- Product Development Models
- Iterative Nature of Product Development Plans
- Attributes of a Good Product Development Model
- Importance of Information Flow in a PDP
- Management Structure and Information Flow
- Importance of Market Research in a PDP
- Concurrent Engineering
- Advantages of CE in PDPs
- Generic Requirements for the Implementation of Concurrent Engineering
- References
Product Development Models
Product development is the process through which new products are brought into the market (Aaker, 2012). In order for a product to be successful in the market, several factors have to be considered to ensure that the new product is capable of overcoming the competition that is present in the market.
At the same time, the product is expected to meet the needs and desires of the consumers so that they become loyal to the new brand. In addition, the new product needs to have solid sales to be profitable in the short run and in the long run hence meeting the goals of the manufacturing company.
TRC is one of the most common product development models that firms use to develop and introduce new products into the market (Aaker, 2012). This method identifies the haphazard and uncertainties that are present while introducing a new product into the market.
Therefore, the research and development team comes up with suitable strategies that can be used to eliminate the possible uncertainties that may come up at any stage in the product development process (Aaker, 2012). To achieve this, this model uses qualitative data that has been collected from various studies that have focused on the product development to come up with an ideal method that is more valid and flexible in application. This model has the following stages:
- Idea generation
- Feature development
- Product development
- Product testing
The figure below shows the various stages of this model (Kotler, 2007).
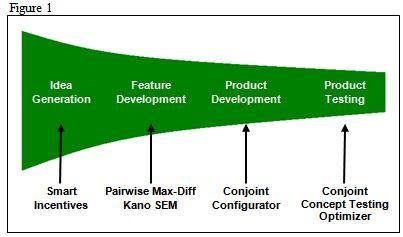
The stages in this model have been arranged in a manner that accommodates any unexpected occurrences. At the same time, the model supports feedbacks from customers, use of new methods or technologies and so on.
As stated earlier, this method mainly utilizes quantitative data that has been collected from other studies. In this respect therefore, this method uses a smart incentive approach in the idea generation stage. This approach is effective in that it utilizes the concepts of creativity and validation. Thus, respondents in a study are used to generate the most appropriate ideas of introducing the new product into the market.
This produces a list of competing ideas from peer groups giving out essential information with regards to market evaluation. At the same time, this information can be used to develop specific features of the product or the entire product. This increases the chances of success of a product entering into the market (Kotler, 2007).
The next step in the process is feature development. This method utilizes the max-diff approach that compares three to five different features of the product to determine which one of these will be more appealing to the customers. This method is superior to traditional methods that only compare the difference between two features of a product. In the product development stage, a number of features are collectively used to build and develop a product.
This stage also utilizes statistical information from respondents. At this stage, respondents are given the chance to select a combination of features that will be used to develop the final product. The features that are highly preferred by the customers are then used to develop the final product.
This process ensures that the final product meets the tastes and preferences of the market that the product is about to enter. Once the final product is available, the product testing process commences. Here, simulation tests are conducted to determine the different combinations of the product that actually meet the tastes and preferences of customers in the target market. This process is effective especially in a highly competitive market that contains a variety of substitutes.
Once this process is complete, information with regards to the strengths and weaknesses of the products are arrived at. Thus, specific modifications of the product become possible to ensure that the product meets the current needs of the market hence being successful in the short run and in the long run.
Walden University has also developed an effective product development model. This product development model has relatively similar stages as compared to the TRC model (Jugger, 2011). However, its main difference is that it has seven stages while the TRC model only has four stages. The following steps are used in the product development process of this model:
- Idea generation
- Screening
- Concept development and testing
- Business analysis
- Product and market mix development
- Market testing
- Commercialization
In the idea generation stage, relevant information is gathered and analyzed with regards to the development of the new product. This is always an ongoing process in many businesses. In this process, information is sourced from within and outside the firm. In this stage, this method mainly utilizes market research concepts such as the use of focus groups comprising of customers, companys sales representatives and channel members.
These individuals are used to provide information with regards to the current market trends and the tastes and preferences of consumers. This method, facilitated with other sources of information, provides a firm with a variety of options that it can utilize to develop its new product (Jugger, 2011). In the screening stage, the ideas that were generated in the first stage are critically evaluated to eliminate less effective ideas.
In the initial stages of this process, the executives and top management officials are used to select the most favourable ideas for the business. In addition, several other research methods can be used to select the ideas that pose higher chances of being profitable, exhibiting low costs of production and so on (Jugger, 2011). Concept developing and testing is then used to evaluate the ideas that were selected in the previous stage.
