Executive Summary
The presented report describes the business activities of Prudential plc, the British insurance company that provides international services, focusing on the Asian market as a promising segment. As the topics raised, external influences are considered, as well as the field of ethics and corporate social responsibility, including their role and impact on the company’s activities. Economic, social, legal, political, technological and competitive impacts are evaluated in the context of their effect on the work of Prudential plc. The current political challenges caused by the UK’s controversial position regarding membership in the EU affect the corporation’s activities negatively, making it difficult to establish partnerships in certain regions. Legal factors are also highly significant due to the specifics of providing insurance services in specific areas.
The organisation has been operating in the market for a long time; nevertheless, overcoming a competitive barrier is a crucial aspect of work. The field of ethics and corporate social responsibility is well developed in Prudential plc. The most important activities in this direction are youth support, contributions to non-profit organisations and investments in infrastructure. All legislative conventions are observed, but there are difficulties in establishing interaction between private and state control boards. Improvements in CSR competition can help expand the organisation’s scope of influence and raise its authority among the target audience.
Introduction
Modern financial organisations that provide services to a wide range of clients monitor various aspects affecting the functioning of their entire complex structures. Some factors, for instance, political, legal, social, competitive and other influences, largely determine activity principles and serve as incentives for relevant changes and innovations not only in the context of external but also internal transformations. As an object of analysis, this report suggests considering the work of Prudential plc, the British financial organisation providing insurance services in many countries and occupying a high position in this market. The specifics of the company’s activities imply adapting to the working conditions in such an industry and analysing a number of conventions and factors effecting on the success of work and customer recognition. To begin with, a number of external influences will be considered, including their implications and importance for Prudential plc. Further, the topics of ethics and corporate social responsibility will be addressed, and the company will be evaluated in the context of these areas. The abilities to adapt to external influences and follow modern working standards makes Prudential plc an organisation with a good reputation and high-quality services.
Company Profile
Prudential plc is one of the oldest UK insurance companies. The organisation that initially provided services to the middle class in giving financial loans was founded in 1848 in London, and subsequently, it was transformed into a transnational corporation (Timeline, 2019). Today, the company interacts with many financial centres, focusing on the Asian market as the most promising sector. In 2010, the organisation signed an agreement to provide insurance services in Indonesia, Thailand and Singapore, thereby expanding its influence (Timeline, 2019). Under the auspices of Prudential plc, a new brand appeared – Eastspring Investments, and new regions began to be developed, in particular, the African insurance segment as a profitable area (Timeline, 2019). In the American market, the company occupies a high position and is one of the recognised leaders in its industry. In addition, Prudential plc is involved in charitable activities and implements CSR programmes by investing in socially significant projects.
Overview of the Primary External Influences (PEST C)
Defining the External Environment
An external environment encompasses a broad range of conditions and factors that take place outside organizations but can influence them to a certain degree. In the business context, the term applies to the elements that are out of organizational control and include societal, economic, regulatory, and political affairs. Understanding the influence of the external environment on the business process within financial organizations is important because any changes, from new governmental decisions to competitor strategies or shifts in socio-economic environments, can impact the way in which companies should provide their services.
The success of financial organisations’ work depends on how effectively the leaders of such companies monitor current trends in the industry and how quickly they respond to relevant changes. However, according to Mole, North and Baldock (2017), there are a number of external factors that determine specific achievements or, conversely, failures in the operational activities of firms. The authors note that challenges and problems often arise due to the fact that leaders of organisations do not take into account some independent elements that influence a particular business regardless of internal transformations and amendments (Mole, North and Baldock, 2017). In relation to the company in question, Prudential plc is actively involved in customer insurance and financial services provided to a wide range of customers, but specific external influences also affect the form’s activities. Among these effects, such drivers should be mentioned as economic, social, legal, political, technological and competitive. The aforementioned factors largely coordinate the direction of work of the organisation under consideration and dictate specific business conditions.
