Executive Summary
The report presents and discusses the information on the transportation needs of employees in Armada and the way to reduce traffic congestion.
The Problem of Traffic Congestion
The impact of traffic congestion is glowing, and it is responsible for the decreasing quality of life. The impact of Armada’s employees on traffic should be reduced as many of them use personal transport daily.
Employees’ Needs
While carpooling is unpopular, the majority of respondents prefer personal or public transport. The specific needs related to the latter include reduced commute times, increased safety, and affordability.
Strategies
The preferred strategy is based on telework opportunities and affordable transportation. To implement the strategy, the company is required to establish a corporate transportation system and create telework schedules.
Introduction
Our company is ranked among the largest private employers in the area, and this fact has a significant impact on our social image. Due to the necessity to identify our employees’ transportation attitudes to generate possible solutions, it was decided to conduct a survey. Therefore, the given report is aimed at fulfilling two important tasks. To begin with, the report presents the results of the survey to demonstrate the trends related to our employees’ transportation habits. Apart from that, the report analyzes possible solutions, paying special attention to the survey results.
The Problem of Traffic Congestion
The problem of traffic congestion in large and medium cities is often listed among the key issues that decrease the quality of life of the urban population in many countries. Traffic congestion is responsible for numerous negative outcomes for people from different social groups. The key outcomes are presented by long trip times and traffic jams. The corporate management team of our company should pay focused attention to the problem under consideration as the problem can also reduce the effectiveness of our employees’ work. Speaking on the present state of the problem, modern researchers indicate that its importance has significantly increased even for medium-sized cities (Stefanello et al. 119).
Our company has more than forty-three thousand employees. Trying to find the best possible decision to be implemented to reduce their impact on the traffic, we had to take into account their preferences and needs. Importantly, our employees are different in terms of wage levels, and it impacts their choices related to transportation.
Employees’ Needs
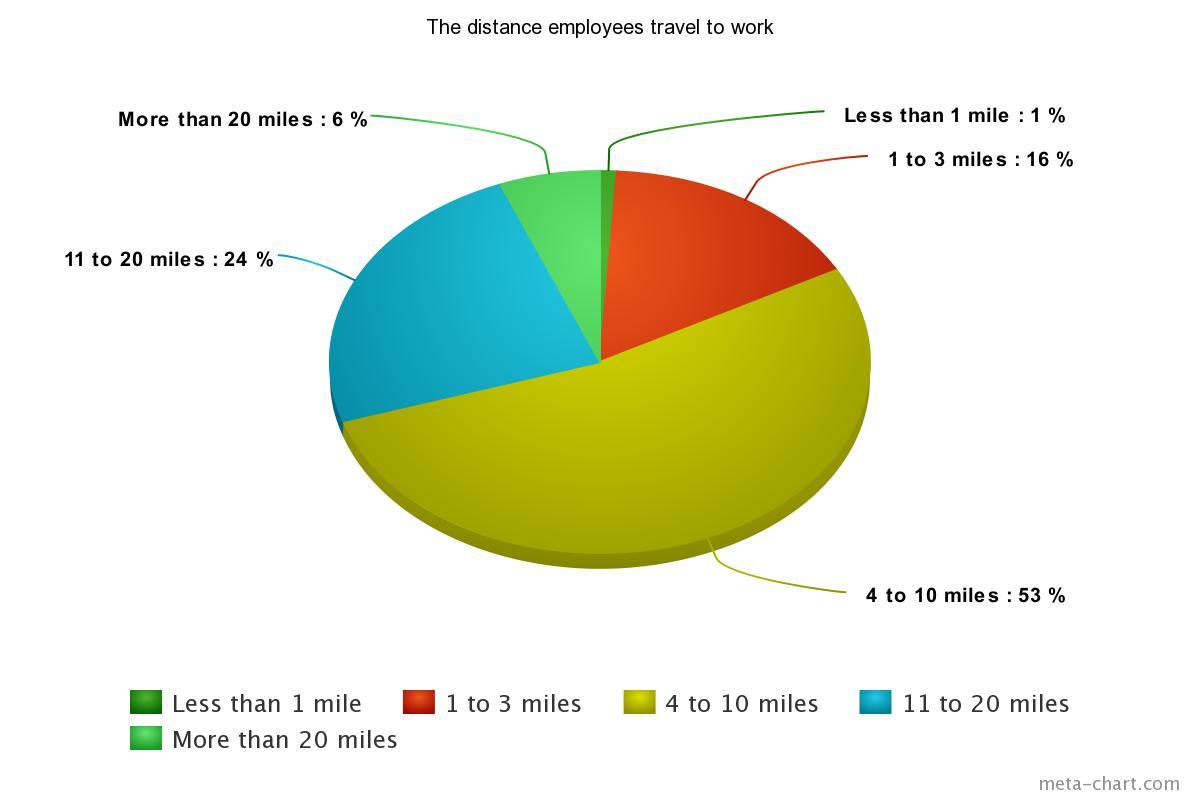
The survey that has been conducted includes five questions devoted to different aspects of the problem. In particular, the survey touches upon the frequency of use of the following transportation options: carpooling or lift-sharing and public transport. Besides, the questions are devoted to factors that can encourage increased use of public transportation, distance traveled every day and the perceptions of telecommuting as an option. The results concerning distance are presented in Figure 1.