Here, the marketing department uses its employees, distributors and customers as the focus groups of the ideas. These ideas are not presented to them in form of actual products but in theory. At this point, the marketing department aims at determining the attitudes and perception of the idea from the market, their purchase frequency and the desired price level. The ideas that are selected are the ones that have a positive feedback from the focus group.
At the business analysis stage, the number of ideas is always cut down to either two or three. It is however essential to note that at this stage, the final product has not been developed yet and the idea is still in theory. The main aim of this stage is to come up with projection regarding to the market size, the expected production costs, financial projections, and competitor analysis.
At this point, it is also essential for the management to determine whether the product ideas that they have are in line with their mission, vision, goals and objectives. In the product and market mix stage, prototypes of the selected ideas are developed. Here, they are presented to the customers for approval.
In addition to the prototypes, the customers also have other auxiliary features and information of the product. These may include the price, distribution chains and so on. The main aim of this stage is to determine the reaction of the consumers to the product. Suggested amendments of the product are then incorporated and the process is repeated once more until a desirable state of the product is achieved.
This process is useful as it is used to determine the large-scale market feasibility of the product. In the marketing stage, the product is made available to a larger testing group. In most cases, this group comprises of a segment of the market. This may be one city, town, or a specific geographic region.
Here, full marketing of the product is conducted. The main aim of this process is to determine the actual performance of the product in the market. The weaknesses of the product are identified and corrected. At the same time, its strengths are maximized. Once this has been done, the product is now commercialized.
Stage-Gate model is also another product development model that can be used to introduce a new product into the market. This method is similar to the other two methods that have been discussed so far. However, the main difference exhibited in this method is that a gate separates one stage of the development project from the other.
Therefore, before a proposed product passes to the next stage, it has to be approved either by the manager or by the steering committee (Eagan, 2010). This decision is based on a number of factors that include but not limited to analysis of risk, business analysis, and availability of essential resources. The following stages are included in this model:
- Stage 0: Discovering
- Stage 1: Scooping
- Stage 2: Developing the business plan
- Stage 3: Development
- Stage 4: Testing and validation
- Stage 5: Product launch
The figure below shows the stages of development of a product using this model (Eagan, 2010).

Discovering is the first step in this model. At this stage, a firm comes up with an idea that it wants to implement to gain competitive advantage over its rivals in the industry and to be sustainable in the short run and in the long run. To achieve this, the firm will usually utilize a number of thinking strategies.
Brainstorming and group thinking are some of the most common methods that are used to generate ideas at this stage (Thomas, 2009). In most cases, it is essential to communicate with customers to understand how the need and use products. Scooping is the second stage in this model.
Here, a company critically analyzes the proposed product and the market in which it is expected to enter. Here, the marketing department needs to maximize on the strengths and opportunities that the product has to overcome. Thus, a SWOT analysis is conducted at this level.
It is at the end of this stage that the product passes through the first gate of development (Thomas, 2009). Developing a business plan is the next step. This level forms the last part of analysis in the concept development of the new product. The first main essence of this stage is product development and analysis.
The benefits of the product to the user are analyzed. In addition, specific features of the product are developed to attract customers and to meet their tastes and preferences. It is also at this stage that a market analysis is conducted to determine its size, segmentation, and trends. This is essential in the developmental process of the product, as it will determine the quantity, quality, frequency, and price that the proposed product shall be manufactured with.
Consequently, the prototype of the product is also developed. It is presented to the staff and consumers and the feedback that is received is presented to the management and steering committee for analysis. The final process of this stage involves a series of analyses such as financial analysis, risk analysis and feasibility tests. Once these processes have been completed, the management or steering committee then decide on whether the product should pass this gate to the next stage or not.
Development of the product is the next step. With the help of the research and design team, building of the final product commences at this stage. To ensure that this process is effective and efficient, the SMART concept is utilized. This ensures that the project is simple, measurable, attainable, realistic and should be completed within a specific time frame (Black, 2007). Testing and validation form the next stage of the product development process.
This process is also referred to as beta testing (Stone, 2008). Here, the product itself, its manufacturing process, consumer reaction and the financial feasibility of the project are tested. However, testing is conducted on different levels. The first level of testing is referred to as near testing that specifically tries to identify any problems or imperfections that may be present in the product. Field-testing is the next level of testing. Here, a relatively larger audience is used to test the product.
Finally, market testing is conducted. This is usually the last stage in the validating and testing process. Here, the product is made available to a specific segment of the market. At this stage, all the aspects of producing, marketing, and distributing the product are put into place.
