Introduction
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are underpinned by the achievement of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), and the SDGs aim at continuing efforts to end poverty in all its forms. They affirm that poverty eradication must be inextricably linked to strategies that stimulate economic growth and address social needs, such as education, health, social protection, and employment opportunities. This also means addressing the challenges of climate change and ensuring environmental protection. Some targets are of prime importance for developing countries – for example, targets 1, 8, and 13.
SDG Goals for Consideration
Goal 1 – End poverty in all its forms everywhere
Goal 8 – Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all
Goal 13. Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
SDGs achievement in Morocco
Morocco has made a number of efforts in recent years to achieve some of the sustainable development goals but still there are a lot of issues and challenges. For SDG1, the dynamics of three indicators is presented below:
Proportion of population below the international poverty line (Fig. 1):
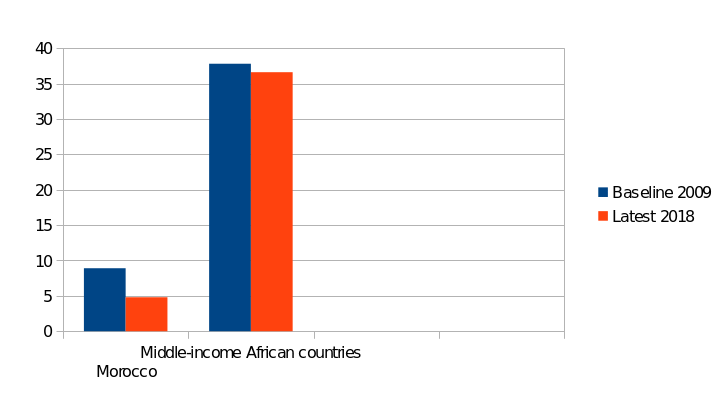
Resources allocated by the government directly to poverty reduction programs (Fig. 2).
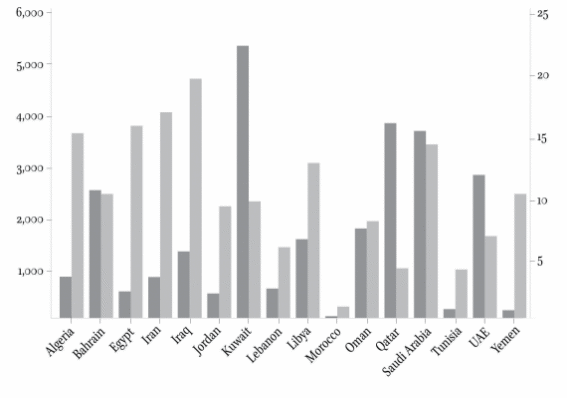
Social spendings and their implications.
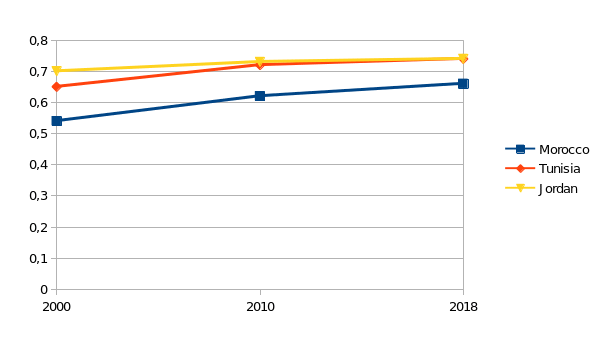
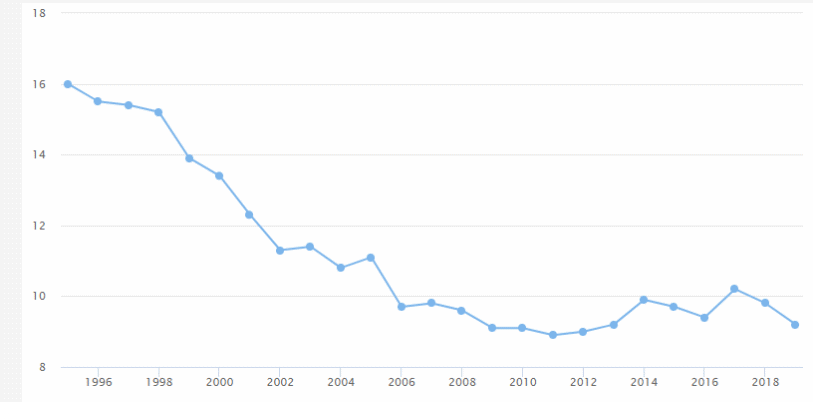
With regard to the SDG8, it should be noted that the unemployment rate in Morocco, having fallen to 9.2 percent in 2019 (down 6.12 percent compared to 2018), could rise to 15 percent this year (Jettou et al. 11). However, this phenomenon is associated with the current coronavirus pandemic. Moreover, it has nothing to do with the overall relative downward trend in unemployment in the country over the past decade (see Figure 4).
