Introduction
- Worsened health condition.
- Pain.
- Discomfort.
- Additional time and resources.
- Creation of a special team.
- Increased repositioning of the patient.
- Diet improvement.
- Moisturizing.
People who come to healthcare facilities and seek professional consultation have health-related issues, as a rule, and want to overcome them. However, experiencing additional problems with movement, they become likely to acquire complications during the hospital stay. Because of surgical interventions, for example, many of them deal with pressure ulcers after three weeks of hospitalization because of inability to change their position without assistance. Even though professionals do their best to reduce such cases, this goal is not reached. This fact allows presupposing that existing guidelines are not good enough for positive change. In this way, it is significant to pay more attention to the methods used to prevent the occurrence of this issue. New approaches should be used to deal with pressure ulcers because they cause discomfort for patients. They worsen the overall health condition of consumers, and their treatment is rather painful. Moreover, it is time- and resource-consuming.
Fortunately, advantageous changes can be experienced if a special team of professionals is created (Moore, Webster, & Samuriwo, 2015). It should focus on the increased repositioning of the patient, diet improvement, and moisturizing.

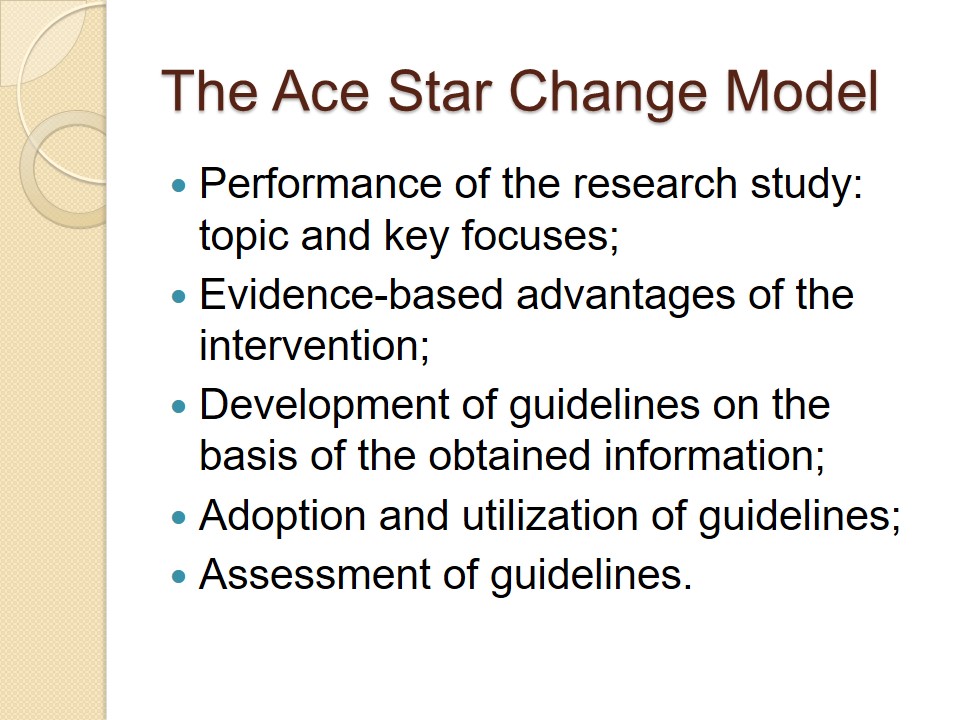
The Ace Star Change Model
- Performance of the research study: topic and key focuses;
- Evidence-based advantages of the intervention;
- Development of guidelines on the basis of the obtained information;
- Adoption and utilization of guidelines;
- Assessment of guidelines.
The ACE Star model provides leaders with an opportunity to implement a change in everyday operations successfully. It focuses on the collection of evidence-based knowledge and its further implementation in practice. The ACE Star model allows making this transformation rather mild so that it does not cause misunderstanding or associated issues. Moreover, it ensures that no significant data gathered in the framework of the research study will be overlooked.
Practice Issue
- Health issues caused by treatment;
- Painful recovery process;
- Time- and resource-consuming procedures.
Inability to move often leads to the development of pressure ulcers in patients. In many cases, they are hospital-acquired, which means that professionals overlook some signs that lead to their occurrence and fail to provide those services that ensure positive health outcomes. Still, the development of additional health complications does not make patients refuse treatment because they have no other options to reach improvement. Nurses and physicians should think of the ways they can prevent the development of pressure ulcers because they are not easily treated (Webster et al., 2017). In particular, this process requires much time and specific procedures that are painful and complicated (Ackroyd-Stolarz, 2014). This issue is tightly associated with practice because it can be overcome if professionals use additional approaches to deal with it and ensure that patients do not acquire it while receiving other healthcare services.