The manner in which the test market shall respond to the product is essential as it determines the decision that the steering committee or the management shall come up with regarding its launch and commercialization. Once the project has been approved, it is launched into the market. The manner in which the product is launched into the market is essential as it will determine the entry strategy that it will utilize and the attitude and perceptions that consumers will have towards it.
Therefore, the firm must have a clear understanding of the market especially in terms of the demand and supply of the product in the market. This is essential, as it will determine the quantity of the product that will be produced at any given time.
At the same time, the management needs to come up with an effective pricing strategy that will ensure that the product is not underpriced or overpriced to maintain a desirable price level. In addition, the management should come up with an effective marketing strategy that is backed up by experienced sales personnel.
Iterative Nature of Product Development Plans
Product development plans are usually iterative in nature. This is due to the fact that in the process of developing a product, it is essential to ensure that it fits the description of the firm. Most importantly, the product should also meet the needs of the consumers in the market (Schein, 2008).
Therefore, in the process of developing a product, it is impossible to meet all these requirements after producing the first prototype. Usually, once the first prototype is launched, several issues are identified. This includes omission an inclusion of specific features that customers advocate for. At the same time, the design or purpose of the product does not fit to its description or it does not tally with the goals and objectives of the company.
In some instances, a newer and more effective technology may be realized after a prototype has been made. It is after such considerations that make it necessary to revise the manufacturing plans of the prototypes with an aim of modifying them to meet these new requirements (Schein, 2008).
A prototype may pass through several modification processes before reaching a sustainable level. It is with the appreciation of these factors that make the product development process to be iterative in nature. Below is a diagram that shows the iterative nature of product development process of Scrum softwares (Schein, 2008).
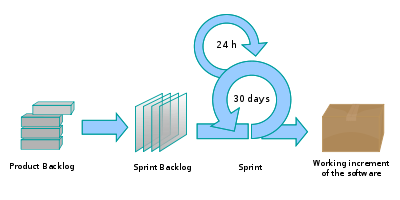
After having a careful look at the diagram, one can notice that the print process is repetitive within every 24 hours for 30 days. It is in this stage that softwares are essentially tested to ensure that they are effective and efficient in operation and that they meet the requirements of users.
Attributes of a Good Product Development Model
For a product development process to be effective in its operations, it needs to possess a number of key attributes. A good product development model must have a platform in which ideas can be generated. It is from these ideas that the final product that will be released into the market shall be generated from.
Therefore, an effective model should use a variety of methods to incorporate ideas from a wide range of sources (Belbin, 2010). This includes the top executives, mid and low level employees, distributors and mainly the customers in the market. Development of desirable ideas is essential as it plays a critical role in ensuring that the final product meets the customers expectations and is in line with the mission, vision, goals, and objective of the manufacturing company.
Once ideas have been generated, an effective product development model should have a developmental phase. It is in this phase that these ideas are presented to a focus group in order for the manufacturing company to gather information with regards to their attitudes and perceptions of the products.
It is essential that product development models incorporate this attribute as it provides critical information with regards to the features of products (which by this moment should be presented as a prototype), which should be incorporated and those that should be eliminated. This is a key step towards producing the final product.
Essentially, a good product development model should also have a testing phase where several constrains of the product are tested using a segment of the target market as a focus group.
By this time, the product should be in its final stages of development. The factors that are to be tested here includes the reaction of the market to the product, its price levels, production and distribution costs, financial feasibility, demand and supply and so on. Once all this information has been gathered, the product can be launched successfully into the market under close monitoring.
A good product development model should also be iterative in nature. This will ensure that the final product that is developed has undergone a series of tests to meet the needs and desires of the target market and the company. At the same time, the model should also allow for information to flow in all direction from the management, employees of all levels and to other third parties such as customers and distributors that are involved in the program.
This will ensure that the final product contains the attributes that satisfy the needs of the target market and the company. This is essential as it ensures that the product reports desirable sales figures and is profitable both in the short run and in the long run. This is essential to build the brand name and image of the company as well as ensuring that it stands at a competitive edge over its rivals.
Importance of Information Flow in a PDP
In the course of their operations, firms normally operate to gain a competitive edge over their rivals and to be sustainable and profitable both in the short run and in the long run. To achieve this, firms usually come up with new products that aim at capturing the attention of the consumers within the market to boost their sales and improve on their brand names. However, to achieve this status, it is essential for the whole process to be based to a program that supports information flow in all directions.
