Name of the Project: New Haripur
Name of the Country: The People’s Republic of Bangladesh
Technical Brief
Gas Turbine: M701F
Mass Flow : 683 kg/s
Temperature: 585 °C
Design Temp.: 620 °C
Pressure Drop: < 500 Pa
Acoustic Requirement
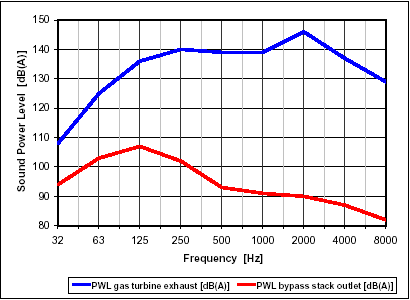
Sound Power Level PWL: 110 dB(A) at Stack Outlet

Description
In the present socio-political condition of Bangladesh, as she is one of the third world countries, a power project like Haripur, participated and partially funded by her private sector is a shining example of success. It was a challenge for the project planner to attain the objectives. Naturally, the socio-economic status of the people determined the principal features of the projects. In this situation, the discovery of the Haripur gas field fueled the hope of the maximum utilization of the gas resource.
But to attain the goal was somewhat to meet both ends. Mainly the socio-economic condition of the people and the pressure from the naturalists’ organization determined its objectives. It was the gas resource of the Haripur gas field, that was to be used as fuel. The amount of carbon dioxide produced from this power project was a constant threat to the green environment existing here. Again the socio-economic condition of the country confronted the foreign entrepreneurs. Consequently for a surety investment from the private sector was necessary.
In Bangladesh, the Haripur Power Project and the Private Sector Infrastructure Development Project have helped finance the 360MW Haripur and the 450 MW Meghnaghat power plants.’
The plant preserves 20 percent of the installed capacity of Bangladesh and, because of the high efficiency about 30 percent of the total energy produced in Bangladesh. It is one of the best operating power plants in Bangladesh. It has the lowest unit cost among all the power producers in the country and is still among the cheapest.
The plant has Bangladesh’s most energy-efficient and gas-fired and combined-cycle technology in the country.
It has an outstanding environmental and safety record since its start-up.’
Principal Objectives
- To produce 360 MW.
- To devise an environment-friendly technology.
- To maintain a low-cost unit.
- To utilize the maximum of the gas resource.
- To sustain under the socio-political condition.
- To assure the foreign stakeholders of their benefit.
- To maintain the lowest possible set-up cost.
- To provide electricity for the people of the area at a cheaper rate
- To remove acute shortages in the power supply.
- To provide a more reliable power supply to agriculture and industry of the country (ADB, 2002).
Constraints
The entrepreneurs had to confront the poor cost-bearing capability of the country’s people. It was needed to maintain the lowest cost unit of energy. But the expected profit of the stakeholders was to be taken into concern. Again the pressure of the environmental groups of the country was one of the main constraints. So it was necessary to ensure the minimum damage to the environment. As Bangladesh is one of the third-world countries, there were some technological constraints in the country. The lack of expert technical hand was acute. So manpower was to be exported from abroad.
Stakeholder Management
- A US$140 million fund was approved by Manilla, Philippines(5 December 2000)- the Asian Development Bank (ADB) to construct the Haripur power plant at Haripur, Noakhali in the southeast Dhaka, Bangladesh. ‘This is the first power project in Bangladesh, that was supported by the private sector. The Project Sector Group (PSG) of the ADB prepared the project.’ (ADB, 5 December 2000).
- It is the first competitively bid and privately-funded power project in the country and will be used as a model for other projects, particularly in the way it was selected and documented.’ (Bangladesh Power Project a Model for Private Sector) The participation of ADB’s plays the role of a comforter factor to the participation of the commercial banks and the Project Sponsor. It was a part of ADB’s plan to support the Government’s attempts to increase the investment of the private sector (ADB, 5 December 2000).
Risk management of the project
The ADB provides a fund of US$50 million and a US$70 million loan is provided by the commercial banks. This providence is made under the ADB’s partial risk guarantee (PRG) scheme. Also, the fund is supported by a loan package from commercial banks that is about US$20 million. The supply is under the ADB’s complementary financing scheme. “AES Corporation will provide equity of US$80 million and the Infrastructure Development Company Limited (IDOCOL) will provide additional financing of US$80 million to complete the total project cost of US$300 million” (ADB, 5 December 2000).