Economic Factors
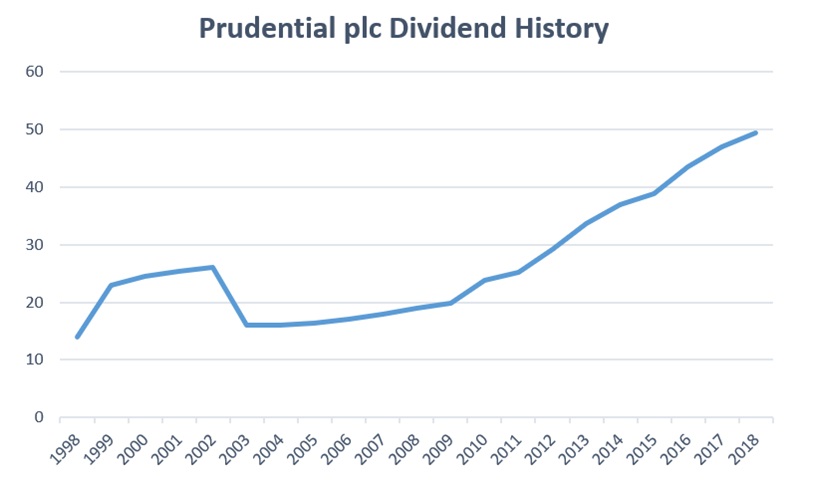
The economic performance of the UK financial sector has a direct impact on Prudential plc. For the success of the company, its management needs to own sufficient assets that are necessary for insurance payments and, at the same time, are independent resources for internal costs. The organisation’s income depends on long-term investments made by customers, which, in turn, excludes expenses on accounting and other procedures (Financial highlights, 2019). Judging by the results of the financial activity of the target audience, the company’s profits due to long-term investment returns in 2019 increased compared with the indicators of 2018 (£ 2,024m and £ 1,669m, respectively) (Financial highlights, 2019). In Figure 1, Prudential plc’s dividend history is displayed, which reflects how much economic sector activity affects the firm’s earnings (Prudential plc dividend history, 2019).
Social Factors
The features of the social sector largely determine the specifics of Prudential plc’s work and influence its business decisions. In particular, according to the company’s official report, social housing and real estate acquisition issues are topics that affect the frequency of clients’ insurance investments and their activity (Prudential plc, 2017). In addition, the educational sector that is also part of the social field has an impact on Prudential plc since contributions to learning and the provision of financial assistance to students play a significant role in the organisation’s work. As Raman (2016) notes, the possibility of influencing the target audience and engaging potential customers depends on the standard of people’s living and their willingness to invest personal funds in insurance. Thus, social impacts are an important aspect of the activities of Prudential plc.
Legal Factors
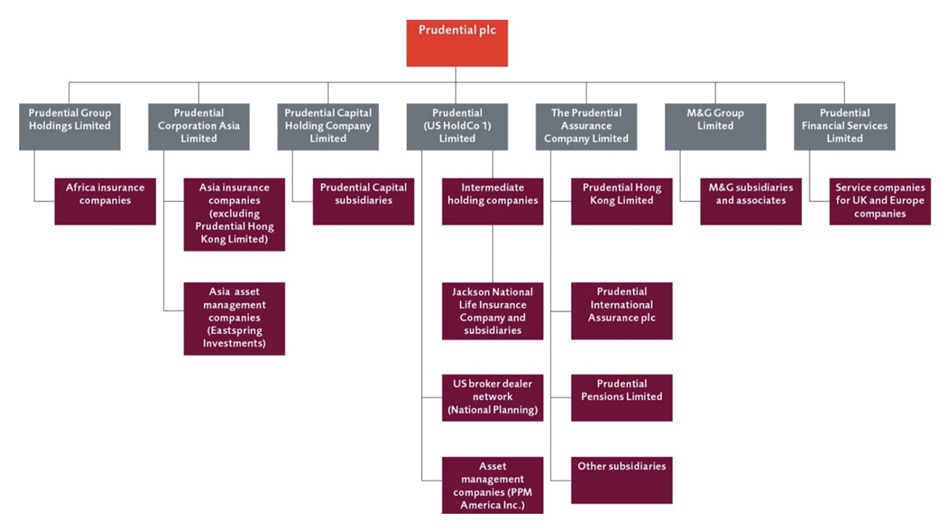
Legal conventions for the development of the financial market are important factors influencing the activities of Prudential plc. In accordance with the existing legislation, the company is obliged to adhere to the conditions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act 2002 since the company provides international private insurance services and is to follow the provisions of this legislative document (Governance and policies, 2019). Also, a certain hierarchy dictated by the legal principles of structuring financial institutions is characteristic of Prudential pls, and the entire system of interaction inside the managerial apparatus is shown in Figure 2 (Legal structure of Prudential plc, 2019). The need to comply with official reporting conditions as part of obligations to tax and other regulatory authorities determines the stringent conditions for the functioning of all the company’s departments. As a result, the leaders of the firm need to consider a number of legal nuances in organising operational activities.
