Brief Synopsis of the Issue
The purpose of this paper is to determine the most appropriate strategies that Pizza Express can use to enter the Nigerian market. The emerging technologies have turned the world into a small global village, and firms are struggling to expand their market share by finding new international markets.
In this study, Porter’s Diamond model will be used to conduct an evaluation of the Nigerian hospitality industry in order to determine some of the benefits, associated risks and costs of operating in this country.
This information will provide a basis of coming up with an appropriate market entry strategy that can be effective enough for this firm to enter the Nigerian market. As Schlosser (2012, p. 67) notes, the strategy chosen should always be cost effective, less risky, and able to yield maximum output.
The aim is to find a strategy that will cost this firm a less amount of initial capital investment, but able to yield the value that this firm desires in its globalization strategies.
Given the fact that Nigeria is one of the emerging markets, a direct market entry would be the most appropriate strategy for this firm. The competition in the market is not very stiff, and this makes it more advisable for this firm to make a direct entry in order to wholly control its operations in this country.
Recommendations
In order to succeed in this foreign market, Pizza Express needs to observe the following recommendations.
- The marketing management should start by conducting an extensive research in order to understand tastes and preferences of the local market in Nigeria (Smith 2006, p. 89).
- The menu that Pizza Express plans to use in the Nigerian market should reflect the main local dishes in the country.
- The market entry strategy should be based upon a comprehensive research in order to maximize on the value generated from the process.
- The management of this firm should consider employing the host country national who understands the market dynamics in the Nigerian market (Jakle & Sculle 2002, p. 34).
Background
Pizza Express is one of the most successful restaurants in the United Kingdom. Started by Peter Boizot in 1965, this restaurant has experienced massive growth over the years, and currently operates over 400 restaurants within the United Kingdom (Scherer 2010, p. 45).
This firm has also been very successful in the European markets. Pizza Express also has a strong presence in India, Hong Kong, and the Middle East markets (Johansen 2012, p. 38). It has been making considerations on how to make entries into some of the emerging markets in Africa. Nigeria is one of the most attractive markets in Africa because of its large population and the rapidly expanding economy.
Currently, it is ranked the highest African economy, surpassing South Africa and Egypt which have been in that top position for decades. The Nigerian economy is one of the emerging economies in the world (Smith 2012, p. 66).
As stated previously, the level of competition in this country is gaining pace, but it can sustain the operations of this firm if it decides to make a direct market entry. The general cost of production, including the cost of labour, rental costs, and the raw products, are considerable law as compared to that in Europe.
However, the purchasing power of the individual customers is also low, making it necessary for this firm to control all its operations in the country. When this firm is fully in charge, it becomes easy to determine the most appropriate prices for its products that will make its products attractive while still allowing its strategies to remain sustainable.
Analysis of Market Opportunities in Nigeria
According to Olaloku (1999, p. 75), with a population of 174.5 million people, Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa and the seventh most populous country in the world. The country also has the largest economy in Africa, making it a very attractive market for a firm such as Pizza Express.
In order to analyze the market opportunities in Nigeria, it is important to use Porter’s Diamond Model to identify some of the unique factors that this firm can benefit from in order to achieve success in this region.
