Executive Summary
Risk analysis is a continuous process that requires discipline and effort from the organizations involved. A constant monitoring of both internal and external environment is important to detect the risk factors. Risks lurk in every aspect of the business. They vary from competitor innovations to new technology in the market. These dynamics in the market bring about disruption to the operational consistency in the organization.
Barclays bank, which is the case study of this paper, has strategies to counter both internal and external risks (Barclays bank, 2010). Apart from financial risk, the bank also faces other environmental and social risk in its expansion and operation. The bank has developed environmental and social impact assessment policy to all its branches worldwide and the policy is applied whenever the bank is providing its services to a sensitive sector.
Private consultants who provide the analysis report on potential risks that the bank may be facing normally carry out environmental and social risk analysis. This is done in accordance with World Bank, international corporation finance policies and equator principles that provide the criteria used in dealing with environmental and social impacts that surround financial institutions.
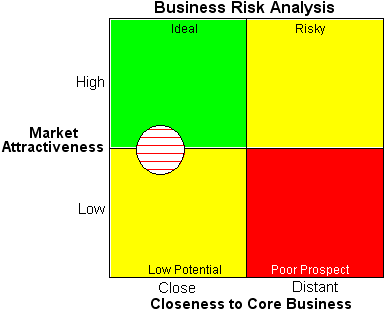
Source: Graig Moteff John rank business risk management.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to assess the risk management strategies and policies utilized by Barclays bank. The study will address
- Risk identification
- Risk assessment
- Risk mitigation
- Risk responsibilities
- Evaluation and reporting
Risk Management Strategy Overview
A risk is the potential of an activity or a process to lead to undesirable outcome. Any human endeavor carries with it a risk, which may be rather difficult to eliminate. For this reason, therefore efforts are normally put in place to mitigate and control the impacts of these risks so that organizations are not adversely affected.
However, there are risks that can be controlled and others that cannot. Risk may be perceived as the probability of bad or good things that may happen to a business depending on the objectives of the business (Porteous & Pradip, 2005).
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing and prioritizing risks factors in order to minimize and control its impact in an organization. The first step in risk management is to identify the kind of potential risk a business is exposed to. This is done by examining the external and internal environment for drivers of the risks.
External drivers will include factors such as competiton, industry changes, government policies, interest rates, foreign exchange and the political environment. Credit and natural disasters.Internal drivers will consist of systems and processes within the organization, security, company’s cash flows and liquidity (Rescher, 1983).
The next stage after identification of risk is to conduct risk evaluation and analysis. This process enables an organization to determine the significance of each risk identified. It also enables the organization develop strategies of action against the risks. Analysis tools in this stage will include PESTEL analysis, S.W.O.T analysis, scenario analysis, industry bench marking, market survey and risk maps. The last step is dealing with the risk.
An organization can accept the risk in some cases that it has no options of overcoming the risk such as in natural disasters. Transfer or avert the risk by insuring the project or venture. Mitigate or reduce the risk by taking preemptive steps (Van Horne & Wachwicz, 2008). This paper will therefore will asses the risk management strategies by Barclays bank (Barclays bank, 2010).
Risk Responsibilities
Every member of an organization has the responsibility of identifying and reporting any potential risk to the appropriate authority within the organization. Most organizations have organs or departments that are dedicated to dealing with these issues. Barclays bank for example has dedicated the responsibility of risk management to environmental and social risk management team.
This team has the mandate of assessing the environment at which the bank operates and identify the risks and social sensitive matters. The team has its head office in London in UK supported by a network of banks representative around the world. The team also offers advice on area of corporate and retail banking which are sensitive in nature.
The team also creates awareness of the Equator Principles framework for project finance transactions within such markets. (Barclays bank, 2010). The bank through the risk management team has identified four major sources of risk from social and environmental analysis. These risks include.
- Market risk: Risk associated by change in market value of asset due to economical factors such as exchange rate, interest rate, inflation, and recession
- Credit risk:-This is the risk perceived that counter party may not meet their obligation as far as credit is concerned
- Operational risk:-results from day to day running of the organization with potential of an activity or a process failing or having a negative results
- Performance risk:-Risk related to employees not using proper guidelines and methods in their workings.
Duties and responsibilities of risk management team include identifying and measuring risks faced by an organization. Risk managers are specialist members of the firm and who posses skills and experience in the risk mitigation. Risk in categories may include but not limited to
- defaults on given by the bank
- losses of banks assets
- losses of investment
- competition
Risk management team therefore has a responsibility to develop policies and procedures to mitigate this risk.
