Introduction
RFID is an acronym for “Radio Frequency identification”. The technology is grossly involved with the collection of data using some special electronic tags. There is a special chip that makes up the tags which are used for data collection. It can be exemplified to normal bar code readers in the way that they identify objects and collect the necessary data for the objects. The main advantage of this technology is the reduction of the human and labor intensity in the process of collection of data (Hatem & Habib, 5).
Data mining is all about the analysis of data from various sources and making a summary of useful information which can be found in the data. There are various tools like special software which can be used in the field of data mining. In this process, diverse information, say from a large database can be used to find how the various items correlate.
The centrality in the management and consequent retrieval of large amounts of data is defined as data warehousing. A data warehouse has a lot of databases managed in a centralized repository of information. When data has been centralized, user access is set to the maximum and further analysis of the data can hence be made faster.
This paper seeks to address the implementation of RFID on data mining and n the United Arab Emirates. The paper will consist of a general insight into the implementation of the technology in the country as it is today, current state of the technology, and an analysis of the projections that are aimed at improving the technology and possible future impacts of the technology in the UAE (Al Jaroodi, 14).
RFID in the UAE
Most of the companies in the competitive market today have focused on the increase in productivity with minimum operational costs. To make this a reality, there has to be an adaptation of the necessary business models as well as a gross improvement in the required business architecture. With the use of RFID, the businesses get more streamlined and also most of the operations are optimized. There are some components which form the general architecture of this technology as shown below
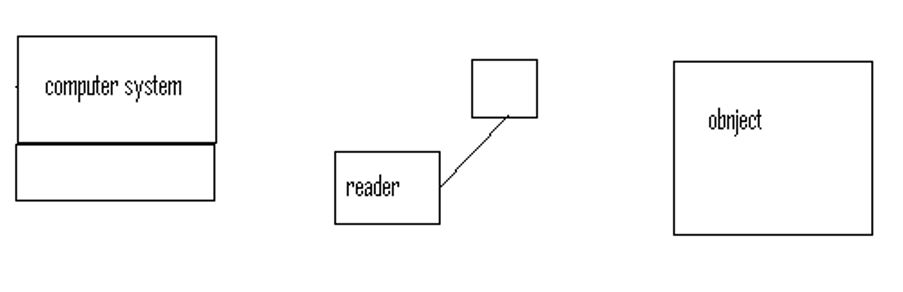
According to the above diagram, there is communication between the computer, the object and the RFID reader in a certain protocol
- The RFID reader sends some electromagnetic waves which carry a signal which is used to identify the object. The objects return back some information to the reader which is used for identification purposes
- The objects have a special RFID tag which is the one that sends the information which has been requested by the object
- The computer has a database in which it stores all the information that it receives from the RFID reader
In the past, most of the readers could not use current mobility systems but used a special connection to the host computer through the Ethernet or through the serial port.
In the United Arab Emirates today, there has been quite some diverse usages of the RFID system for example in the process of electronic tolling or in one of its modes called SALIK. In this technology the tags which are used in the system are passive RFID tags. In the system motorists are supposed to buy a prepaid card which is then fixed to the windshields of their cars. Once the car passes through the toll stations, a certain fee is automatically deducted from the card on the screen. Depending on the gate that the motorist will use to pass some certain area a standard fee for that gate is deducted. This is a technology that helped in the reduction of congestion within the busy areas of the country and the cities.
In the employment of this technology, it takes advantage of the passive RFID tags as stated. The tags get some power from the transceivers which are located at the gates of the toll stations. This means that the tags do not require having additional power like the use of a battery. The mode of information retrieval in the RFID as discussed earlier is automated and so the data is relayed to the central warehouse (data repository) in a remote manner and through the use of the tags. This is due to the fact that the incorporation of the tags to be read by radio waves helps the readers to be able to read them even from longer distance depending on the mode which is applied.
This system has had a lot of advantages to the United Arab Emirates. The traffic at the gate is put under control as the vehicles do not necessarily have to stop to pay the toll fees as the process is monitored dynamically and in real time.
Another application is the one which is in use by the Damas stores in Dubai. In this stores which majors in jewellery, there are special tags which are fitted into the objects in store that make the object pass through the inventory records once a reader gets the information. This was mainly aimed at the reduction of theft. Due to the status of the information in the central database, any transaction or running of a reader on any of the stored items takes place almost immediately. This is aimed at the revolution of stock checks.
