Background Theory
The success of a project depends on balancing all resources available in order to achieve the target goal. In this context, the main focus is on an efficient schedule, on the work of high-qualified team members, on the balanced distribution of tasks appropriate for team members and their competence levels, and on the effective manipulation of the available budget to complete the project tasks within the set deadline (Gido & Clements 2014, p. 18; Meredith & Mantel 2011). In addition, according to the project management theory, the project will be successful only in those cases when a project leader pays much attention to communicating with the team members (Reiss 2013).
Following Burke (2013), the keys leading to successful project completion are the constant monitoring of a schedule and budget, the prediction of possible risks, and the guarantee of effective teamwork. In this context, a good project manager needs to correlate the project schedule and a budget and refer to the team’s productivity (Burke 2013, p. 21). According to Kerzner, to organize an efficient schedule, it is necessary to set adequate tasks for clearly stated time periods and refer to possible risks (Kerzner 2013, p. 54). To guarantee the focus on the available budget, it is possible to outsource the work and save costs associated with inviting a low number of best-qualified employees (Heagney 2012; Reiss 2013). Still, the team’s productivity is the key to project success, and much attention should be paid to supporting team members and their activities.
The Best Score
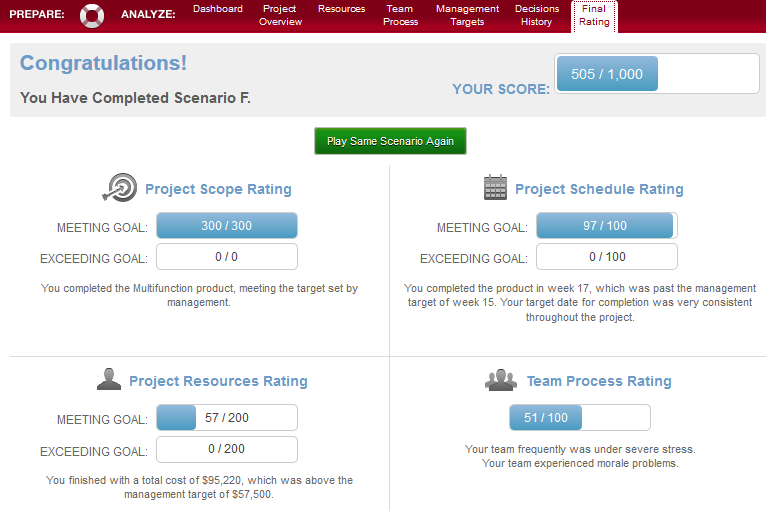
The best score for completing the simulation task is 505 out of 1,000 (Figure 1). The best outcomes associated with this result are the completion of the multifunctional product ordered by the management team and the focus on the project schedule. The product was released in week 17 of the project, and the delay was only two weeks. These outcomes became the results of the strategy chosen during the first weeks of the project. First, it was necessary to guarantee that the team working on the project is high-qualified. Five employees were selected to perform tasks, and their average skill level was medium-high.
This approach guaranteed the high-performance level and the lowest level of errors. Outsourcing for performing support tasks was also chosen as an approach to reduce costs and to provide high-qualified team members with more opportunities to perform their primary duties. The work of teams was supported by the regular communication sessions with the help of daily standups and regular status reviews.
Furthermore, much attention was paid to the construction of prototypes in order to predict possible problems in the product at different stages of its development. The testing of prototypes every three weeks (weeks 4, 8, 12) was selected as the best strategy to achieve high results in developing the advanced multifunction printer. Problems observed at weeks 5, 8, and 12, which were associated with technical problems, the car accident, and the increased competition affected the development of the project significantly. These problems were addressed by increasing the number of invited staff, and these techniques led to significant increases in the project costs that became higher than the available budget.
Self-Reflection
The result demonstrated after the completion of the simulation is rather low, and it can be improved with the focus on identified challenges determined during the completion of the project. Six runs were completed before achieving the result in 505 points. A new strategy proposed according to project management theories was applied to the simulation each time, and relevant conclusions were made. Thus, I have succeeded in overcoming such problems as inabilities to address the project schedule and to complete the multifunction product based on advanced technology.