Technological Factors
The growth of the technology sector is one of the significant reasons for the development of Prudential plc and its innovative approach to organising activities. Annually, the company invests about $ 1.6 billion in this industry, and engaging qualified employees to work with high-precision financial strategies is one of the areas of work (Technology careers, 2019). Information technologies as tools to attract customers are being improved regularly. As a result, as Malik (2015) states, Prudential plc allocates funds to study the available mechanisms for interacting with the target audience through modern means of communication. This innovative approach is largely determined by external technological factors.
Political Factors
In the context of political influences, these aspects have an impact on the activities of Prudential plc and form a certain background of work, which is important to consider. One of the manifestations of this effect is the British government’s decision to leave the European Union, and this step creates difficulties for the organisation’s work in the international arena (Risk factors, no date). In addition, there are certain conditions that dictate the principles of selecting executive officers from a company and voting. There are principles according to which “organizations themselves cannot contribute to candidates and party committees” (Profile for 2020 election cycle, 2019, para. 1). As a result, the features of the functioning of the administrative apparatus and decision-making at a high level require compliance with political conventions and rules.
Competitive Factors
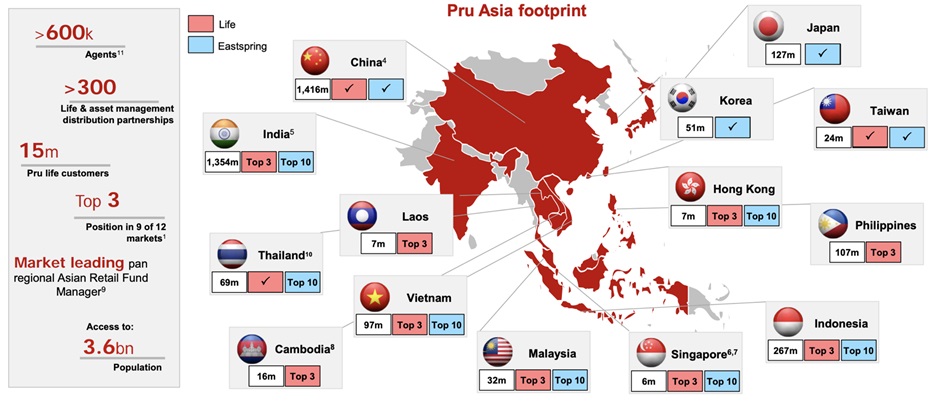
Competitive factors are significant influences that determine the activities of Prudential plc and stimulate the company to develop. The range of international alternative organisations (Manulife, MetLife and others) that customers can choose for insurance services is wide (Prudential’s competitors, 2019). This, in turn, encourages the management of the company to take the necessary measures to overcome this barrier. In general, Prudential plc does well in competition and is among the top three international companies in the Asian market, which is reflected in Figure 3 (Media & investors, 2019). At the same time, possible fluctuations in consumer interest may affect the rating of the organisation. Therefore, such influences coordinate the work of the company significantly.
Overview of Importance
As applied to the operations of Prudential plc, political factors have a strong influence, as the presence in the international market increase the sensitivity to changes. For instance, in the environment of political chaos, investors are hesitant to input money into their operations of the company while stakeholders’ trust is lowered. In the political climate characterized by high levels of bureaucracy and corruption, the company’s business operations may be significantly limited due to barriers in attaining licensing, contracting deals, fraudulent agreements, as well as frequent lawsuits. Within such a context, the organization’s sustainable development is threatened because of the continuous societal disruption as well as the changes in the justice system that endangers the rule of law.
Technological factors also have a strong influence on the operations of Prudential plc. The rapid pace with which technological advancements progress points to the increasing importance of companies being able to capture technological trends for achieving business advantage. For example, the company should consider the type and the rate of investment into technological solutions that competitors make to stay relevant in the market. Research and development activities also play a detrimental role in the shaping of the technological advancement of a financial organization because the market is characterized by creative disruption. To maximize profits and re-invest in future technological advancement, it is recommended for the company to invest in disruptive technologies.
Finally, the PEST C analysis showed that economic factors also have a strong influence on the shaping of the organization’s competitiveness. Such components as foreign interest and exchange rates, labour market conditions, saving rates, inflation, and others are essential to consider because they point to the overall economic environment of a country. On the one hand, for example, the growth rate of GDP will point to whether an organization will be able to pursue its long-term strategies and growth objectives. On the other hand, high rates of unemployment in a country signal the availability of surplus labor that can be hired for lower wages.
