Quirky Business Model Canvas
Quirky considers itself a “community-led invention platform” (Quirky par. 1). The company collaborates with inventors in order to come up with the most innovative products for making everyday life easier. To evaluate the way in which the company approaches business, it is important to complete the business model canvas used for describing, changing, and challenging the business model in relation to nine features: key partnerships, key activities, value propositions, customer relationships and segments, channels, cost structure, revenue streams, and key resources.
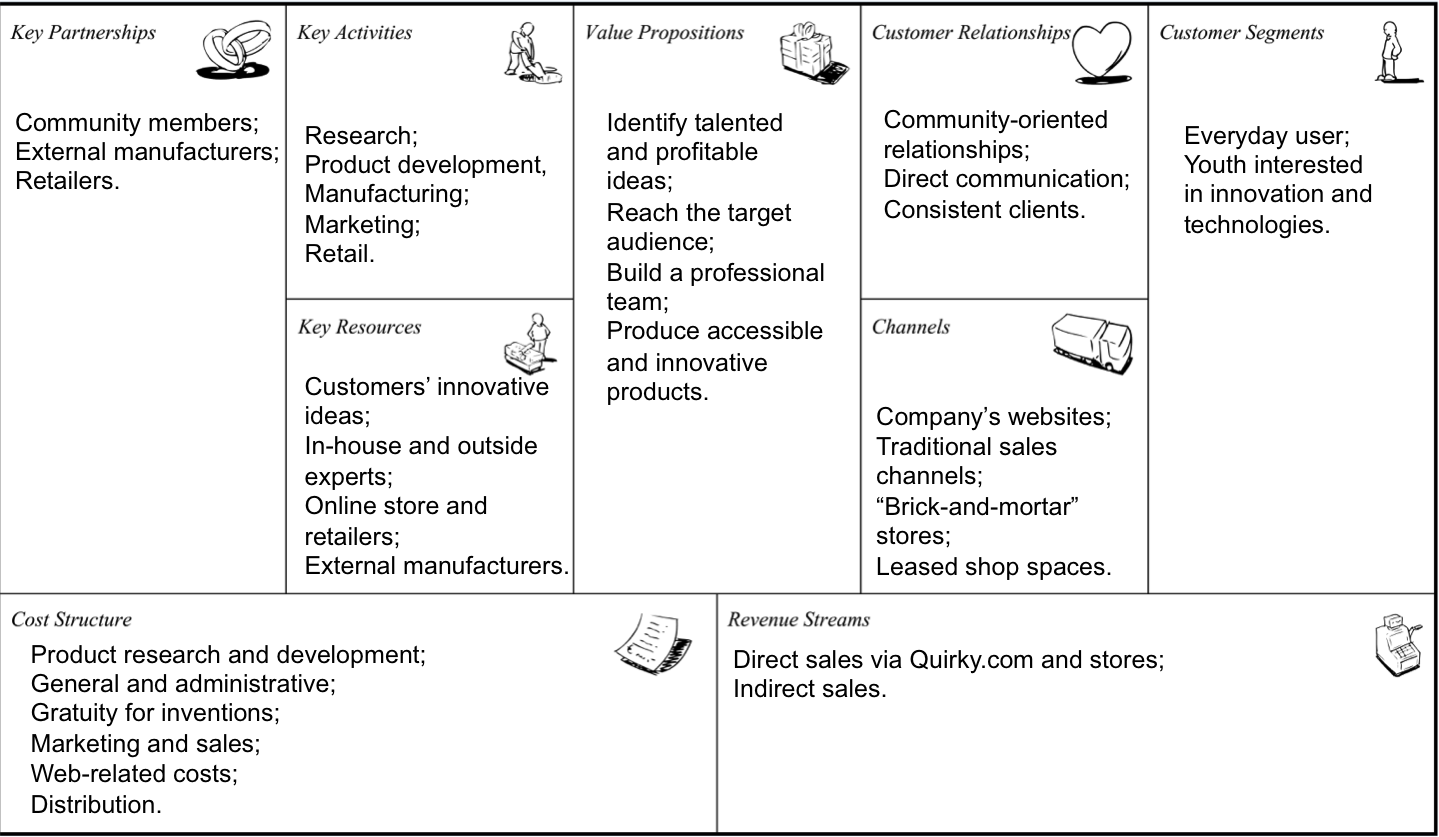
Business Model Changes and Additions
Because Quirky develops and manufactures products that are issued to the world on a regular basis, it is hard for the company to achieve and sustain a long-term profit margin. Thus, to improve the company’s profit margins, it is necessary to achieve greater than average units for sale. This can be easily implemented in the case of Quirky since there are many products that can be sold to customers at any one time. By doing that, the company will increase the purchase velocity at the same time as lowering the cost per sale (Finkel par. 20).
