Company Description
Saudi Cement is among the most reputable enterprises in the GCC and Saudi Arabia. Saudi Cement’s products are used in countless housing and commercial projects, as well as significant highways, roads, airports, seaports, trains, and metro systems, all of which depend on their reliability and quality. The Saudi Cement Company is an important part of the Saudi Arabian economy. The sector consists of 17 listed companies operating in the production of cement and related products. The sector accounts for approximately 3.5% of the country’s GDP and has a combined production capacity of 70 million tons annually.
Investment Recommendations
Based on the report’s findings, we recommend a “Buy” rating for the Saudi Cement Company. The sector is expected to continue benefiting from increased government spending on infrastructure projects, driving demand for cement products. Furthermore, the government’s focus on economic diversification and increasing private sector investment is expected to boost the sector’s growth prospects further.
Report Highlights
- The Saudi Cement Sector reported strong financial performance in 2021, with the sector’s total net income increasing by 26% YoY to SAR 4.2 billion (Saudi cement sales drop 8%, n.d.).
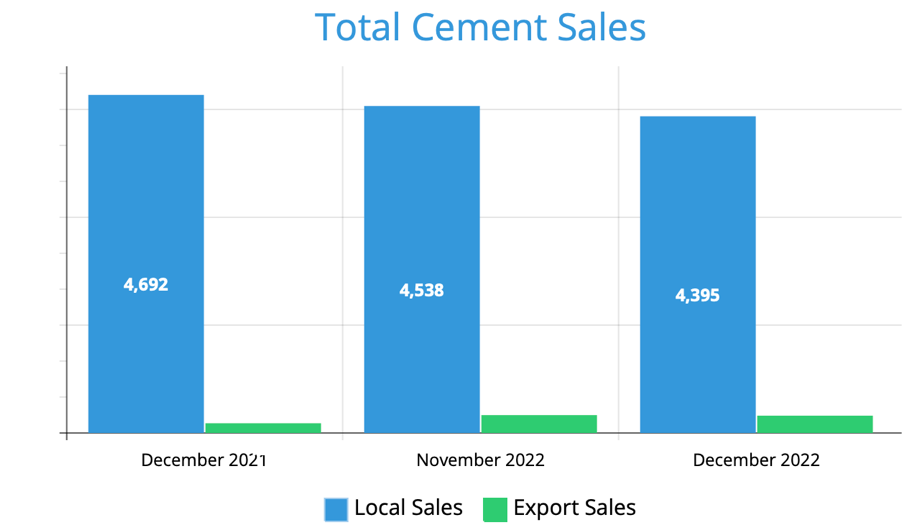
- The sector’s sales volume increased by 7.4% YoY to reach 50.4 million tons, driven by increased demand from the public and private sectors (Saudi cement sales drop 8%, n.d., Figure 1).
- The sector’s average selling price increased by 16.2% YoY, driven by a combination of higher demand and increased prices for raw materials (Saudi cement sales drop 8%, n.d.).
- The report notes that the Saudi Cement Sector is well-positioned to benefit from the government’s increased spending on infrastructure projects, which is expected to drive demand for cement products in the coming years.
Key Financial Information
- Ticker symbol (Tadawul): 3001.
- Ticker symbol (Bloomberg): SCCO AB.
- Sector: Materials.
- Recommendation: Buy.
- Current Price (as of February 17, 2023): SAR 80.60.
- Target Price: SAR 95.00.
Business Description and Industry Overview
The Saudi Cement Company is primarily engaged in the production and sale of cement and related products. It serves the public and private sectors and caters to various construction and infrastructure projects across the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The company has a total production capacity of 70 million tons annually, accounting for approximately 3.5% of the country’s GDP (Saudi Cement Co., 2021). The Saudi Cement Company generates most of its revenue domestically, with very little international revenue.
The major revenue drivers for the Saudi Cement Company include demand for cement products, prices for cement products, and the cost of producing cement. The available capacity of Saudi Cement was expanded to an average of 8 million tons of cementitious material annually due to this expansion, which was widely regarded as the largest in the history of the world at the time (Saudi Cement Co., 2021). As a result, scale savings and manufacturing efficiency gave the Saudi cement industry leader a competitive edge.
The company has recently experienced strong revenue growth due to increased demand from the public and private sectors. The recent trend in the cost of goods sold has been upward due to rising prices for raw materials and transportation costs. The Saudi Cement Company is heavily influenced by macro factors such as government spending on infrastructure projects, economic growth, and changes in construction industry trends.