Statement of Work
Name of the Project
- Country: The People’s Republic of Bangladesh
- Project: Haripur Power Plant Development Project (Loan Agreement: December 11, 2007; Loan Amount: 17,767 million yen; Borrower: The Government of People’s Republic of Bangladesh)
Necessity and Relevance of JBIC’s Assistance
To bridge the gulf between the supply and demand of electricity for sustainable economic growth is one of the leading necessities. The present power generation of the country is about 3,700 MW. It falls short of the peak-hour claim of around 4,600 MW (as of 2005). This situation forces the government to carry out a newer plan.
To eliminate the supply and demand gulf, and thereby stabilize the supply of electric power, the posing challenge is to promote the efficiency of the power sector of the country by increasing the efficiency of power plants and by lessening the system loss of electricity. The challenge is to create a fruitful operation and maintenance system and to fix reasonable power rates and at the same time to secure funds.
Policies of the power sector in Bangladesh and the position of this project.
In its Vision Statement on Power Sector Reforms (2000), the government of Bangladesh attempts to procure the national goal of “providing access to affordable and reliable electricity to all by the year 2020.”
In order to procure it the government of Bangladesh attempts of drawing investments.
Project Objectives
The objective is to face the increasing demand for electricity. The goal is to be implemented by constructing a power plant in Haripur of Narayanganj District, in the outskirts of Dhaka, to provide Bangladesh with scopes to compete in the industrial sector and to improve the livelihood of the common people.
Project Description
- Target Area
- Haripur, Narayanganj District
- Project guideline
- Construction of a gas turbine power plant
- Engineering and consultation services
- Detailed design,
- Bidding assistance,
- Construction monitoring
- Supervision
- Total Project Cost
- 54 million dollars (estimated)
- Schedule
- October 2000–September 2007. The definition of project completion is “when Long Terms Service Agreement is completed.”
- Implementation Structure

Environmental and Social Consideration
Finding out :
- Environmental impact and
- Land Acquisition and Resident Relocation
The extension of this project falls into the category of a thermal power sector project which has an adverse effect on the environment under the “Japan Bank for International Cooperation Guidelines for Confirmation of Environmental and Social Considerations” (established in April 2002).
Measures for preventing pollution
This project has to face the environmental standards of Bangladesh by adopting various steps regarding air contamination, water contamination, and noise pollution. It also includes the installation of a safe exhaust system, wastewater treatment facilities, and noise absorbing system.
Social Environment
This project is going to be located in a residential area. So it needs resident relocation.
Monitoring
The executing agency engaged by the project authority will monitor the air quality, water quality, noise, etc.
Strategic project plan
The strategic project plan of Haripur can be divided into three phases.
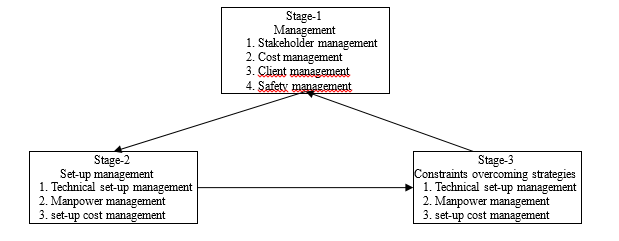
All three phases needed to be implemented concurrently. The first phase included the strategies of managing the safety, the stakeholder, the clients, etc. The second phase included strategies of the main body set-up of the project. This phase included estimation and implementation of the main features of the project. Then the third phase included the strategies to overcome the constraints of the project.
The chairman of the project was responsible to manage the power business for Bangladesh. The business currently consisted of 2 Combined Cycle power plants with a capacity of 920MW. It represented 30% of the installed capacity of Bangladesh, with combined annual gross revenues of $158MM, EBITDA of $69.9MM and NOPAT of $16.6MM and a total staff of fewer than 200 people.’ (Source: Resume of J. Edward Barndt)
The chairman is the Chief Executive of the plants. He is responsible for all P&L, O&M and Asset Management, including all Commercial and Legal aspects of these businesses.’ (Source: Resume of J. Edward Barndt) The chairman had to build a Safety and Environmental management culture at these facilities’. He had played a crucial role in the sale of the power starting in Dec. 2006 with closing targeted in late Sept. 2007.’
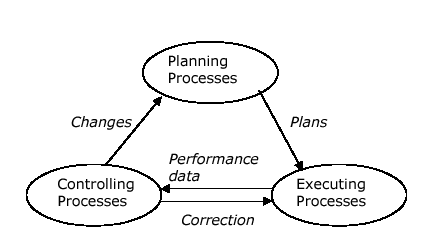
(The underlying theory of project management is obsolete1)
Cost of management
Effective project management must include the effective management of all four of the following: (i) Stakeholder management, (ii) Cost management, (iii) Safety management, (iv) Quality management). Cost management is a crucial one. The success of a project depends on its cost management. The cost management of the 400/132kV substation in NAD AL SHIBA is mentioned below.