Research Questions
- What are the main adverse influences of pressure ulcers treatment?
- What exactly affects patients’ organs?
- How can these influences be prevented?
- What are the most common results of pressure ulcers treatment?
- What benefits can be observed due to the creating of a specialized team?
To implement a change project, researchers should let their sample that includes healthcare employees acknowledge what they want to achieve with the help of change. For them to formulate a range of main objectives, researchers should develop a set of questions they want to answer due to their study. In this very case, the focus should be on the following:
- What are the main adverse influences of pressure ulcers treatment?
- What exactly affects patients’ organs?
- How can these influences be prevented?
- What are the most common results of pressure ulcers treatment?
- What benefits can be observed due to the creating of a specialized team?

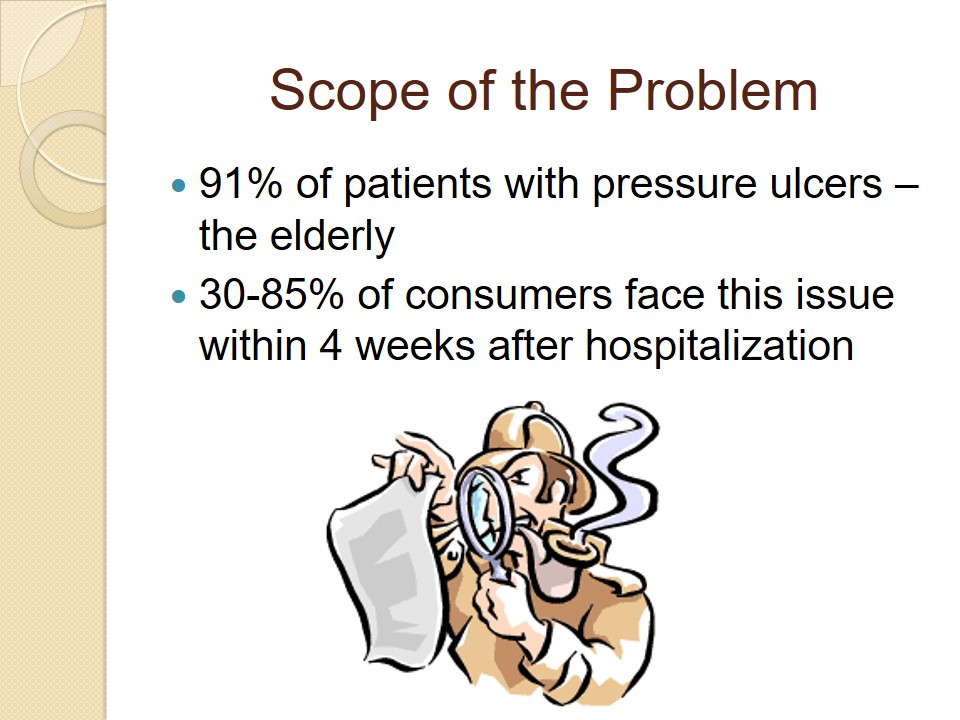
Scope of the Problem
- 91% of patients with pressure ulcers – the elderly.
- 30-85% of consumers face this issue within 4 weeks after hospitalization.
Pressure ulcers are usually observed in those patients who have issues with movement. As a rule, these are the representatives of the elderly population (more than 90%). While it is normal for healthcare facilities to have less than 2% of patients who develop pressure ulcers during a hospital stay, these rates are much higher. 30-85% of consumers face this issue within 4 weeks after hospitalization (Agrawal & Chauhan, 2012). These rates are critical because they lead to the increased morbidity and mortality as well. Suffering from pressure ulcers in addition to the main health issue, patients become more exhausted and have no strength to fight the