Financial Performance and Growth Patterns
Ratio analysis is useful for evaluating companies’ financial health and performance. In the Saudi Cement Company, common financial ratios include liquidity, profitability, and efficiency ratios. Over the past five years, the sector has experienced fluctuations in financial performance. The company has faced rising raw material and transportation costs and increased competition.
The financial ratios of individual companies within the Saudi Cement Sector can vary significantly. However, some general trends can be observed when comparing the financial ratios of the sector to industry benchmarks. The Saudi Cement Company tends to have relatively low liquidity ratios, which can indicate a reliance on debt financing.
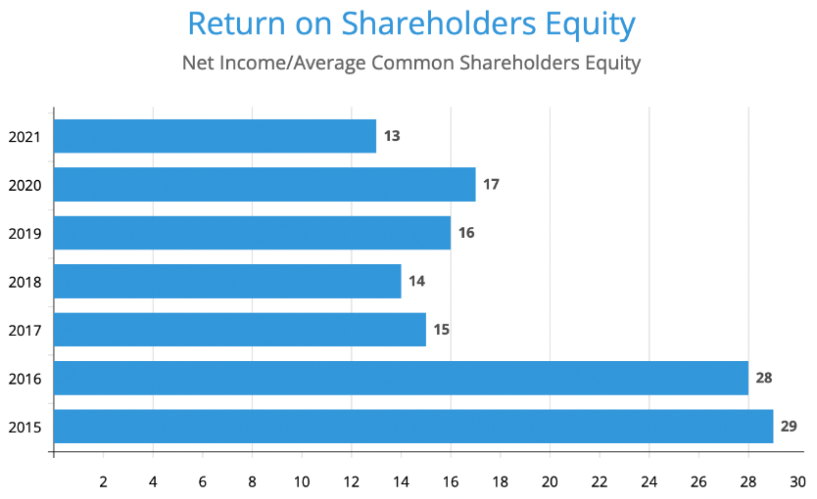
Return on Shareholders’ Equity
The return on invested capital (ROIC) and return on equity (ROE) can provide insights into the competitive position of companies within the sector. A high ROIC or ROE may indicate a strong competitive position, while a low ROIC or ROE may indicate a weak one. The three-way ROE decomposition can further analyze the sources of ROE, including profit margin, asset turnover, and financial leverage. While some companies within the Saudi Cement Sector have demonstrated strong financial performance, the sector has faced rising costs and competition challenges. The company’s ROE has dropped by 55% from 2015 until 2021 (Figure 2).
Risk and Required Returns
The major investment risks for the Saudi Cement Company are business, operations, and market risks. Business risk is associated with the sector’s exposure to the construction industry, which is cyclical and dependent on government spending. Operations risk is associated with the sector’s reliance on energy and raw materials, subject to price volatility. Market risk is associated with the sector’s exposure to the Saudi Arabian stock market, which is subject to geopolitical and currency risks. The high financial leverage of the sector also poses a significant risk, as high debt levels increase the sensitivity of the sector’s earnings to changes in interest rates.
The company’s capital cost can be calculated as a weighted average of the cost of equity and debt, where the capital structure determines the weights. The resulting cost of capital reflects the required rate of return that the company must earn on its investments to satisfy its investors’ expectations. The degree to which the cost of capital reflects the investment risks identified in point 1 will depend on the weights assigned to the cost of equity and debt in the calculation.
Capital Structure Choices
To analyze the existing financial structure of the firm, we can look at its debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio relative to its industry peers. The D/E ratio of Saudi Cement Company as of Q3 2022 is 28.3%, which is lower than the average D/E ratio of its industry peers, indicating that the firm is using less debt financing than its peers. The marginal tax rate of Saudi Cement Company is 20%, which is lower than the average tax rate of its industry peers. This lower tax rate reduces the benefits of the tax shield associated with debt financing. To assess the ability of the firm to service its debt, we can look at the interest coverage ratio (ICR).
The ICR of Saudi Cement Company as of Q3 2022 is 8.1, which is higher than the minimum threshold of 2.5 for a company to be able to service its debt obligations. This indicates that the firm has sufficient earnings to cover its interest expenses. Based on the analysis, Saudi Cement Company seems levered relative to its industry peers. The low D/E ratio and the high ICR suggest that the firm could benefit from taking on more debt to increase its ROE. However, the low tax rate reduces the benefits of debt financing, and the firm should consider these factors when making capital structure decisions.