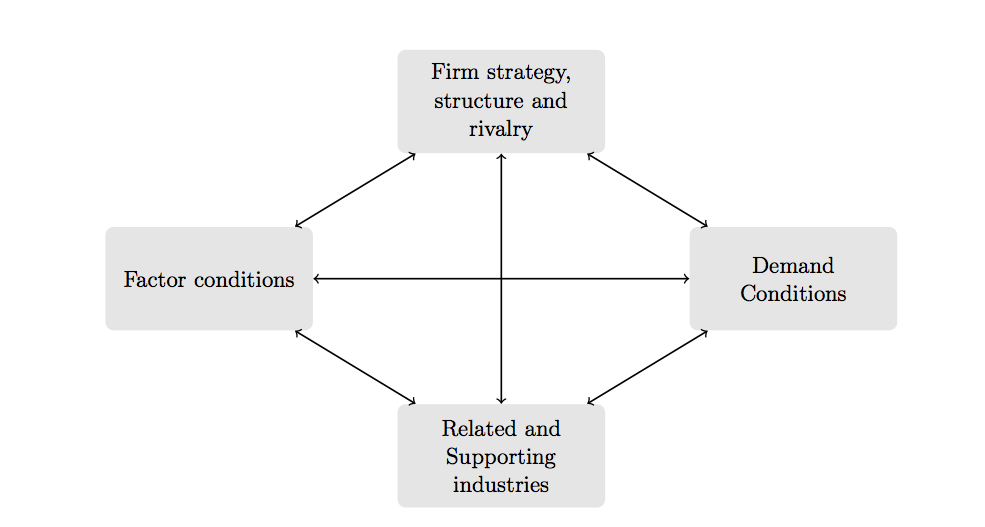
As shown in the above model, there are four specific areas that need some serious considerations when analyzing a country. The following areas need to be analyzed in order to understand how Pizza Express stands to benefit from the Nigerian market.
Factor conditions
According to Abdullahi (2008, p. 94), “Factor conditions can be seen as advantageous factors found within a country that are subsequently build upon by companies to more advanced factors of competition.” With a population of 174.5 million people, the country has enough workforces that can help this firm to achieve its strategic objectives in the market.
Most of the Nigerian youths have vocational training, and this means that Pizza Express will have enough skilled workforces to hire. The main language in this country’s major cities is English, a fact that eliminates language barrier (Hargreave & Hill 2001, p. 66) Most of the raw materials needed for the company’s products are also readily available within the country.
Demand conditions
Nigeria has a large population, with a large number of people staying in the cities of Lagos and Abuja (Diejomaoh 2005, p. 88). The hospitality industry in Nigeria has experienced massive growth over the years. This massive population creates a very attractive demand for the products that is offered by Pizza Express.
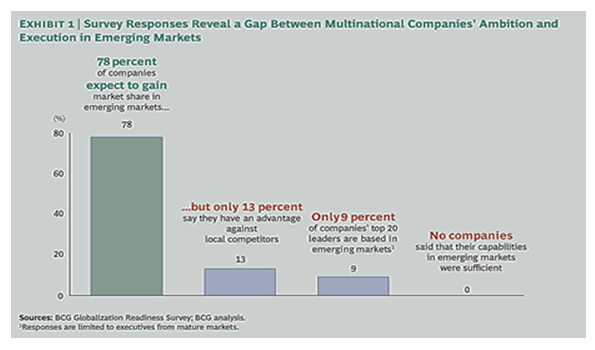
There are high chances that the products from this firm will have enough local demand in Nigeria if they meet local requirements. As Pendrys (2011, p. 82) notes, most of the multinationals have not exploited the opportunities in the emerging markets fully. This is demonstrated in the data below. Pizza Express should avoid this trend
Related and supporting industries
The hoteliers heavily rely in the tourism industry to support its operations. Tourism industry in Nigeria has experienced massive growth over the past one decade. The government has been supporting tourism industry by marketing the tourism products in the country to the international market (Sacco & Schott 2011, p. 52). Local tourism has also been expanding, further boosting the hospitality industry.
Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
According to McDonald & Burton 2002, p. 53), the strategy that a firm uses in different markets may make it succeed or fail depending on the nature of that particular market. This means that it is important to understand the market before coming up with an appropriate management structure. The following is the management structure used by Pizza Express in its global operations.
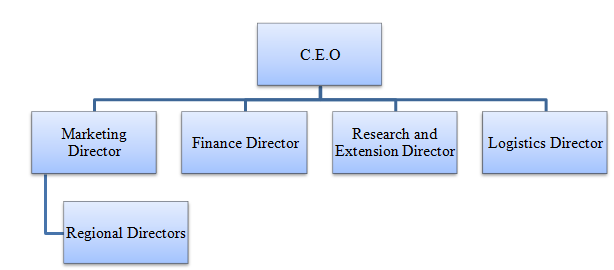
As shown in the diagram above, the regional directors are answerable to the marketing director of the firm. Although they are given the powers to make independent decision that is informed by the local forces, all strategic decision always need the approval by the marketing director.