disease. Realizing the significance of this healthcare issue, governmental bodies allocate additional resources targeted at dealing with the increased prevalence of pressure ulcers. Millions of dollars are allocated annually to deal with this problem, but it is not resolved yet. It is also significant to consider the fact that healthcare professionals are not able to focus on the patient’s disease because they are to address additional complications at the same time.
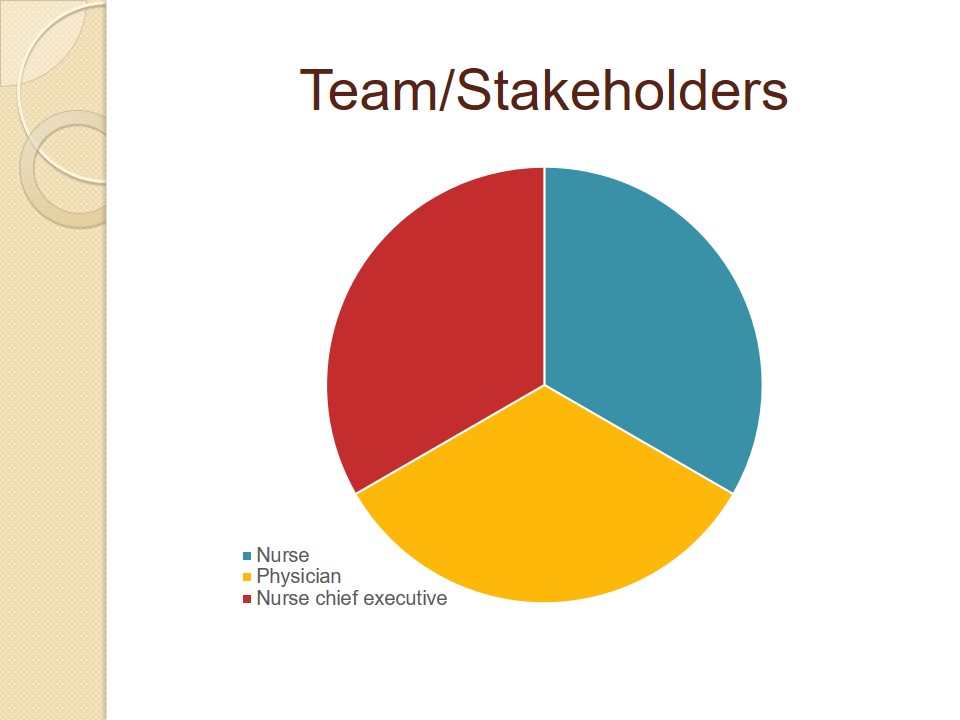
Team/Stakeholders
In order to reduce the prevalence of pressure ulcers, healthcare leaders should consider the necessity to create specialized teams. In this way, they are to consider the representatives of different departments. In this way, new teams will be able to develop the most advantageous decisions, considering opinions of different professionals (Samuriwo & Dowding, 2014). They should consist of at least three members, such as a nurse, a physician, and a chief nurse executive.
Evidence to Support the Need for Change
In order to develop a new approach to reduce the number of patients who suffer from pressure ulcers, several credible sources were assessed. It was revealed that the creation of a specific team that consists of diverse healthcare professionals is the most advantageous intervention that has not yet been used. This team should focus on the treatment of open wounds that is why its members should have enough experience associated with the required interventions. Researchers believe that the participants should include not only nurses but also physicians. Moreover, the creation of a team can be managed in two ways: professionals can start operating after additional education or can already be ready to perform their duties due to the previous experience.

