Meeting the needs and wants of the customers by developing products or services from which they could derive maximum benefits and are of value to them is termed as quality. Quality function deployment (QFD) had its origin in Japan during the 1960s; it helps a company to know the needs of the customers and helps it in meeting those needs. It has been a handy tool for the interdisciplinary teams. QFD includes members from marketing, sales, purchase, and quality control. QFD matrix is a great communication tool; it could be successful only if it is used efficiently. QFD was first employed by automobile manufacturers. It strives to get the customers’ view of quality throughout the product life cycle. “QFD therefore represents a change from manufacturing process quality control to product development quality control.” (Ghiya, Arizona & Chapman n.d., p. 593).
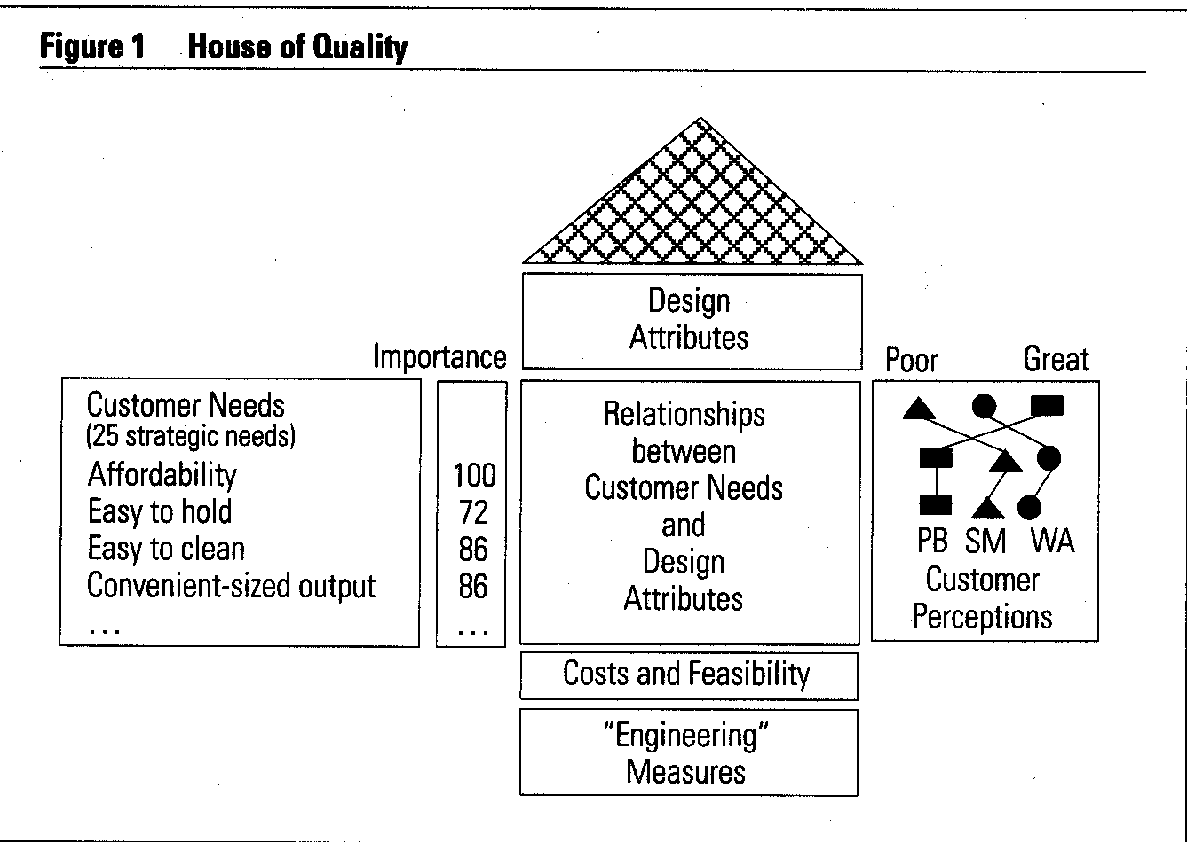
The needs and requirements of the customers are identified and classified into a planning matrix known as the “House of Quality”. It is so called because it looks similar to a house with a roof on top and helps in communicating the needs and wants of the customer. It gives way to market measurement and helps eliminate physical contradictions. The main objective of the QFD is to translate the demands of the customers into target values that can be derived from the product. Their main objective is to fulfil the customer needs thereby increasing the level of satisfaction among them. QFD could light its path to foreign markets and could help to spot opportunities to develop products much before the demand by the customers. (Poel n.d., p. 21). QFD helps in maintaining the product quality. It assists the design teams in developing new products based on the needs of the customers and ensures that they are satisfied with the products and the value that is derived. QFD work is divided into four parts. They are:
- Market analysis to establish needs and expectations.