Risk Identification
Risk can be identified in the course of a project life cycle or a business operation. It can also be identified by systematic analysis of both internal and external environment. Identification of risk in an organization is a very important aspect in risk management. It reveals potential uncertainties imminent to the organization.
A company may fail in its success goals simply because of ignoring the risk element in the environment in which it operates. Risk identification reduces the cost of mitigation and enable an organization develop systematic approaches to counter the risk. In Barclays bank, the environmental and social risk management committee is responsible for risk identification.
In identifications of potential risk, Barclays does this through a contracted consultant who assesses both the internal and external environments for indicators of risk. Generally, the consultant will identify financial and social risk in the environment in accordance with the equator principles. The report compiled by the consultant is then transferred to the Risk assessment team for further examination.
In the internal analysis, the tower Perrin approach is used. This approach works with management at each level and tries to identify the risks involved and prioritize on risk factors. This method helps in identifying the risks that are threat to the strategic objective at business, tactical and operational levels.
Value at risk analysis looks at assets return distribution and predicted return values to identify potential risk in the market. Other methods of risk identification may include scenario analysis and expert opinion. In identifying the risk, an organization should consider
- Proper description of the risk factor or event
- Probability of the risk occurring
- Impact schedule i.e. time period the risk would impact on the organization
- Scope impact-the effect the risk will have in the organization
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is the process of determining the chances of a risk to occur and its impact on the organization. Impacts on cost, quality and strategy of the organization are considered in assessing the potential risk factors. The banks risk assessment team is responsible for assessing both the environmental and social risk. A communication line is established between operational managers, lending teams and risk management policy team.
The operational managers will liaise with risk policy team and brand reputation committee to assess the proposed risks. The environmental and social risk management team will provide the guideline for the assessment (Standards Association of Australia, 1999).
The teams will advice on sensitive issues that emerge from the risk identification report for further development. At this point qualitative and quantitative assessment is done. Risk projection by variance and standard deviation are done to see the extent at which the risks pose the threat to the organization (Heldman, 2005).
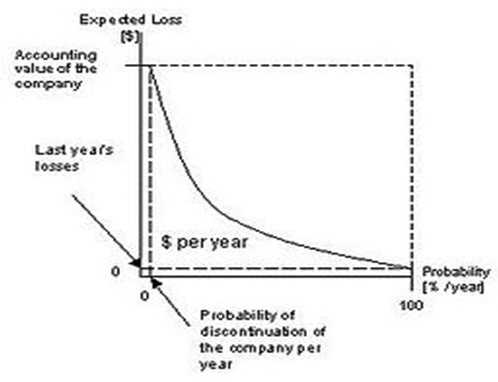
Risk assessment model
Qualitative and quantitative methods of analysis should be utilized at the juncture. Qualitative methods of risk analysis may include tree based techniques, dynamic event tree analysis, dynamic event logic analytical methodology and marcov modeling. Quantitative methods of analysis on the other hand are able to measure the variables of the risk factors. Quantitative methods involve use of variance and standard deviations in measuring the probability of risk occurring (Carol & Sheedy, 2005).
Risk Response
Based on the risk assessment report by environmental and social risk management team, the bank then implements the findings into policies that can transform all the branches of the bank worldwide with risks being categorized into environmental and social. Training is then done to create awareness of the risk assessed (Gorrod, 2004). Risk response may take the following form
- Transference-this involves changing the risk impact to other contractors ie insurance companies.
- Mitigation-these are actions taken to reduce the impact of the risk factors. Such methods may include taking preventative actions and monitoring of projects.
- Avoidance- involves activities that prevent the risks. This may involve changing the kind of project or process that is vulnerable to risk.
- Acceptance-when the risk factor is overwhelming and no other action may be taken to avert the risk; the organization may own the risk and accept its impact to the organization in the event the risk happens.
- Deferment transferring the risk factor to be dealt with later in the future time
Mitigation
Risk mitigation is steps taken to reduce the risk realized as per the assessment report. It involves two plans: (i) identify various means to reduce the impact of the risk (ii) developing a contingency plan incase the risk reoccur in future. Risk contingency plan will develop a blueprint for risk mitigation and assign resources to deal with specific risk.
Mitigation schedule is then initiated. Review and update to the contingency plan is done. In Barclays bank for example, decision is made whether to own the risk mitigate the risk or transfer the risk. This will depend upon the kind of risk realized. Training of employees who are in direct contact with customer is one of the mitigation policies the bank employs.
For technical risks, technical solution to the potential risk is developed by the banks strategic organ to mitigate the risk (Hallenbeck, 1986). In mitigation of risk will include identification of critical point in the organization and mitigation strategies incorporated in this critical point.