The aim of developing a new product is to satisfy the needs to consumers in the market (Belbin, 2010). At the same time, the new product needs to portray the image of the manufacturing company. Therefore, to get information from the target market with regards to their tastes, preferences, attitudes and perceptions of the product, it is essential for the product development program to have a framework that supports and incorporates information from the public.
At the same time, the same program should come up with means through which information from within the organization, with regards to the program, is analyzed. The figure below can be used to show how information flows in a program development process (Belbin, 2010).
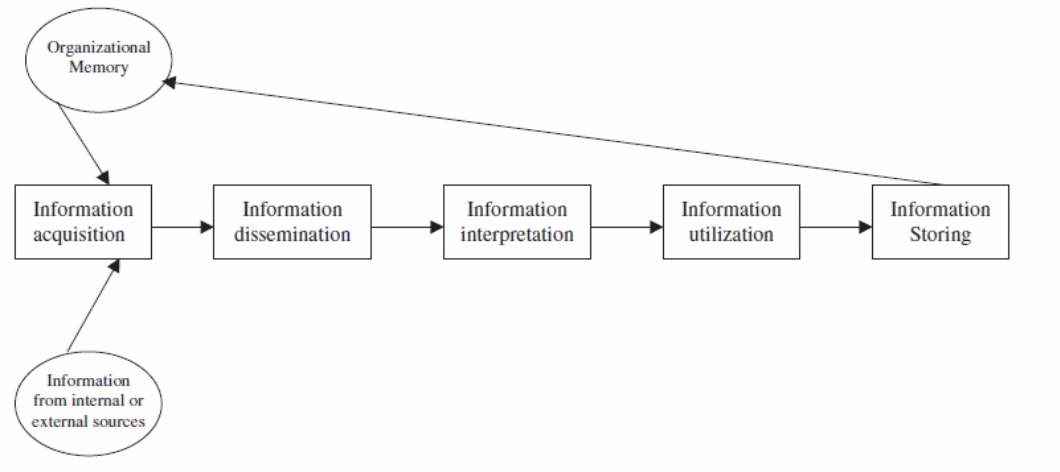
Firms usually have a lot of information and experiences in the course of their operations. This information forms the organization memory and is usually stored and retrieved whenever necessary. At the same time, a firm uses information from other sources in the course of information acquisition while developing a new product. This information is disseminated, interpreted, and utilized to form the new product. Once the process is complete and the product has been launched, the information is stored for future use.
It is also important to note that the product development process is iterative in nature. Therefore, information flow is essential to support this concept to ensure that the final product that is arrived at meets both the needs of the customers and the company as well. Thus, a good PDP must have definite feedback loops while testing the product before launching it.
Essentially, communication with regards to the changes in features and design of the product to other employees is also essential is it avoids repetition of work and ensures that everyone is aware of the status of the product in its development process. Thus, information flow is essential to design an effective and efficient product.
Management Structure and Information Flow
Companies incorporate a management structure that best suits their operations to ensure that they are sustainable in the short run and in the long run. According to Sign (2009), managerial structures can be divided into:
- Centralized managerial structures
- Decentralized managerial structures
In centralized managerial structure, all the power of the organization is concentrated on the top managerial levels. Due to the amount of power they have, the top management level exercises tight control over the affair of all the divisions or the departments that constitute the organization. On the other hand, power in decentralized Managerial structure is distributed among all the departments or divisions of the organization who work in unity to achieve the goals and objectives of the firm.
Therefore, in centralized managerial structure, information only flows in one direction; from the top managerial level to the other lower levels. Due to this fact, information is always highly distorted before reaching the lower levels. At the same time, information cannot be passed from lower levels up to the management.
Therefore, while designing a product, the views and ideas of other individuals will not be considered. As a result, the overall outcome of the new product will not be efficient, as it was not based on vast ideas from individuals within and outside of the organization. This greatly reduces the chances of the product being successful once it has been launched.
In a decentralized system, information flows in all directions. This ensures that information is still intact while moving from one level to the next in the company. Therefore, individuals of all levels of the company are included while developing the new product. At the same time, information from outside sources such as customers and distributors is always utilized in the program.
Thus, the final product will portray the views of the company and its target market. This is essential, as it will increase the chances of the product entering successfully into the market, being profitable and sustainable in the short run and in the long run. The figure below shows a comparison of traditional product development methods and concurrent engineering (Belbin, 2010).
Importance of Market Research in a PDP
“
Before a product is launched into the market, the management of the organization must conduct an intensive market research to ensure that all factors of the market have been considered. This is essential as it will provide a clear understanding of the size of the market, its segmentation, and the taste and preferences of the consumers found in the different segments (Jugger, 2011). Additionally, market research also provides information with regards to the market trends.