- Examination of competitor’s abilities.
- Determination of the key factors that contribute to the success of QFD
- Translation of key factors into product and process characteristics.
Rules for QFD
- The scores of requirements of the customers are provided on the ratio scales by adopting the methods as suggested by Keeney, Kirkwood, and Edwards.
- The scores that are provided on the ratio scale are normalized and summed up into one so that they can be used as weights.
- The relationship scoring system is also entered on the ratio scale. Steps are also taken to ensure interval scale column score.
- The score will be in the form of real numbers ranging from 0-9.
- 3 is three times more correlated than 1.
- 9 is three times more correlated than 3 and nine times more correlated than 1.
- If zero is scored, then it means that there is no correlation.
- The column scores could be attained if the methodology of scoring meets the measurable value function criteria.
- The HOQ scores cannot be used as weights for another HOQ.
- The final scores are used as recommendation.
(Burke, Kloeber & Deckro n.d., p. 18).
Usage of the Quality Function Deployment method Applications
- Identify the needs of the customers and efforts are made to fulfil those needs.
- These needs are then translated into actions or physical attributes.
- Then the focus is made for the development of quality product and service for the customers.
- Guaranteed customer satisfaction is provided by developing the product or service of good quality from which they could derive maximum benefits.
- It helps to lower cost and increase reliability,
- It could be applied in any industry such as IT, service industry, manufacturing industry, software, communication etc.
Benefits
- The product objectives based on customer requirements are not misinterpreted at the subsequent stages.
- The marketing strategies or sales points do not become lost during the translation process from marketing through planning to execution.
- Efficiency is improved as the misinterpretation of design, objectives, marketing perception, and critical control points and the need for changes is minimized.
- It increases the coordination among the team and promotes team spirit. It reduces the time required for implementation.
- It helps in increasing the satisfaction level of the customers and efforts are made to see that every demand of the customer is fulfilled.
- It helps in collecting all the information required for the development of new products.
- QFD is customer driven and creates focus on customer requirements and prioritizes the resources.
- “QFD helps companies to make the key trade-offs between what the customer demands and what the company can afford to produce”. (Quality Function Deployment (QFD)—can it be used to develop food products? n.d., p. 328)
Steps in Quality Function Deployment
The steps involved in the QFD process are as follows:
- The requirements of the customers are identified and classified into product planning matrix and then efforts are made to fulfil these needs thereby increasing customer satisfaction.
- Evaluations of available concepts are done and most appropriate concept is selected at this stage.
- The requirement of the customer is conveyed through the assemblies or subsystem.
- Next stage is the extraction of lower-level product requirements and specifications from subsystem/assembly requirements.
- The manufacturing process is then determined.
- Processes such as set-up requirements process and quality control process will help determine the achievement of the proper assembly of materials. (Quality function deployment n.d.).
Application of QFD Model in chocolate
“Chocolate is a mixture of cocoa paste, cocoa butter, and sugar. Nowadays, we know its precise chemical composition. It is considered as a complimentary food, since all three organic substances exist (although not well balanced): carbohydrates (starch, diverse sugars), fats (cocoa butter), and vegetable proteins.” (Chocolate has been called an antidepressant, tonifier, stimulant, euphoriant, and even aphrodisiac. n.d.).
Chocolate is a preparation made from the fruit of the cacao tree and used as a flavouring. It is also used as an ingredient of beverages and various kinds of confectionaries. The word chocolate is derived from the Aztec word for their cocoa-based drink – xocolatl. The recipe for chocolate will vary from country to country – according to the taste and culture of the country.
The typical bar in Britain is made up of:
- 10% cocoa mass
- 14% cocoa Butter
- 25% milk
- 45% sugar
- 5% vegetable fat.
The best plain chocolate can contain up to 70% cocoa solids. This is the favorite type of chocolate in Continental Europe. It is made by mixing the cocoa paste with cocoa butter and sugar. Without sugar the chocolate would be quite bitter. Milk gives the chocolate a creamy taste and texture. Cocoa beans are roasted and ground to produce three main products. This is the general preparation of any chocolate. (Teacher’s note- design and technology 2009).
First thing before developing a new product is to identify the requirements of target customers. Then the next step is to convert the requirements to suitable attributes which will satisfy the customers. The main steps in the process of development of new product are as follows:
Idea Generation
The first step for development of a new product is the gathering of ideas about the product options. In order to generate ideas for new product primary market research methods such as focus group interviews with customers, suppliers, sales force are carried out in this stage.