These mitigation strategies will form part of organizational procedural guidelines, which later may become standard practice in the organization. In financial institution such as banks, these procedures are referred to as internal control policies (Moteff, 2005).
Risk Monitoring and Reporting
Risk monitoring and reporting is a very important aspect of risk management. The risk management policy is constantly reviewed and environmental and social social team discusses any necessary change and relevant changes are made. Group brand and reputation committee is responsible for reporting any perceived or potential risk that the bank might be facing to the risk management team.
The committee is also responsible for monitoring and evaluating the risk policy adopted by the bank. Review of risk management strategy is continuously reviewed to determine its effectiveness in dealing with potential risks. Review of the risk monitoring is also important to detect the trigger event that lead to the occurrence of this risk. This will enable the organization in future to manage risk effectively.
Risk status reports should be delivered to risk management team regularly. Risk management should be a continuous process in the life cycle of a project. Risk management process involves risk identification, planning, analysis; monitoring and control of the risk factors must be a priority of an organization.
A risk management strategy must have an objective of reducing the chances and impact of the risk in an organization and should form part of organizational policies. This way the organization will be best prepared for future unforeseen misfortunes.
Risk contingency planning
A risk contingency plan is a detailed process to address immediate unforeseen risk. An organization having a contingency plan ensures that future risks are dealt with. A risk contingency plan will need a project manager to
- Putting in place enough resource in terms of human capital, material resources and finances to deal with unforeseen future uncertainty
- Criteria in dealing with the risk
- Develop training material for dealing with the risk
- Develop a contingency plan schedule
- Review of contingency plan
Contingency plan enables an organization to ensure viable capability of a firm to respond to future risks. Enable the support and communicate with employees on measure to mitigate future risk in an organization.
References
Barclays bank, (2010) Case Studies. Web.
Barclays bank, (2010) Social and environmental risk governance. Web.
Barclays bank, (2010) Social and environmental risk management in lending. Web.
Carol, A. & Sheedy, E. (2005). The Professional Risk Managers’ Handbook: A Comprehensive Guide to Current Theory and Best Practices. PRMIA Publications.
Gorrod, M. (2004) Risk Management Systems: Technology Trends. Finance and Capital Markets. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Hallenbeck, W. (1986) Quantitative risk assessment for environmental and occupational health. Chelsea, Mich: Lewis Publishers.
Heldman, K. (2005) Project Manager’s Spotlight on Risk Management. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons.
Moteff, J. (2005) Risk Management and Critical Infrastructure Protection: Assessing, Integrating, and Managing Threats, Vulnerabilities and Consequences. Washington DC: Congressional Research Service.
Porteous, B. and Pradip, T. (2005) Economic Capital and Financial Risk Management for Financial Services Firms and Conglomerates. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Rescher, N. (1983) A Philosophical Introduction to the Theory of Risk Evaluation and Measurement. New York: University Press of America.
Standards Association of Australia, (1999) Risk management. North Sydney: Standards Association of Australia.
Van-Horne, J. & Wachwicz, J. (2008) Fundamentals of financial management: tools of financial analysis, 13 Ed. Boston: Pearson international edition.
Appendices
Risk Activity Responsibility
Framework of risk management
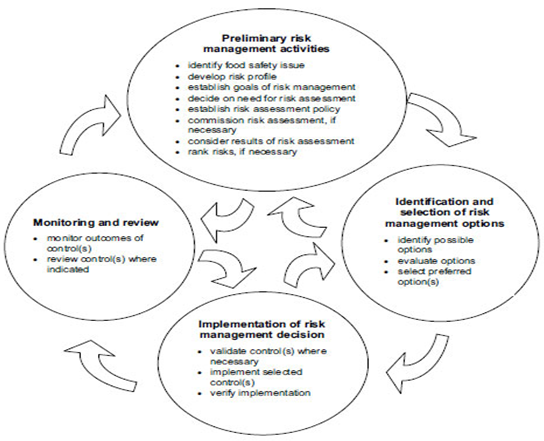
Risk assessment model

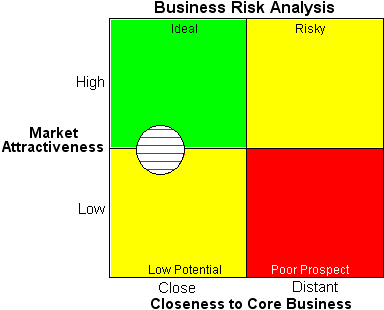
Business risk model