Abstract
Saudi Arabia has been confronting issues with finishing infrastructure projects on time and cost. It has been recorded that 85% of complex infrastructures are delayed for several reasons. Studies have distinguished the low-offer bidding technique as a critical factor in causing such deferrals. The low-bid framework overlooks other aspects that are vital to project performance and delivery. Thus, contextual analysis was performed recognizing the reasons for projects postponements and cost overruns. Literatures were reviewed in accordance with the proposed model. The construction division in Saudi Arabia is the biggest and quickest developing business sector in the Gulf Area. This solid monetary position has urged the Saudi Government to take the chance to actualize complex infrastructure projects. In the last seven years, Saudi Arabia has been encountering a development blast, with more than 23,500 progressing projects and the estimation of every single current undertaking totaling US$ 869 billion. However, project delays and cost overruns affect the economy. Since the NPMO is in charge of restructuring project management practices, it is normal that the organization understands the challenges ahead. By implication, the proposed best practices in mitigating project delays and cost overruns can be categorized in two folds.
The main sort is the national difficulties, where implementation practices help in keeping all activities adjusted to the national procedure and take an interest in accomplishing it. The organization must detail those activities to help in promoting effective leadership. Secondly, NPMO can give proposing controls, which bolster better task administration adjustment. The second kind of difficulties is the task administration procedure, where the NPMO can help in enhancing these practices by supporting the utilization of important information, aptitudes, instruments, and techniques. This may incorporate working with instruction services, preparing organizations, and leagues. Project management is a basic administrative field to figure and execute procedures and best practices. Therefore, project management professionals ought to urge their Government to play a concentrated part in enhancing infrastructure management. This part may vary in view of the national designs and the national task administration development. Consequently, we proposed the BV PIPS model for project approval. In an examination of many contextual analysis and the aftereffects of BV PIPS, Saudi Arabia’s bid framework was recognized as a potential reason for project challenges.
The present framework was investigated and altered to the BV PIPS. The proposed contract framework utilizing BV PIPS, which can be executed in Saudi Arabia, was made with proprietor side. Besides, the study demonstrated that contractors and investors would benefit from the new proposal. Based on the proposed model we can summarize the benefits of BV PIPS. The proposed model will enable stakeholders give careful consideration to project implementation. Planning is the most fundamental segment of project management and the greatest weapon against cost overruns and delays. Therefore, stakeholders must analyze the project scope, which is documented for referral purposes. The proposed model assists the organization to evaluate each bid based on the contractor’s performance. In numerous intricate undertakings, you may need to use external contractors to do some portion of the project. Before you employ a merchant, consider previous performance, logistics delivery, delivery date implementation, and project quality. Mandating the country’s NPMO to organize the project management practice would regulate the project scope. Battling extension implementation is the greatest test for a project chief. The engineers need to include their preferred designs, the customers begin requesting things that were not initially approved, and the testing group needs an adjustment in a portion of the design. While a portion of the progressions may be called for, an uncommon design adjustment may cause delays. Thus, the NPMO must control and persuade to avoid delays and cost overruns.
Introduction
For complex infrastructure projects, the capacity to adjust is the distinction amongst progress and delays. Complex infrastructure projects experience the ill effects of critical under management throughout the project life cycle. Poor evaluation, for instance, contracts with the developers and agents, design, and material requirements, to mention a few. The organizing and conveyance of complex infrastructure projects are challenging and complex. The life span of these undertakings requires a methodology that suitably mirrors the vulnerability and delays. Complex infrastructure projects include countless partners entering the undertaking life cycle at various stages with various parts, obligations, administrative abilities, risk bearing limits, and clashing interests. While the many-sided quality of these activities requires division of parts and duties among very specific players, this prompts dangers among stakeholders that emerge during the project life cycle. Project delays are pernicious bringing about time overwhelm, cost overrun, disagreements, legal tussle, and infrastructure abandonment. By implication, these complexities affect project time, expenses of non-beneficial laborers, administrators, and hardware, costs caused by disturbed development and material delivery and extra overhead costs.