Given the expected rivalry expected in the Nigerian market, it is necessary to embrace a more decentralized management approach (Wales & Reaich 2004, p. 75). The director of the firm in the Nigerian market should be allowed to make decisions based on the local forces in the country in order to make the firm to be relevant in the local context.
Country Attractiveness
It is always important to investigate attractiveness of a country before making a decision to make an entry into it (Aaseng 2001, p. 36). Although it is a fact that Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa and with the largest economy, this does not make it automatically attractive.
There are some factors that need to be considered before considering this country as an attractive market for Pizza Express’ products. The attractiveness of the country can be analyzed in a tabular form as shown in the table below.
Attractiveness of the Nigerian Market
Company Situation Analysis
In order to manage some of the external forces in the environment as identified in the above analysis, Pizza Express needs to have appropriate strategies and capabilities that may make superior in market management. The following SWOT Analysis Model can help understand the internal factors of this firm
Readiness to go overseas
Pizza Express has made positive progress in the European markets within the past one decade. The firm has also made successful entry into India, Middle East, and Hong Kong. This success means that this firm has the capacity to make successful entry into the Nigerian markets in its quest to expand its market.
The firm has enough financial strength and a team of experts in international marketing that can enable it to make a successful entry into the Nigeria market. Its many years of experience in this industry put it at even better position to achieve success in the Nigeria market.
Global Sourcing and Production
According to Pendrys (2011, p. 85), the sourcing strategies applied by a firm will always determine its capacity to succeed in the new market. Global sourcing is always attractive when the local raw materials are more expensive than the international prices. In such cases, Pizza Express may need to outsource these materials from other countries where the prices are cheaper.
Products that can cheaply be available within the country should be purchased locally. At the firm level, the management should identify products that it can easily manufacture on its own, and those that require sourcing from other suppliers at reduced costs.
The production strategy should focus on the quality of the products, the costs associated with the production, and the needs of the local market. The firm should be able to produce high quality products that meet the expectations of the market at affordable costs.
Market Entry Strategy
There are a number of market entry options that a firm can use when making an entry into the global market. Some of the most popular entry modes in the market include direct market entry, joint venture, use of subsidiaries, franchising, or mergers and acquisitions. Each of these strategies has its own strengths and weaknesses.
The strategy chosen for the entry into the Nigerian market is the direct entry approach (Dalgleish 2006, 87). This firm should consider pulling its resources to make a direct entry into this market because of a number of reasons.
The market in Nigeria is very attractive not only because of its large population, but also the rapidly expanding economy. Being an emerging market, this country has few established firms that will offer stiff competition to Pizza Express. The graph below shows some of the leading industries in this country.
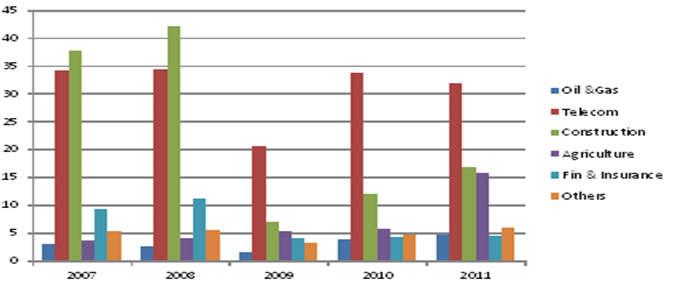
It is clear from the above data that hospitality industry does not have stiff competition as compared to other industries. This makes it more desirable to use direct market entry because it will take a short period to establish itself if it uses appropriate technologies. The main strength of making a direct market entry is that Pizza Express will have full control over its operations locally, unlike in cases of partnership.
The management will have the independence to make strategic decisions based on its market analysis, and the strategies used by the firm. The firm will also enjoy all the profits without sharing it with other parties. However, there are some weaknesses of this entry mode that may pose some serious challenges.
Direct entry will mean that the firm will need to spend more in putting up the structures, hiring of the right staff, and conducting an extensive research on the market. All the losses that the firm may incur in its operations will also be paid by the firm. However, these weaknesses can be managed through effective strategies by the regional management unit.