However, focusing on completing the project within the best possible timeframe and with the focus on the new technologies, and made inadequate decisions regarding the distribution of tasks among the team members and achieved the overbudget that is inappropriate in a situation of funding the project by the management team. In spite of the fact that the overbudget was expected because the schedule was extended to two weeks, the total costs were exceeded by two times.
Having analyzed the issue, it is possible to state that the problem was in my attempts to cover extra tasks with the focus on exceeding the number of high-qualified team members, and the team could complete the planned tasks only with a focus on using more human resources because of high levels of stress and low productivity. This approach was rather ineffective because such risky decisions result in significant increases in costs. As a result, the level of team satisfaction decreased significantly, and all available hours were spent completing tasks within the planned timeframe other than communicating on the project problems. The consequence of such a weak strategy was the lack of understanding of the situation and the constantly increasing stress level.
During previous simulation runs, I paid much attention to increasing the productivity of the team and focused on communication and coordination work, but I failed to correlate the work of the team and its positive moods with the schedule. The levels of the work stress were low, but productivity was also average, and overtime was not allowed. As a result, I could not address risky situations and unpredicted problems.
At the current stage, I can analyze the aspects of the project management theory with references to my successes and failures in completing the simulation. I should state that to improve my results in the future and to apply the theoretical concepts and strategies not only in part but also completely and effectively; I need to focus more on the relationship between team productivity and communication with the team members. Thus, the productivity of the average number of employees with the medium skill level can be higher than the productivity of the low number of high-skilled employees, but such a strategy is also a cost-saving one.
In addition, much attention should be paid to risk management strategies applied to projects. The simulation demonstrates that there are many unpredictable risks associated with the project completion, and they can be addressed efficiently when the budget is planned and organized properly to address the needs for each week and save costs for responding to risky situations and identified problems.
Assessment of the Simulation
The proposed simulation is effective in demonstrating the basic factors that can influence the decision-making process during project completion. The opportunity to run the simulation several times to achieve better results also allows testing different strategies, techniques, and tools proposed within the context of the project management theory and practices. In addition, the simulation is appropriate to demonstrate how different decisions depend on each other and what factors can influence the effectiveness of the selected strategy or tactic significantly, leading to negative results and unpredicted outcomes. Thus, the simulation represents only the basic steps of the real-life product development process.
Errors in the simulation can be more properly addressed during the real-life process of the new product development because a project leader is able to monitor the project progress consistently and respond to possible challenges in a timely manner. As a result, the selected strategy can demonstrate its inappropriateness during the first days of a new week, and the task of a project leader is to address these problems and challenges immediately. In addition, the development of the new advanced product is influenced by more factors in real life, and the overall decision-making strategy can become more complex. The problem is in the fact that the simulation provided the opportunity to change costs per week only with references to managing human resources, when other factors are also influential, and they are usually reflected in typical project management plans and schedules (Gido & Clements 2014).
Focusing on the necessity of managing a real project, I would use the strategies that are different from those ones used in the simulation. However, the simulation is helpful for me to understand how communication with the team members can influence the productivity and the timeframes associated with the project completion. Moreover, the simulation is important to demonstrate what factors, including risks, need to be taken into account while planning the budget for the project.
Reference List
Burke, R 2013, Project management: planning and control techniques, Routledge, New York. Web.
Gido, J & Clements, J 2014, Successful project management, Cengage Learning, New York. Web.
Heagney, J 2012, Fundamentals of project management, American Management Association, New York. Web.
Kerzner, HR 2013, Project management: a systems approach to planning, scheduling, and controlling, John Wiley & Sons, New York. Web.
Meredith, JR & Mantel, SJ 2011, Project management: a managerial approach, John Wiley & Sons, New York. Web.
Reiss, G 2013, Project management demystified: today’s tools and techniques, Routledge, New York. Web.