This includes consumers purchasing power, quantity and frequency. This information is essential in determining the demand and supply of the market as well as setting up the price of the commodity. After conducting a market research, the management will be able to come up with the most cost effective supply chain that will ensure that the product reaches to each and every targeted customer.
At the same time, the company will be able to come up with effective marketing strategies that will boost the sales of the product, improve its brand name, and ensure that it is sustainable in the short run and in the long run.
Concurrent Engineering
Concurrent engineering is a relatively new style of product development. Unlike the traditional product development models that took a lot of time to come up with decisions and designs that pertain a product, concurrent engineering is parallel and incorporates all aspects that are required in the development of a product during the initial stages (Jugger, 2011).
The iterative nature of concurrent engineering ensures that all factors that may affect the production of the new product are looked focused upon during the early stages of development to ensure that the product fits the description of its purpose.
Concurrent engineering is an essential tool especially in companies that operate at the present day and time where the business environment changes rapidly. This methodology ensures that such companies come up with quick, effective, and responsive solutions to the problems that they may face in the course of their operations.
Advantages of CE in PDPs
Concurrent engineering is a new method used in the product development process. Concurrent engineering guarantees that a company will stand at a competitive edge over its rivals in the same industry (Sign, 2009). This is because the method can be used in small and large companies. Using this method guarantees cost efficiency while producing new products. At the same time, it ensures that the product is effective and perfectly fits its description.
Despite the fact that incorporating concurrent engineering may be capital intensive, the method will become beneficial in the long run operations of a company. Concurrent engineering also increases the operation efficiency of a company. This is because it reduces the cost of production, increases the quality of the product, enhances the production cycle, and ensures timely delivery of products. Any problems that may be associated with the product are identified during the early phases of development and corrective measures are taken.
This method also reduces the time taken in design and development. This is because if offers effective communication between the firm and customers hence being able to produce a product that meets their needs and expectations. Thus, companies that use this method are able to produce high quality products at lower costs within a definite time, which are able to meet the needs and expectations of their target market.
Generic Requirements for the Implementation of Concurrent Engineering
For concurrent engineering to be effective and efficient, it needs to follow the SMART concept (Sign, 2009). Here, the proposed project needs to be simple in terms of its features and appearance. In addition, the project has to be measurable. This is essential as it determines the level of progress of the project.
The project also needs to be attainable. This will ensure that the company is able to achieve its set goals and objectives once the new product is launched. The proposed product also needs to be realistic. It should fit the needs and expectation of the target market as well as those of the manufacturing company.
Finally, the product should be developed within a specified time period. This is essential in terms of planning, setting budgets, controlling expenditure, and delivering the final product into the market at a specific time. If considered, these issues will be essential in ensuring the success of a concurrent engineering process being successful.
It is also essential to ensure that concurrent engineering is iterative in nature. This is essential as it guarantees that the final product that is released into the market meets the needs and expectations of the target market as well as that of the manufacturing company and other stakeholders.
To achieve this, problems that may be associated with the product during its developmental stages should be identified and solved during its early stages of development. This will ensure that the product fits its description and is manufactured within the shortest time possible undertaking minimal costs.
The project should also be carried out in a systemic manner. It is the nature of concurrent engineering to conduct processes in a parallel manner. This sequential flow of process should incorporate all the members of the product development team. This therefore makes it essential to ensure that teamwork exists among individuals, departments and on special cases, among organizations.
This ensures that the product is developed in the most effective manner thus enabling it to fit its description. This will sustain the success of the product in the short run and in the long run. Once all these considerations are put in place, concurrent engineering always surpasses traditional product development models.
References
Aaker, M 2012, Product Development: Methods and Practices, Sage, London.
Belbin, A 2010, Consumer Approaches in the 21st Century, Prenstile Hall, New York.
Black, D 2007, ‘Strategic Practices’, Journal of Consumer Behaviour, vol. 1 no. 2, pp. 12-30.
Eagan, C 2010, Information Gathering and Processing, Sage, London.
Jugger, M 2011, ‘Field Operations and Product Development’, Business World, vol. 1 no. 2, pp. 55-71.
Kotler, D 2007, Product Development Models and Structures, Thousand Oaks, Boston.
Schein, S 2008, Organization Management, Longhorn, Chicago.
Sign, P 2009, Consumer Practices, A&A, New Delhi.
Stone, G 2008, Market Analisis: An Organizational Approach, Sage, London.
Thomas, T 2009, New Product Development Approaches, Oxford University Press, Oxford.