- Name of the Project
- Country: Abu Dhabi
- Project: NAD AL SHIBA Substation, Dubai
- Energy: 400/132 kV
- Owner: The DUBAI electricity and water authority
- Main contractor: MITSUBISHI Electric Corporation
- Sub-contractor: ACTCO general contracting company
- Project Objectives
- To meet the growing electricity demand is a necessity. The expansion of new trade and commerce all over this area has forced the authority to establish a new substation.
- Project Description
- Target Area
- NAD AL SHIBA, Dubai
- Project guideline
- Construction of a gas turbine power plant
- Engineering and consultation services
- Detailed design,
- Bidding assistance,
- Construction monitoring
- Target Area
- Supervision
- Total Project Cost
- 159 million dollars (estimated in the context of Haripur power plant)
- Schedule
- October 2008 to 2020. The definition of project completion is “when Long Terms Service Agreement is completed.”
- Total Project Cost
- Implementation Structure (same as Haripur)

Environmental and Social Consideration findings
- Environmental impact and
- Measures for preventing pollution
This project has to face the environmental standards of Abu Dhabi by adopting various steps regarding air contamination, water contamination, and noise pollution. It also includes the installation of a safe exhaust system, wastewater treatment facilities, and noise absorbing system.
Monitoring
Like the Haripur project, the executing agency engaged by the project authority will monitor the air quality, water quality, noise, etc.
Strategic project plan
The strategic project plan of NAD AL SHIBA Substation, Dubai can be divided into five phases.
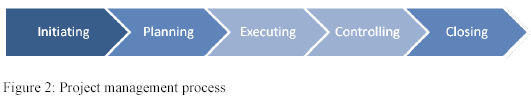
(The underlying theory of project management is obsolete 1)
All five phases include initiating, planning, executing, controlling, and closing. Limitations of flow charts can be overcome by analyzing the constraints in the execution. The critical path analysis in dealing with activity is dependent on the theoretical diagram. The first phase includes the strategies of managing the safety, the stakeholder, the clients, etc. The second phase included strategies of the overall plan of the project. Indeed this phase includes also the successful cost management of the project. The following is a diagram of the construction management of a project:
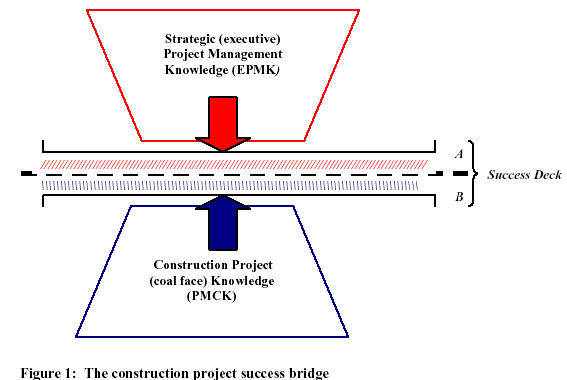
This phase included estimation and implementation costs of the main features of the project. In project management, two types of costing methodologies can be followed. Both the fixed time-oriented costing methodology and the activity-based costing methodology are effective but according to the environment of the work, both methodologies can be adopted.
“Activity-based costing is a costing methodology where costs are allocated to products and services based on the number of transactions or events involved in the process of providing the product or service” (Small Business Encyclopedia, 2005).
Cost management in project accounting is different from standard accounting. The cost management of a project is designed to survey the financial progress of a project. But the standard accounting is to survey the overall progress of an organization. The duration of Projects can be few days or a number of years. Financial reports in Project Accounting are special to track the project process. Project Managers are able to assess and survey the project budgets accurately utilizing cost management. Also, he is able to “ensure that the project is proceeding on budget. Project managers can quickly address any cost overruns and revise budgets if necessary” (Audit and Evaluation Directorate, October 2007 and Tenrox, 2008).
Costs that are allocated to any project may be divided into a work breakdown structure (WBS). “In utilizing project accounting, you have the flexibility to report at any such level and can also compare historical as well as current budgets” (Audit and Evaluation Directorate, October 2007 and Tenrox, 2008).
References
ADB (2000). Bangladesh Power Project a Model for Private Sector. Web.
ADB (Asian Development Bank). (2002). Web.
Audit and Evaluation Directorate (2007). Project Management Processes and Practices. Audit report. Web.
Rwelamila, P M D. (2007). CONSTRUCTION PROJECT MANAGEMENT EDUCATION PROGRAMMES IN SOUTH AFRICA – ADDRESSING THE GAP. Second International Conference World of Construction Project Management. Web.
Small Business Encyclopedia (2005). Activity-Based Costing. Barron Series. Web.
Tenrox (2008). Project Accounting. Web.