The construction division in Saudi Arabia is the biggest and quickest developing business sector in the Gulf Area. This solid monetary position has urged the Saudi Government to take the chance to actualize complex infrastructure projects. In the last seven years, Saudi Arabia has been encountering a development blast, with more than 23,500 progressing projects and the estimation of every single current undertaking totaling US$ 869 billion. In spite of this noteworthy spending profile, a United Nations Development Program Report showed that Saudi Arabia was not advancing in executing compelling administration and accomplishing complex infrastructures (Elawi et al. 2016). This was unmistakably exhibited by the quantity of undertaking enduring delay, which expanded from 900 construction projects in 2010 to 5000 in 2015 (Elawi et al. 2016). The issues experienced on project delays in Saudi Arabia have been caused by the low level of customer association amid a significant number of the most venture exercises. The absence of customer association in the development of open tasks has been distinguished as the fundamental driver of numerous operational issues, for example, cost overruns, project disputes, design blunders, vulnerabilities in plans and details, and expanded support costs.
This exploration will endeavor to examine primary contributing components causing project late conveyance and spending cost. Likewise, the paper will propose remedies to address such factors utilizing successful management structure, project administration approach and undertaking administration best practices to limit as well as wipe out these impediments. The examination recognizes techniques for improving project management procedures and prompts the proposition of approaches to enhance the current unacceptable circumstance, with a specific goal to have positive results in Saudi infrastructure projects.
Background of the Proposal
Project management procedures can be defined as the utilization of learning abilities, devices, and systems to extend exercises to meet the task necessities (Elawi et al. 2016). In any case, since project management alludes to the three areas, which include program, task, and portfolio, the word project specified in the description covers the three domains. Another area to be viewed as a fundamental piece of project management procedures is “benefit management”. It includes recognizing, investigating and arranging, conveying, transiting and managing benefits (Elawi et al. 2016). Receiving benefit management will help in crossing any barrier between procedure definition and project management. Another hole that can be evaded by benefit management is the misalignment between project administration and operations administration (Al-Sultan 1987).
In view of the above discourse, project administration practices can be re-imagined as applying the learning, aptitudes, instruments and strategies to extend, program, portfolio, and benefit to every single related movement to get the key objectives. Establishing project management practices can be viewed as a brief task of building an arrangement of approaches. NPMO additionally can be viewed as a continuous activity, which gives autonomous confirmation on complex infrastructure projects. Likewise, it bolsters partners and enhances the way they oversee and deliver infrastructure projects. For government and private divisions to organize and keep their upper hand, a dynamic system and light-footed execution ought to be embraced. From a procedural perspective, methodology creation can go in sequences, and each cycle can be overseen as an undertaking since it is an impermanent task and will deliver a remarkable record (Elawi et al. 2016). Along these lines, project management procedures will enable them to deliver their methodology record in a proficient way.
Consequently, project execution contains general operations and setting up new activities. The operation group will be influenced by the management practices, because any improvement in the operation must be monitored. Consequently, a base level of project management responsiveness is required for team members, while the activities’ groups are required to extend administration practices to deal with their drives. Because of this dialog, it is vital for all groups to rehearse project management at various profundities, in view of their needs. It ought to be a crucial piece of any specialized ability.
The Mandate of the National Project Management Organization in Saudi Arabia
Since the NPMO is in charge of restructuring project management practices, it is normal that the organization understands the challenges ahead. By implication, the proposed best practices in mitigating project delays and cost overruns can be categorized in two folds. The main sort is the national difficulties, where implementation practices help in keeping all activities adjusted to the national procedure and take an interest in accomplishing it. It likewise will continue detailing those activities to help basic leadership. Secondly, NPMO can give proposing controls, which bolster better task administration adjustment. The second kind of difficulties is the task administration procedure, where the NPMO can help in enhancing these practices by supporting the utilization of important information, aptitudes, instruments, and techniques. This may incorporate working with instruction services, preparing organizations, and leagues.