Attracting more potential customers and thus increasing the long-term profit can also be achieved by paying attention to the speed of sales processing. The faster the time between order and delivery, when it comes to online sales, the lower the cost for a produced unit will be. Thus, Quirky should incorporate new methods of order delivery into their business model, so that purchase velocity is increased. Automation, creation of templates and pre-order steps are efficient and can help the business minimise the time it takes to process customers’ orders.
Key activities of the company are predominantly targeted at giving customers the best value possible; however, there is little information available on the way the company evaluates resource wastage in terms of production. A system designed for the evaluation of the supply at hand, the time it takes to sell out the inventory, as well as the efficiency of the designed marketing plans should be added into the key activities since this will help with an increasing long-term profit margin (Finkel par. 25).
Assessment of the company’s spending, as well as looking for methods of boosting income should also be added into the business model canvas as the main activities of the company (The Marketing Donut par. 11).
Product Development
According to Reid Hoffman’s article on short versus long-term profit, “innovation comes from long-term thinking and iterative execution” (par. 11). Thus, in order for Quirky to reach the desired long-term profit margin, it is important to focus on development cycles that take years rather than shorter periods such as quarterlies. Due to the fact that the company develops, manufactures, and markets products at an ever-increasing rate, there is no time for successful products to linger and capture the greatest audience possible.
This is evident through the actions of traditional retailers that only retain on their sales lists the most successful products made by Quirky. Despite the creation of “brick-and-mortar” stores where each product is introduced and explained, the everyday user is most likely to stumble upon Quirky products on the shelves of the department stores. This detrimental issue is not due to flaws in distribution channels but rather in the pace with which the company produces new products. The attention of customers is focused on one product only for a short period of time until the next innovation appears.
Devoting more time to researching and testing of new products may increase Quirky’s ability to differentiate between potentially successful and unsuccessful products before they go on the shelves. Instead of spending excess time and resources on marketing different products at the same time, Quirky could target all of its efforts towards promoting the most successful product and give customers some time to appreciate it before moving on to the next innovation. The rapid pace of emerging products can only damage the company’s reputation since there is no distinct dedication to a product that is truly effective and necessary for everyday use.
It could be beneficial for Quirky to establish a business model that is similar in nature to that which Apple uses to issue its product. It takes at least a year for the company to issue a new iPhone, iPad, or another gadget. This gives time to build customer excitement about a new product. Purchasers get to know the new features and start to use them on a daily basis.
Only then do they begin anticipating new features that will be presented in the next gadget. On the other hand, Quirky’s goal is providing accessible and innovative products to everyone. Since the company’s main resource of ideas are regular people that want their day-to-day life improved, it would be complicated to fail to respond to their needs and desires on a regular basis. Again, Quirky could come up with a schedule of innovations that would be known to potential customers. This way people who want to buy a particular product will be left in anticipation regarding the release of next-generation products.
In-house Manufacturing Analysis
For now, Quirky operates with outsourced manufacturing plants in Asia. Because this brings many benefits to the business and because many products require materials that are common and much cheaper in Asian markets, it will not be easy to move the manufacturing in-house. However, there are also benefits to this type of manufacturing, so the most effective solution is manufacturing some items in-house while outsourcing others. The potential benefits of in-house manufacturing include flexibility, the ability to quickly react to market demands, quick prototype testing, customisation, and low costs for low volumes (StellaDoradus par. 4). Thus, the choice of what should be manufactured in-house and what should be outsourced can be based on those factors mentioned.
In addition, other criteria like competitive advantage and the preservation of unique methods of manufacturing may draw more of Quirky’s manufacturing in-house since there is an increased ability to control the process (Wallingford par. 2). If there are instances in which additional costs caused by outsourcing are too high, it is an obvious idea to bring the manufacturing of these products in-house. Thus, in cases when the costs for transactions are greater than the benefits or possible savings, it is much more effective to manufacture products in-house. Furthermore, if there is little to no opportunity for the business to leverage the capital or expertise when implementing the outsourcing method, then the manufacturing should be brought in-house.
Issues with Third-Party Retailers
One of the largest challenges Quirky has to deal with is the fact that third-party retailers were never prepared for the constant flow of new products (Stanford Business 8). With the steady stream of innovations provided by Quirky, the traditional sales channels chose to only distribute the ‘hottest’ products, leaving the rest behind. Furthermore, the holiday seasons were characterised by the same products being displayed on the shelves over and over again, given that there were many products developed. Thus, with the rapid pace with which the company develops, the most suitable solution is increasing the direct selling activities in order for customers to get a much fuller experience from the brand.