Idea Screening
In this step critical evaluation of ideas by the company is made depending on the number of ideas. Acceptable ideas will move on to the next step.
Concept Development and Testing
In this step the marketer tries to get initial feedback from customers, distributors and its own employees with the new ideas. Generally, focus groups are gathered where the ideas are presented to a group.
Business Analysis
The key objective at this stage is to obtain useful forecasts of market size, operational costs and financial projections.
Product Mix Development
In this stage company initiates their research and development department to make the design of the product. Once the initial design is made they will try to get response from the potential customers.
Market Testing
Market testing means testing the acceptability of the product. This is done by selecting a particular segment.
Commercialization
This means distribution of newly developed product in the target market with appropriate marketing strategies.
(Strategy in action.ppt n.d.).
The direct application of QFD matrix in connection with customer requirements would lead to low discrimination. In order to test the acceptability of the new design, an exploratory study with non-probabilistic samples will have to be conducted. It will be meaningless to ask about the customers’ requirements of innovative products or products which customers are not aware of. In these cases, the current customer satisfaction tends to be close to neutral and the competitive analysis based on customers’ answers is not possible in the QFD matrix. The competitive analysis for the customer requirements was not included in the QFD matrix.
Problems
QFD is used as a tool for enhancing competitiveness. It is used to fulfil the needs and wants of the customers without sacrificing their satisfaction level. Some of the problems associated with QFD model are as follows:
- The demands of the customers are dependent on the product: The priorities of the customers are not clear. They are not able to express their demands with respect to new products. This might be due to the customer’s lack of awareness about the new product. In order to overcome this, it is better to make some improvements in the existing product.
- Customer demands cannot always be represented by a linear additive value function: Customers’ stated preferences and actions differ. Much importance is given to the achieved level of safety and costs. For many people safety is the most important factor while for some it is cost factor that is most important. This leads to the misrepresentation of the preferences. If a problem is suspected, revealed performance technique is used. The customer demands can be represented by an additive value function.
- Huge amount of investment is required for developing a QFD.The matrix will be too large and the independent subsystems should be analyzed independently. The demands of the individual customer may not be aggregated into demands of the collective customer. (Poel n.d., p.27).
- The correlation between the demands of the customer and engineering characteristics may not always be non-negative or constant.
- The importance of customer demands cannot be translated into engineering characteristics.
- The target values will be unclear.
Conclusion
QFD is a customer-oriented methodology designed to incorporate quality and customer requirements into every phase of a product development process. QFD plays a major role in prioritizing the goals and objectives of the company and thereby improving its performance. It is a flexible tool that can be adapted for use for a variety of activities such as manufacturing processes, design of new products, or future planning. The main goal of QFD is to satisfy the consumer by translating the customer requirements into design targets and quality assurance points. QFD is not designed as a general planning process. It is aimed at planning one specific product as opposed to quantifying the worth of alternatives (solutions). Therefore, the results of QFD are not intended for use as anything more than a general guideline for choosing priority items. The traditional QFD approach uses important ratings and customer satisfaction of the product of the company and its competitors to establish priorities among customer requirements and deploy them in the design process.
Innovative products try either to fulfil unarticulated customer needs or to fulfil current needs in different ways. Designing new products, particularly products that incorporate innovative requirements, is a difficult task because customers are not used to these requirements and the company does not have competing products to evaluate. In these cases customers tend to give lower importance to the innovative requirements, hindering their adoption by the project team.
References
Burke, E, Kloeber J M & Deckro, R F n.d., Using and abusing QFD scores.
Ghiya, K K, Arizona C & Chapman W L Qfd: Validating Robustness.
Hauser J R n.d., How Puritian –Bennett used the house of quality, (provided by customer).
Kusiak, A n.d., Quality function deployment and process models, The University of Lowa, Web.
Poel, van de Ibo n.d., Methodological problems in QFD and directions for future development Quality function deployment (QFD)—can it be used to develop food products? n.d.
Quality function deployment n.d., (provided by the customer).
Strategy in action.ppt n.d., (provided by the customer).
Total Quality Management 2007, vol. 18, no. 6, pp. 599–612 (provided by the customer).
Chocolate has been called an antidepressant, tonifier, stimulant, euphoriant, and even aphrodisiac. What is chocolate in reality n.d., PastryWiz.Recipes, Web.
Teacher’s note- design and technology 2009, Skill Space, Web.