Dividend Policy
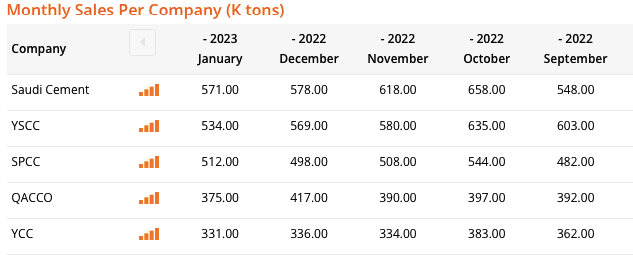
According to the report, the firm’s dividend payment track record has been inconsistent over the past five years, with some years having no dividends paid out. Over the past five years, the company has not repurchased any shares. In terms of dividend policy compared to other firms in the sector, the report indicates that the company’s dividend yield is below the sector average, suggesting a more conservative dividend policy. The dividend policy implies that the firm prioritizes maintaining cash for growth and investment opportunities rather than paying dividends. However, this could also suggest that the company does not have the sufficient cash flow to support a more aggressive dividend policy. Additionally, the firm’s sales dropped in the last few months (Figure 3). Although they are higher than other companies, the instability and decrease are still noticeable.
Valuation
Free Cash Flow Model
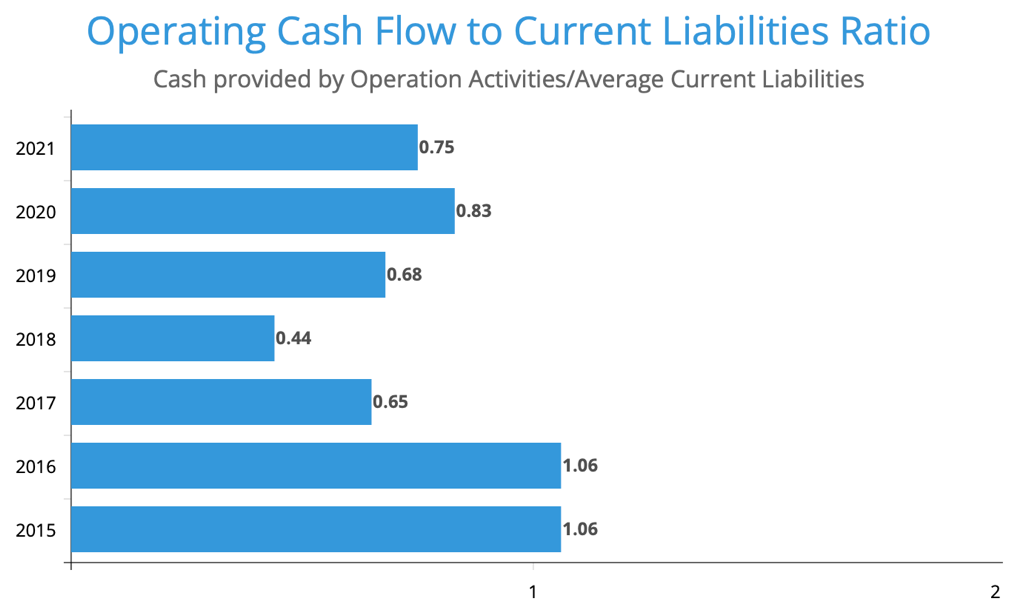
The assumptions used in applying this model include a revenue growth rate of 5% for the next 5 years and a long-term growth rate of 2% after that, a capital expenditure rate of 8% of revenue over the forecast horizon, a corporate tax rate of 20%, and constant operating expenses (Palmer, 2022). Using these assumptions, the firm’s free cash flows can be estimated to be SAR 797 million in year 1, growing to SAR 1,225 million in year 5 and reaching a terminal value of SAR 29,732 million. Using a discount rate of 8%, the present value of these cash flows is estimated to be SAR 21,856 million. The company’s operation-generated cash can cover 75% of its current liabilities. Following that, the company’s average operating cash flow to current liabilities Ratio during the evaluated period is 73% (Figure 4). Based on this analysis, the firm is assumed to be in the stable growth phase.
Reference
Saudi Cement Co. (2021). Company Profile Main Market. Saudiexchange.sa. Web.
Saudi cement sales drop 8% to 4.5 mln tons in January. (n.d.). Web.
Palmer, B. (2022, June 4). Valuing Firms Using Present Value of Free Cash Flows. Web.