Carpooling
Carpooling belongs to the number of transportation habits that are the focus of the survey. As a practice, carpooling is associated with numerous advantages for people with middle income as it allows reducing the amount of fuel used and positively impacts the environment (Song et al. 4). Despite the benefits of carpooling, our research shows that the majority (64%) of Armada’s employees never use this practice. At the same time, almost half of employees (23%) report the frequent use of carpooling. Specific reasons that explain the unpopularity of the option may include increased travel time caused by the necessity to visit a few locations daily. Also, the role of personal relationships cannot be overstated (Yu et al. 141).
Increase the Use of Public Transport
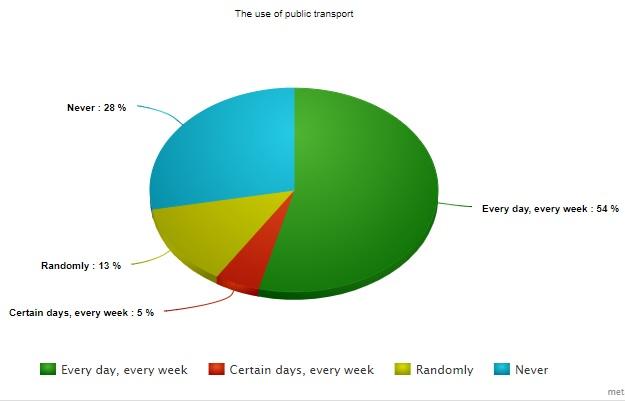
Considering the great role of public transport in the infrastructure of our city, the opinions concerning the use of public transit system were studied. Our research indicates that more than half of employees in Armada, Inc. (54%) use public transport daily (see Figure 2). Less than a quarter of the sample (18%) claim that they use public transport a few times a week or even less often. Finally, 28% of the workforce must never use public transport. Considering the number of people who do not use public transport and carpooling, it is clear that almost one-third of the sample uses private transport, which is the significant reason for growing road congestion daily.
The survey also indicates that the majority of people who never use public transport or do it rarely (41% of the sample) indicate that there are no reasons that could encourage them to take public transportation. Thus, 46% of employees from this group do not appreciate the idea to use public transport at all. At the same time, other respondents indicate the presence of factors that can encourage them to start using public transport. Among these factors, there is increased safety (28%) and reduced fares (31%). Also, 41% of respondents appreciate the idea of reduced commute times.
Telecommuting as a Solution in Specific Cases
Telecommuting is regarded as an option that allows alleviating traffic congestion in the area; despite the seeming simplicity of the decision, unequal opportunities that this decision involves should be taken into account. According to the research, almost half of employees (43%) do not see telecommuting as an appropriate option about the nature of their responsibilities. At the same time, 30% of employees believe that they can work from home randomly. 20% of the sample state that they can work at home a few times a week whereas 8% believe that can use the practice daily. The benefits of telecommuting (such as increased employee happiness) are to be discussed during further meetings with the heads of departments (Asgari and Jin 1).
Strategies
Based on the survey results, an effective strategy reducing employees’ impact on traffic would be based on two alternatives. To implement it, our company will be required to offer safe and affordable transportation services and create a remote work schedule for those who cannot use public transport due to objective reasons such as the necessity to travel more than 20 miles every day or special physical needs that cannot be met with the help of public transport.
Despite increased costs, the decision will allow retaining employees and ensuring workplace flexibility (Coenen and Kok 564). The implementation of the strategy will allow reducing the number of people who use personal transport daily at least by 30%. Within the next six months, our company is to create its corporate transport system with more than thirty buses, and the routes will be created based on employees’ personal information.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Finally, the most appropriate solution based on the survey will be the creation of a corporate transport system for employees. Considering a substantial number of people who cannot use public transport due to different reasons, these people will have an opportunity to discuss their remote work schedule with immediate superiors. Therefore, the company is recommended to do the following:
- Establish a corporate transport system (high quality of transportation + affordable transport cards);
- Provide those with special needs with an opportunity to telework.
Works Cited
Asgari, Hamidreza, and Xia Jin. “Toward a Comprehensive Telecommuting Analysis Framework: Setting the Conceptual Outline.” Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, vol. 24, no. 96, 2015, pp. 1-9.
Coenen, Marja, and Robert Kok. “Workplace Flexibility and New Product Development Performance: The Role of Telework and Flexible Work Schedules.” European Management Journal, vol. 32, no. 4, 2014, pp. 564-576.
Song, Fei, et al. “Feasibility and Issues for Establishing Network-Based Carpooling Scheme.” Pervasive and Mobile Computing, vol. 24, 2015, pp. 4-15.
Stefanello, Fernando, et al. “On the Minimization of Traffic Congestion in Road Networks with Tolls.” Annals of Operations Research, vol. 249, no. 1-2, 2017, pp. 119-139.
Yu, Biying, et al. “Environmental Benefits from Ridesharing: A Case of Beijing.” Applied Energy, vol. 191, 2017, pp. 141-152.