Ethics and Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) conditions are important aspects of modern business organisations, including both financial and non-profit companies. Assisting in the development of certain areas of life and investments aimed at promoting essential social tasks form a positive image of companies and give them the right to use available resources for conducting activities. Prudential plc is the company that is also involved in CSR and carries out important work in specific areas. According to the firm’s reports, the corporation provides support to young people in difficult situations, invests in construction and, in particular, Newark infrastructure and also makes contributions to non-profit organisations (What we believe, 2019). According to Sethi, Martell and Demir (2017), Prudential plc is on the list of companies practising CSR development in the international arena. In addition, due to its high status, the organisation adheres to the principles of fair market interaction and promotes relevant corporate ethics strategies. Analysing these areas of work and discussing their impact on the activities of Prudential plc can help find out the most important manifestations of CSR and its role in forming the corporation’s business.
Influence on the Organisation’s Policies and Decision-Making
Since Prudential plc advances the principles of CSR and adheres to certain strategies that enhance the company’s image in the face of potential customers, its activities influence current policies and decision-making. Charitable and volunteer assistance require allocating additional funds that are significant in the context of addressing relevant public objectives. Moreover, those activities that are part of the CSR spectrum are not the direct goals of Prudential plc’s business development and, accordingly, are the tactical steps that explain the implementation of unique development strategies. As a result, the influence on the internal and external working conditions may be observed, and their specifics are reflected in various areas, including financial, ethical and other aspects of work. Thus, sponsoring non-profit organisations, supporting youth and contributing to infrastructure have a big impact on Prudential plc.
Youth Support
In the context of this CSR practice, Prudential plc organises funds and programmes to help young people with employment and improve their professional skills. According to the company’s official report, the organisation distributes affordable budgetary funds in order to achieve the goals of providing educational opportunities for children from primary and secondary schools (Prudential plc, 2018). This aim is achieved through constant investment in this area. The corporation’s revenues imply distributing this sponsorship as a separate budget segment that is not spent on the needs of Prudential plc. When organising its business, the company takes into account the need to invest a share of income in the educational sector. Decision-making on the allocation of funds is accompanied by the assessment of the state of this social sector, and the poor and needy children receive the necessary support, which contributes to their continued successful employment. Such a strategy is reflected in the internal policy of income distribution and the use of individual channels for the realisation of profits as sponsorship.
Financial support provided to opportunity youth is expressed in significant investments. According to O’Sullivan (2019), the management of Prudential plc has a special plan. The author states the company wants to implement it by 2025, and about $180 million will be allocated to help young people from 15 to 29 who are not able to receive education (O’Sullivan, 2019). This activity is far-sighted and can serve as a valuable tool in enhancing the credibility of the corporation in the international arena. Disputes and disagreements over the UK’s exit from the EU complicate the comprehensive development of Prudential plc business in all the world regions. Work on youth support is an important part of the charity programme to stimulate public attention to this problem, thereby creating a positive image for the organisation. In addition, young people who receive assistance may subsequently seek to become part of the Prudential plc team, which is an additional contribution to the future of the company. Therefore, this form of CSR can help the company in question develop in its sector productively.
Contributions to Non-Profit Organisations
Another activity of Prudential plc that characterises the company as that adhering to CSR principles is contributions to non-profit organisations. During the implementation of this programme, the corporation has donated about $850 in grants and sponsorship to promote projects that are not funded by private and other representatives (Corporate giving: committed to funding change, 2020). These contributions are aimed at developing such areas as history, wellness and other socially significant sectors. This practice does not influence the work of the company from a legislative perspective but defines the redistribution of budget funds and taxation. Since such contributions can only be classified as charitable, they are allowed by the law. In accordance with existing regulations, many community investments are not permitted, except for charitable ones (Community investment policy, 2020). Therefore, Prudential plc does not violate legal provisions and acts as a valuable sponsor for many non-profit organisations.
The corresponding departments of the company are involved in CSR work in this area. According to available data, Prudential plc provides assistance to pension funds that are not government-sponsored and consist of direct contributions from participants (Prudential Retirement announces a new reinsurance counterparty, 2019). This activity, in turn, is favourable to the reputation of the corporation. People who have decided to take out insurance policies will be more likely to contact this organisation if they know that the company’s management makes contributions to the development of the pension sector. This practice is a visionary solution that potentially increases the interest of the target audience in the services of Prudential plc and opens up opportunities for the corporation to attract new customers.