Action Plan
- Data collection and analysis;
- Development of guidelines and recommendations;
- Allocation of roles;
- Training;
- Change implementation;
- Monitoring;
- Evaluation and spread of findings.
For the initiation of the pilot study, researchers should create a training program for the professionals (Li, 2016). It should include education associated with the teamwork, patient repositioning and moisturizing, diet peculiarities, etc. It would also be advantageous to provide nurses and physicians with reimbursement for them to be more motivated to follow the plan and ensure that their initiativity is not overlooked. In general, an action plan will consist of those steps that ensure the analysis of evidence-based data and evaluation of the intervention developed on its basis.

Timeline for the Plan
- Week 1-2: data collection;
- Week 3: data evaluation;
- Week 4: development of recommendations;
- Week 5: allocation of roles;
- Week 6-10: training and education;
- Weeks 11-21: implementation and supervision;
- Week 22-23: evaluation of outcomes;
- Week 24: conclusions.
To implement change within a healthcare system, it is vital to develop a timeline that can be used to guide the project and ensure that it will be accomplished before the deadline. Considering the fact that pressure ulcers occur after 3-4 weeks of hospital stay, the implementation of the pilot program can last for about 4-6 months, depending on the circumstances (Quaeem et al., 2014). In particular, there is a possibility that the leadership of the setting and its employees will be unwilling to accept the discussed change.

The Nurse’s Role and Responsibility in the Pilot Program
As it was previously mentioned, a specialized group should consist of various healthcare professionals. In this way, a possibility to develop the most advantageous treatment decisions can be developed. Nevertheless, nurses are expected to be involved in the pilot program more than physicians are because they are the ones who provide the majority of care and associated services to patients. A nurse involved in the project is expected to provide direct care to patients with pressure ulcers, ensuring that they are appropriately treated. A chief nurse executive, in his/her turn, should lead a team and monitor the way it worked to provide patients with high-quality services. Moreover, he/she should focus on the creation of a positive environment within the team because it improves cooperation and makes it easier to implement required changes.

Procedure
- Collection of evidence-based information.
- Development of guidelines.
- Training.
- Change implementation and supervision.
- Assessment of findings.
- Conclusions.
Even though the implementation of the pilot program is likely to be rather time-consuming, there is a necessity to follow the developed timeline and accomplish every procedure, starting with the collection of data and ending with the assessment of the effects of the proposed alteration. Addition attention should be paid to supervision. Right after training, professionals may face difficulties in practice because they are not used to new procedures. Being managed along with the very change implementation, this process will definitely minimize the possibility of error.

Next Steps
- Spread of research findings;
- Initiation of policies;
- Enforcement of change;
- Development of guidelines for universal utilization;
- Further research studies focused on wound healing factors.
As soon as this research study is conducted and its advantages for practice are outlined, researchers will spread them to other professionals to receive access them. New policies considering the creation of specialized teams at hospital settings will be developed. As a result, this intervention will be used further in the research setting. More generalized guidelines will be created to encourage other professionals to accept this change. Moreover, it will encourage other researchers to conduct studies that focus on the same issue but include a larger sample size and address other limitations. In addition to that, further research will not require critical changes, considering its implementation. The major focus will still deal with the opportunity to minimize the number of hospital-acquired pressure ulcers.

Spread of Findings
- E-mails.
- Meetings.
- Conferences.
- Scholarly journals.
- Oral communication.
Dissemination of findings should be managed after the accomplishment of the research study. It provides stakeholders with an opportunity to understand that their efforts were not in vain and realized what was done properly or what changes should be done additionally. Moreover, it provides an opportunity for other professionals to understand whether there are some practical changes that can benefit them and their patients.
In this very case, dissemination of findings can be done in several ways. Fists of all, stakeholders can receive this information with the help of e-mails, as this is a method that allows saving time and resources. Further, professional meetings and conferences can be used to share research results. Finally, information can be published in scholarly journals. It is also possible that the most general points will be discussed among professionals orally in the frameworks of a typical conversation.