In the United Arab Emirates, there has been a proposal of an integration of this technology with the use of wireless sensor networks for management of buses. Due to the expense that comes in with normal wire cabling, a wireless solution is one of the best ideas in which either the user can use Bluetooth or Zigbee which will help in the extension of the reader of the RFID waves. Bluetooth has the advantage of allowing for the creation of personal area networks which have a short range. It is also simple to maintain the Bluetooth connection. The rate of data transfer using this mode is generally 1Mbps though it has a high level consumption of energy and also a range of about 10 meters which makes it not practicable (Cheng-Ming, 150).
On the other hand Zigbee saves more energy though the data rates are much lower as compared to Bluetooth. It is a low cost technology which also allows for meshing of the devices which means that multiple nodes can be communicating with a surety of information reception even with the failure of one of the nodes. Due to the style of the proposed implementation which is in a bus station, the low cost of the technology allows the possibility of having the ability to transmit the information from various spots which can be affordable to fix.
In this application, the communication of the object and the reader is triggered once the object approaches the reader. In such a case, without any object in scene, the reader is often not active. On the approach of the object the software being held by the reader is informed of the approaching object via the mode of transmission used, in this case Zigbee (Qing-Jie K. et al, 41).
The RFID middleware in use is the one which is responsible for handling such an event. It sends a command back to the RFID reader so that it can be set to a mode in which it is prepared to read. The reader at this point reads the tag which is attached to the object and consequently sends its identity information to a computer which holds the central database. On passage of this object, the reader becomes inactive again and waits for the next object.
Using this approach, it is possible to track the movement of buses in the area on a real time basis and thus the management can be able to handle time related issues. On reception of this information, the central database (data warehouse) can have a live display of the information which helps keep the passengers at bay or else duly informed of the movements. The operators can also take advantage of this information to fully utilize the available buses considering that all the movement is dynamically tracked and can hence be dynamically diverted.
To have effective monitoring, all buses can have RFID sensors which monitor the inflow of passengers in real time without the intervention of any person. Also there can be other external sensors which inform the administrators of the whereabouts of their fleet as the bus is recorded once it gets to a station and once it gets out. The displays used in real time can be LCD screens.
Moving back to the concept of data mining and data warehousing, there is a consistent utilization of this two principles in line with RFID. The information which is gathered from the buses comes in two major ways. The passenger traffic in and out of a bus and the arrival of a bus to a station and from a bus station are monitored. When this data is collected, it is relayed to a centrally located computer using RFID technology and other middleware. This information is noticeably collected from a number of buses and relayed to one single place which can hence be referred to as the data warehouse. Data mining occurs in the way that the management has access to this data and can be able to adjust the bus movements. With such information, the operators can foretell their earnings as they have all the needed information before them. Data mining, being the concept of analysis with the capability of making a distinct summary is thus established (Chien, 15).
Conclusion
Despite the age of this technology, it has picked a lot of pace in the realm of management and the chain of supply. The technology has enhanced the management of data and performances of different organizations to high standards. This paper has discussed the various ways in which the technology has been implemented in the UAE. It is recommended that more research should be done on how the network should be enhanced to make it more mobile. If this was to be enhanced, then a better management of many systems would occur.
References
Al Jaroodi, Jameela et al. “Middleware for RFID systems: An Overview” 2009 33rd Annual IEEE International Computer Software and Applications Conference (2009)
Cheng-Ming, Jimmy Li, “An Integrated Software Platform for RFID-Enabled Application Development,” in proc. IEEE International Conference on Sensor Networks, Ubiquitous, and Trustworthy Computing, (2006).
Chien, Yeun. “SASI: A New Ultra-Lightweight RFID Authentication Protocol Providing Strong Authentication and Strong Integrity,” IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing 4(4), (2007).
Hatem, Ben. & Habib, Haman. “Bus Management System Using RFID in WSN” European and Mediterranean Conference on Information Systems 2010 (2009).
Qing-Jie Kong. et al “A fusion-based system for road-network traffic state surveillance: a case study of shanghai,” IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 37-42 (2009)