Implementation of Market Entry Strategy
According to Carney (1995, p.48), effective strategies can only be beneficial if they are applied effectively within a given context. When making direct market entry, the management should follow some specific steps in order to achieve the desired results. The first step when using this strategy is to conduct a market research in order to understand the local environmental forces.
The management should then recruit the relevant workforce, mostly the host country nationals who will take part in the implementation of the strategies. When this is done successfully, the firm will need to rent outlets within strategic locations in the major cities. Abuja and Lagos would be the first two locations that this firm should target. Finally the business can be launched based on the set strategies discussed above.
List of References
Aaseng, L. & Aaseng, L. 2001, Business builders in fast food, Oliver Press, Minneapolis. Web.
Abdullahi, H. 2008, History and structure of the Nigerian economy: Pre-colonial period to 2007 and beyond, Usmanu Danfodiyo University Sokoto, Lagos.
African Economic Outlook 2012, Nigeria. Web.
Carney, G. 1995, Fast food, stock cars, and rock ‘n’ roll: Place and space in American pop culture, Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Lanham. Web.
Cate, A. 2011, The fast food detox: The 14-day plan to help you eat clean and get lean, HarperCollins, Pymble.
Cook, S. 2004, Measuring customer service effectiveness, Gower, Burlington. Web.
Culc 2014, Global Market Assessment: Nation-Level Explanations: From Local to Global: Strategies for International Development, Coventry University, London.
Dalgleish, S. 2006, Fast food, Smart Apple Media, North Mankato.
Dana, L. 2010, Entrepreneurship and Religion, Edward Elgar Pub, Chicago. Web.
Diejomaoh, V. 2005, Economic development in Nigeria: Its problems, challenges, and prospects, Princeton, New Jersey.
Duram, L. 2010, Encyclopedia of organic, sustainable, and local food, Greenwood Santa, Barbara. Web.
Emerson, R. 2009, Fast food: The endless shakeout, Lebhar-Friedman Books, New York.
Hargreave, J. & Hill, T. 2001, Fast food Felicity, Nelson Thornes, Cheltenham.
Hayes, D. & Laudan, R. 2009, Food and nutrition/ editorial advisers, Dayle Hayes, Rachel Laudan, Marshall Cavendish Reference, New York.
Jakle, J. & Sculle, K. 2002, Fast food: Roadside restaurants in the automobile age, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. Web.
Johansen, L. 2012, Fast food vindication: The story you haven’t been told, Murray Press, Los Angeles.
Lambo, T. 2007, Nigerian economy: A textbook of applied economics, Evans Brothers, Ibadan.
McDonald, F. & Burton, F. 2002, International business, Thomson Learning, London.
Olaloku, F. 1999, Structure of the Nigerian economy, Macmillan, London.
Oshikoya, T. 1990, The Nigerian economy: A macroeconomic and input-output model, Praeger, New York.
Pendrys, E. 2011, Memoirs of a fast food man, Cengage, New York. Web.
Rosoman, C. 2008, Therapy To Go: Gourmet Fast Food Handouts for Working with Adult Clients, Jessica Kingsley Publishers, London.
Sacco, P. & Schott, J. 2011, Fast food dating: Your 2 cents: over one thousand served, DoctorZed Publishing, Adelaide. Web.
Scherer, L. 2010, Fast food, Greenhaven Press, Detroit.
Schlosser, E. 2012, Fast food nation: The dark side of the all-American meal, Mariner Books, Boston.
Smith, A. 2006, Encyclopedia of junk food and fast food, Greenwood Press, Westport. Web.
Smith, A. 2012, Fast food and junk food: An encyclopedia of what we love to eat, Greenwood, Santa Barbara.
Thornes, C., Adedeji, A., Sheu S. & Vollrath, D. 2014, Structural Change in the Nigerian Economy. Web.
Torelli, S. 2011, The fast-food kitchen, Harvest House Publishers, Eugene.
Wales, J. & Reaich, N. 2004, Business studies AS: The complete companion, Nelson
World Bank 2013, Nigerian Economic Report, World Bank, New York. Web.