Forms that will be Used
Forms for professionals and their patients that are focused on their feedback are needed.
It cannot be said the implementation of the proposed project cannot be maintained without specially developed formed; however, their utilization is likely to be rather advantageous. In particular, they are expected to improve the process of supervision. Feedback obtained from healthcare professionals and their patients regarding the successfulness of the developed intervention should be gathered because it allows revealing whether professionals followed provided guidelines and acted according to training. Moreover, it can show if patients observe improvement of their condition and are positively impressed by the implemented intervention. This information will not only provide an opportunity to find out whether the change will be beneficial for all involved stakeholders but also reveal how it should be altered in order to improve result more. Specific forms will make it easier for both professionals and their clients to share their observations and attitudes regarding the treatment. In this way, it is also vital to ensure that they are properly distributed among the sample. What is more, the use of these forms will make it easier for the sample to share significant data. Thus, they will spend less time to provide data and researchers will save their time dealing with the necessity to gather data from these forms. The utilization of specific forms will definitely be advantageous for stakeholders. Moreover, no information will be lost during its transformation.

Resources Available to the Staff
- Relevant data can be from online databases.
- Approach the PubMed, EBSCO, and NCBI sites.
- Professionals can share information.
- Dressing should be bought from authoritative suppliers.
- Assistance can be provided by other professionals.
For the staff members who will be included in teams, it will be advantageous to search for information that is associated with the mentioned change. Of course, they can focus only on data provided during education and training, but it is not likely to be enough for experienced professionals who are willing to benefit their clients. Thus, the members of the sample should address various sources, including online databases and peer-reviewed articles. Moreover, assistance provided by other professionals can turn out to be a rather advantageous of significant for practice information because they can share their knowledge and skills.
Resources needed for the implementation of the research study also include such things as appropriate dressing. Fortunately, there is nothing new considering it, because the specialized dressing is needed regardless of the participation in the pilot program.

Summary
Pressure ulcers are often faced by patients who spend more than three weeks in a hospital. They influence people’s well-being negatively and even increase mortality rates. Their treatment process is rather complex that is why it requires revision. Creation of a specialized team can change this situation to better. According to the change model, this process should include education and training of the personnel. The focus should be made on new treatment approaches and their assessment.

References
Ackroyd-Stolarz, S. (2014). Improving the prevention of pressure ulcers as a way to reduce health care expenditures. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 186(10), 370-371.
Agrawal, K., & Chauhan, N. (2012). Pressure ulcers: Back to the basics. Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery, 45(2), 244–254.
Li, D. (2016). The relationship among pressure ulcer risk factors, incidence and nursing documentation in hospital-acquired pressure ulcer patients in intensive care units. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 25(15-16), 2336-2347.
Moore, Z., Webster, J., & Samuriwo, R. (2015). Wound-care teams for preventing and treating pressure ulcers. CochraneDatabase of Systematic Reviews, 9(1), 4-22.
Quaeem, A., Humphrey, L. L., Forciea, M. A., Starkey, M., Denberg, T.D., & Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians (2014). Treatment of pressure ulcers: A clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Annals of Internal Medicine, 162(5), 370-379.
Samuriwo, R., & Dowding, D. (2014). Nurses’ pressure ulcer related judgements and decisions in clinical practice: A systematic review. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 51(12), 1667.
Webster, J., Bucknall, T., Wallis, M., McInnes, E., Roberts, S., & Chaboyer, W. (2017). Does participating in a clinical trial affect subsequent nursing management? Post-trial care for participants recruited to the INTACT pressure ulcer prevention trial: A follow-up study. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 71(1), 34.