Commitments to Infrastructure
As a CSR practice that defines Prudential plc as a company with a high level of social responsibility and ethical background, commitments to infrastructure are promoted. The corporation provides millions of dollars to revitalise individual cities and helps thousands of people gain access to modern and advanced life support systems (Newark: seeing the promise of prosperity, 2020). Both British objects and buildings in other world regions are repaired and improved not only in order to create a more attractive and aesthetic appearance of cities but also provide comprehensive assistance to the population. As Prudential plc aims to promote high standards of service to its customers, the organisation seeks to create support for the development of urban infrastructures for a more comfortable life for its potential clients (Prudential plc, 2016). The renovation of residential complexes, innovations in the field of medical facilities and other activities underline the company’s interest in CSR through infrastructure development.
The corporation in question monitors the available areas for investment in infrastructure carefully since this type of activity largely influences the internal development of Prudential plc and its decision-making process. By creating the necessary conditions for a comfortable stay of people, the company, thus, has an opportunity to promote its insurance services more successfully through effective interaction with the population and brand popularisation. In case a large number of citizens are aware of the organisation’s contribution to the development of urban infrastructure, this will be a good reason to turn to the specialists of this particular company for help. In addition, promoted innovations in the field of communication with customers are an additional incentive to maintain high operational activities and optimise internal organisational processes within Prudential plc. Therefore, such a useful and wide-spread CSR practice has bi-positive implications.
Evaluation of the Effectiveness of the Organisation’s Response
Effective Response
When assessing the company’s response to ethics and CSR policies, one can note that Prudential plc has managed to create a sustainable system of interaction with many social institutions, thereby providing relevant and valuable services. According to the official information, of 18,302 large insurance organisations, the corporation in question has a rating of 92/100 on the CSR proposal scale (Corporate social responsibility (CSR), no date). This result proves that a competent and demanded social policy helps the company to occupy a high place in the services market due in large part to productive steps in the field of CSR. Based on the information from the same source, Prudential plc is involved in addressing environmental issues, although, in community and employment assistance areas, its activity is also high (Corporate social responsibility (CSR), no date). As a result, the organisation ensures stable growth and attracts new customers due to such productive practices.
Another proof of the success and relevance of the promoted CSR practices is the tax system within the company. The organisation’s official report of 2019 proves that corporate profits exceed its tax deductions significantly in all regions without exception (Prudential plc, 2019). In addition, CSR activities are a special type of corporate work that has distinctive tax principles. Since the company cannot provide financial assistance to communities directly in the form of investments in business development, the organisation provides charitable support. This type of investment is allowed by law and, at the same time, does not imply mandatory contributions to the treasury. The ability to carry out significant social work in many areas is simplified and opens up prospects for valuable interventions. Thus, CSR practices at Prudential plc meet many of the needs of various industries and are successfully implemented without a threat to the financial stability of the corporation itself.
Ineffective Response
Despite the success and relevance of Prudential plc’s ethics and CSR practices in the context of official development programmes, some ineffective outcomes may be traced. According to Dupire and M’Zali (2018), a competitive environment is a significant obstacle for many firms promoting socially important projects. Based on the official statistics, a number of international corporations are ahead of the organisation in question in addressing CSR practices, for instance, Apple or Google (Corporate social responsibility (CSR), no date). Despite potential incentives for the faster development of this area of work, Prudential plc cannot compete with such recognised market leaders, thereby yielding to them in the outcomes of interventions. Although the goals of ethics and CSR projects do not imply a struggle for leadership, a stronger position can contribute to a higher recognition of corporate success. Therefore, this aspect of the organisation’s work is its weakness.
Another omission of Prudential plc in the context of addressing ethical issues and CSR practices is its implicit activity. All investments and sponsorship funds aimed at the development of certain areas and communities appear in official reports, but at the same time, they are unknown to the general public. As Karaosmanoglu, Altinigne and Isiksal (2016) state, such an omission may be fraught with the insufficient recognition of business organisations regarding their valuable interventions. In addition, the inability to realise a stable system of intermediation between public and private financial flows slows down the process of work in this area. Prudential plc is the company with a long history of development, but its business sector does not imply management activities in its market segment. As a result, the lack of authority to establish effective interaction between private and municipal stakeholders and control the distribution of financial assistance complicates CSR activities. Therefore, the implicit nature of interventions does not allow the corporation in question to obtain the highest possible recognition among different categories of consumers.