On the other hand, renting shelf spaces in retail stores will not solve the issues Quirky has when it comes to traditional third-party retailing since this method is not reliable enough. In order to find common ground with third-party retailers in terms of selling Quirky products, the company should seek businesses that are adept at selling innovative items manufactured by different companies in one place. Stores like Target are too broad in their specification; and although they are convenient for the majority of customers, many cool and unique products are just lost among an overwhelming range of stock items.
Because innovations come directly from the public to Quirky developers, direct sales will increase customer loyalty (Ondieki et al. 274). To broaden direct sales opportunities, Quirky should market its online store as the most efficient revenue channel since it offers customers ease of buying desired products without the need for going to stores. On the other hand, for customers interested in the history of products, how they were developed, as well as how they look in real life, Quirky can start opening specialised shops across the country. This will put the company closer to potential clients, improve the interpersonal relationships with them, as well as ensure a higher level of influence.
Since strengthening relationships with customers is what direct sales are suitable for, Quirky can also provide repair services for customers that have issues with their products. Furthermore, stores can offer refunds or replacements for items bought in the online shop so that customers do not spend time on returns via post. Despite the fact that direct sales will strengthen relationships with clients, third-party retailers still bring profit. Thus, there is no point in only reserving one sales channel, instead, similar to practices implemented by Apple, Quirky can broaden its experience with direct sales by opening more shops at the same time as collaborating with third-party retailers that will be interested in all innovative products and not just best-sellers (Dickens par. 10).
Partnerships with Established Consumer Companies
Modern consumer companies can significantly impact the way customers think and live – they influence what they drink, wear, use, and eat. Such companies can also alter client thinking when it comes to deciding which are the most ‘trendy’ places to shop. In general, consumer companies are the most innovative businesses that go beyond the limits of markets or department stores, they reinvent markets and create new products that than capture unique niches within markets (Caldbeck par. 1).
One of the most significant features of Quirky is the innovation-oriented approach aimed at bringing new and fresh products for customers at accessible prices without compromising on quality. Collaboration with large consumer companies will be beneficial for Quirky in bringing its products to a larger audience; one that already follows the modern trends dictated by corporations. However, there is a risk of becoming overshadowed by the ‘corporate machine’ of a larger brand, and, effectively, get subsumed by that brand.
There are many positive attributes that make Quirky a unique company. It has the potential to become a massive consumer brand that can dictate market trends. Similar to Dyson dictating trends when it comes to urban appliances, Quirky can dictate trends that come directly from potential consumers since they are the primary source of innovation and inspiration. In this sense, Quirky is much more a ‘consumer company’ than any other brand – customers that greatly contribute to the development of new products are rewarded for their ideas, encouraging them to come up with more innovative, and, most of all, useful products.
Thus, in case Quirky partners an established consumer company, there should be a common goal of offering innovative and accessible products to potential users, rather than becoming a global ‘corporate machine’ the main aim of which is to earn more money. For example, companies like Dyson could offer a great opportunity for cooperation since it is focused on extensive research in order to come up with state-of-the-art technologies that change the way consumers look at home appliances (the latest Supersonic hairdryer). Making the life of customers easier is also one of the most important aims for Quirky, and since customers come up with some of the ideas themselves, Dyson could well facilitate extensive research on new products, engaging a team of professionals thus reducing the time and costs Quirky pays for research conducted by external specialists.
Works Cited
Caldbeck, Ryan. The 25 Most Innovative Consumer and Retail Brands. 2013. Forbes. Web.
Dickens, Andy. Direct Sales vs Channel Sales – What’s the Difference? 2015. Web.
Finkel, David. 5 Simple Ways to Improve Your Profit. 2015. Inc. Web.
Hoffman, Reid. Short-term Profit Taking vs. Long-term Value Creation: The Future of PayPal. 2014. LinkedIn. Web.
Ondieki, Sixtus, Walter Okibo, Andrew Nyang’au, Philemon Obenge, Wesonga Nyongesa, and Dennis Nyamasege. “Effects of Direct Selling Strategy on Customer Loyalty by Commercial Banks in Kisii County.” International Journal of Business and Social Science 5.3 (2014): 274-282. Print.
Quirky. What Is Quirky? n.d. Web.
Stanford Business. Quirky: A Business Based on Making Invention Accessible. Stanford, CA: Stanford Graduate School of Business. 2013. Print.
StellaDoradus. The Advantages of Manufacturing Your Products In-House. n.d. Web.
The Marketing Donut. Ten Ways to Increase Your Margins. n.d. Web.
Wallingford, Jeff. Viewpoint: When Companies Shouldn’t Outsource Manufacturing. 2012. IndustryWeek. Web.