure that the current customers are maintained. This is essential since the market is becoming more open to other bigger and more aggressive multinational companies.
Conclusion
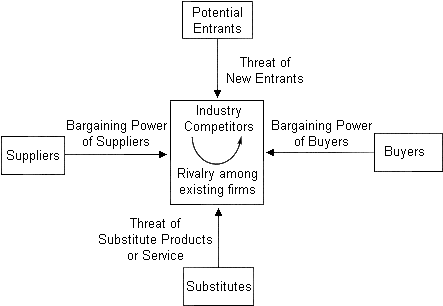
Industry analysis can be done using the chain analysis, porters five forces model and the PEST analysis. The best tool for PGLs case would be Porters model which gives a structure modeling an industry as affected by five forces, i.e. supplier power, barriers to entry, threats of substitutes, buyer power and degree of rivalry (Quick MBA, 2008).
- Rivalry. PGL should analyze the level of competition it faces in the market both local and international. It should know the main competitors and the concentration ratio. when competition is high prices will reduce, but it should seek competitive advantages over its rivals.
- Threat of substitutes; this is the consideration of how the services of PGL can be offered by other companies, especially at lower prices.
- Buyers bargaining power: this analyses the power of the buyers in financial terms and if they can collude to buy together.
- The suppliers bargaining power: when looking at this, PGL would know the strength of the position of some of the other companies on whose services they may depend.
- Entry of competitors into the market; through this analysis PGL would know how the hurdles that exist for potential competitors to join the market. (Value based management.net, 2008).
References
- MindTools. Using the Greiner Curve.Web.
- QuickMBA. Strategic Management. Porter’s Five Forces. Web.