Areas for Improvement
Based on the analysed responses of Prudential plc regarding ethics and CSR promotion practices, some areas deserve particular attention and improvement to achieve better performance. In particular, a competitive environment is an important aspect that impedes the popularisation of the company’s role in the international market. Dupire and M’Zali (2018) emphasise the significance of maximising the disclosure of ethical priorities before implementing CSR interventions in order to reach a larger market segment and gain recognition. This measure implemented as a mechanism to attract public attention to ongoing work to help communities may have a positive effect on the growth of interest in the corporation. Consequently, an increase can be achieved in the position in the international insurance arena. Therefore, the promotion of CSR activities may be important in the context of strengthening the business of Prudential plc and stimulating its competitive advantage.
Regarding the identified gap in the organisation of sustainable interaction between private and municipal boards in controlling the distribution of sponsorship funds, this issue is less relevant. Prudential plc is the company that adheres to all the legislative conventions for the development of its business; otherwise, it could not conduct activities at the international level. Accordingly, even in the absence of a stable base of interaction with various stakeholders, the results of CSR interventions do not deteriorate significantly. The corporation may have to spend more time to organise investment channels and resolve all the conventions to justify specific steps. Nevertheless, this will not affect the results of investments significantly and will not reduce the value of work in this direction. Thus, this area of improvement is not a crucial priority.
Conclusion
The external influences considered affect Prudential plc and determine its role in the international market, but the abilities to withstand these impacts and promote effective ethics and CSR practices make the corporation’s work successful. Such factors are considered as economic, social, legal, technological, political and competitive. Their roles in Prudential plc’s business formulate specific policies and serve as drivers for developing and involving the necessary strategies for interacting with the target audience. As practice shows, the company copes with any impacts effectively because it still occupies one of the leading positions in both the Asian and global insurance services markets. As a specific area for assessment, the ethics and CSR practice is considered. Based on the analysis conducted, one can argue that Prudential plc implements programmes for investing in socially significant projects productively and addresses important areas for development. Youth support, investments in infrastructure and contributions to non-profit organisations are the spheres of influence. Despite a high competition rate in the CSR segment, crucial improvements are not required because the company performs all the tasks reasonably and introduces relevant programmes to help specific communities legally.
Reference List
Community investment policy(2020). Web.
Corporate giving: committed to funding change(2020). Web.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) & environment, social, governance (ESG) metrics (no date). Web.
Dupire, M. and M’Zali, B. (2018) ‘CSR strategies in response to competitive pressures’, Journal of Business Ethics, 148(3), pp. 603-623.
Financial highlights (2019). Web.
Governance and policies (2019). Web.
Karaosmanoglu, E., Altinigne, N. and Isiksal, D. G. (2016) ‘CSR motivation and customer extra-role behavior: moderation of ethical corporate identity’, Journal of Business Research, 69(10), pp. 4161-4167.
Legal structure of Prudential plc(2019). Web.
Malik, A. (2015) ‘Corporate social responsibility initiatives of LIC and ICICI Life Insurance Company’, International Journal of Advanced Research in Management and Social Sciences, 4(12), pp. 286-299.
Nicandrou, N (2019) Asia strategic overview. Web.
Mole, K., North, D. and Baldock, R. (2017) ‘Which SMEs seek external support? Business characteristics, management behaviour and external influences in a contingency approach’, Environment and Planning C: Politics and Space, 35(3), pp. 476-499.
Newark: seeing the promise of prosperity (2020). Web.
O’Sullivan, C. (2019) Prudential Financial announces $180 million global investment to solve complex challenges facing opportunity youth, promoting financial wellness of the next generation. Web.
Profile for 2020 election cycle (2019). Web.
Prudential’s competitors, revenue, number of employees, funding and acquisitions (2019). Web.
Prudential plc (2016) Environmental, social and governance report 2016. Web.
Prudential plc (2017) Environmental, social and governance report 2017. Web.
Prudential plc (2018) Corporate responsibility review: a long-term view. Web.
Prudential plc (2019) Managing our tax affairs responsibly and sustainably. Web.
Prudential plc dividend history (2019). Web.
Raman, P. (2016) ‘Improving customer satisfaction by increasing the reach: Life Insurance Corporation of India’, Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies, 6(2), pp. 1-21.
Risk factors (no date). Web.
Sethi, S. P., Martell, T. F. and Demir, M. (2017) ‘An evaluation of the quality of corporate social responsibility reports by some of the world’s largest financial institutions’, Journal of Business Ethics, 140(4), pp. 787-805.
Technology careers (2019). Web.
Timeline (2019). Web.
What we believe(2019). Web.