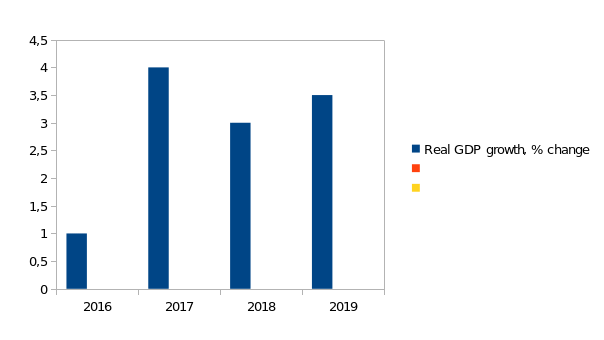
Annual growth rate of real GDP per is presented on Figure 5.
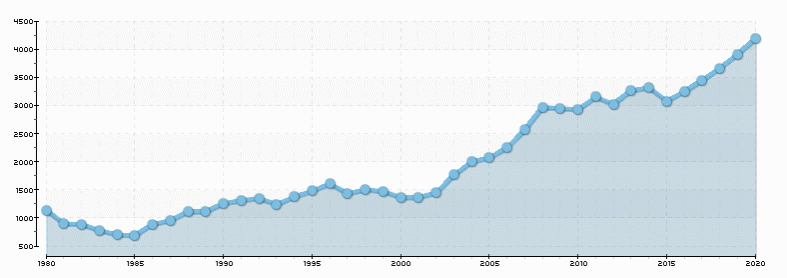
The real GDP growth is presented on Fig. 6.
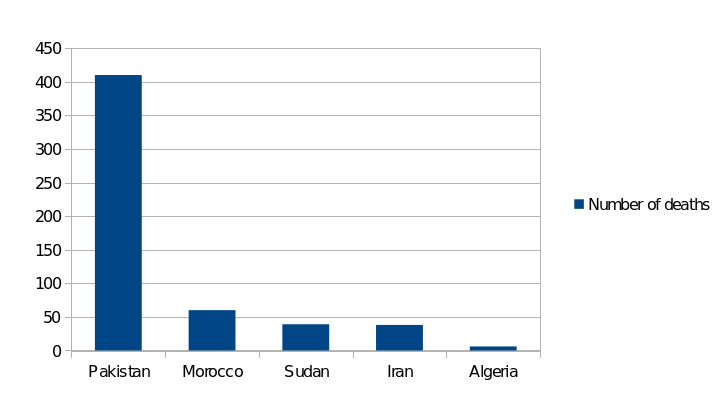
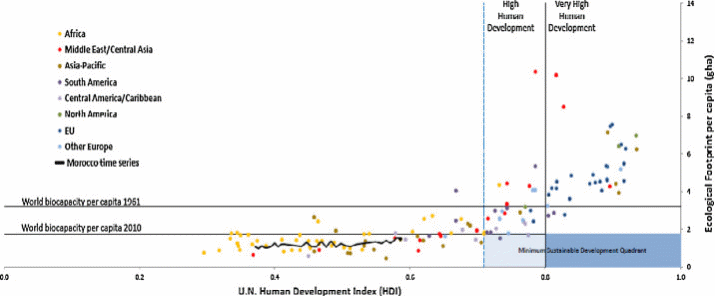
As to the SDG13, below, three indicators of its achievements are presented (Figures 7-9).
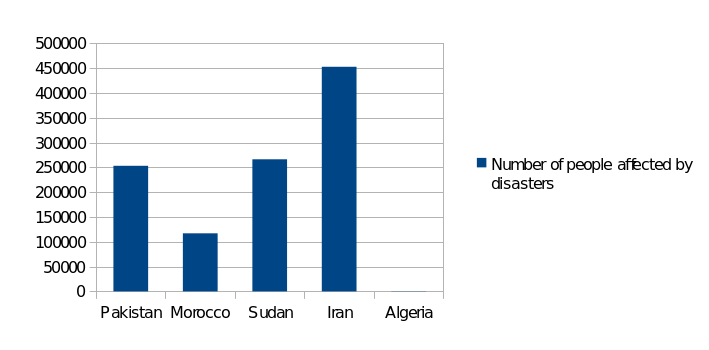
Finally, on Fig. 9, built with the help of specialized software, there is a depiction indicating the tendency of the countries with the highest HDI to have higher per capita ecological footprints.
Works Cited
Jettou, Driss, et al. “Morocco’s Preparedness for the Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals 2015-2030.” Kingdom of Morocco Court of Accounts, 2019, Web.
“Morocco’s New 2020 Budget Puts Social Services at Core of Priorities – Minister.” The North Africa Post, Web.
Sarr, Babacar, et al. “The Macroeconomic Effects of Labor and Product Market Reforms in Morocco.” IMF Working Papers, 2019. Web.
UN. “The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2019.” Web.