NPMO administrations come as the aftereffect of its capacities. These capacities initially were gotten from the NPMO key goals. It is a reason to review project management practices and adjust contract opportunities to the vital destinations, which are nation-based and associated with economic conditions. Therefore, it will position the NPMO accurately to contribute in conquering the national difficulties as discussed in this proposal. The mandate of NPMO addresses infrastructure project challenges at a national level. In this manner, it is important to comprehend current practices. That is precisely the importance of task administration development. Notwithstanding the present national development in Saudi Arabia, NPMO ought to characterize what development level the nation should target and how. It is normal to have an assortment between various elements of the development. Government and private sectors must demonstrate distinctive adherence to best practices. Nevertheless, the fundamental point of measuring national project development is to guarantee effective and efficient services, which is influenced by the NPMO.
In view of the proposal to national evaluation, NPMO management will endeavor to support all zones. Therefor the proposal will enhance quality management practices and mitigate project delays and cost overruns. The benefits will be summarized below.
- Enable task administration application by gathering abilities, information, instruments, and strategies.
- Suggest regulations and arrangements, which empower project management.
- Monitor and regulate national tasks and project execution.
- Encourage development change by adjusting or making development display.
- Create project management center and repertory to catch, make, bind, and share data and best practices.
Project management is an administrative field to execute procedures and best practices. Therefore, project management professionals ought to urge their Government to play a concentrated part in enhancing infrastructure management. This part may vary in view of the national designs and the national task administration development.
Saudi Arabia (SA) has been encountering a development blast for as far back as three decades. The construction sector is thought to be a major business, evaluated to be worth more than $4.9 trillion yearly (Price and Al-Otaibi 2010). The Saudi project has been recognized as the biggest in the inlet nations as the country spent $775 B on development ventures from 2008-2013. For 2014, the Finance Ministry designated $92 billion for development ventures and $104 billion for 2015. In 2016, $232 billion was spent on government development ventures. Numerous analysts have judged the execution of the Saudi development industry as low. Previous studies have recognized that 60% of open projects in Saudi Arabia encounter delays (Price and Al-Otaibi 2010). An investigation revealed that the normal defer rates varied from the first contract terms in Saudi Arabia by 15% to 35% and in another examination by 49% (Elawi et al. 2016).
Moreover, 70% of general infrastructure projects in Saudi Arabia confronted cost overruns (Al Turkey 2011). Thus, the non-performance of projects in Saudi Arabia has more than $147 billion in question. Past examinations demonstrated that a standout amongst the most critical components for the postponements was the low-offer criteria. By implication, contract workers were chosen in view of cost alone, disregarding worker’s efficiency pattern. Notwithstanding the construction delays, there were likewise costs issues. In this proposal, defer factors, cost overruns, and the low-offer criteria were examined. Thus, we proposed the Best Value Performance Information Procurement System (BV PIPS).
Problem Statement for the Proposal
Postponements in conveying infrastructure projects on time can make significant issues to investors, the government, and the economy. It has a genuine influence on money related responsibility, investor’s image, and the environment. The postponement in project delivery in Saudi Arabia is worsened because of sharp change in the cost of the materials. Al-Khalil and Al-Ghafly (1999) recognized that, task proprietor inclusion, contractor capabilities, design outline, and project framework are vital elements for project delay in Saudi Arabia. The author examined delays in public sewage projects. As a result, delay components were coded and categorized for analysis. The author concluded that project delays occur most in government awarded contracts. Imperative causes are financial issues, changes in the plan and extension, delay in settling on choices and endorsements by the proprietor, troubles in obtaining work permits, and coordination and correspondence issues.
Abu Nemeh (2012) argued that contractor’s performance is a significant reason for delay. Thirteen (13) noteworthy measures were considered. These measures are identified with contractual worker resources and abilities. He distinguished contractual worker execution as one of the real reasons for delay in projects in Saudi Arabia. Al-Khalil and Al-Ghafly (1999) talked about the primary driver of disappointment in the Construction industry in Saudi Arabia by studying 68 contractors and around 34 unique reasons for disappointment. The examination presumed that absence of experience, poor estimation rehearses, awful decisions in controlling organization’s strategy, and national droop in the economy are the extreme variables. Elawi et al. (2016) considered the primary driver of postponement in complex infrastructure projects. The review secured an arbitrary example of contractors, consultants, and proprietors. They assembled the delay causes into nine noteworthy categories. The groups include financing, materials, legally binding connections, changes, government relations, labor, planning and control, hardware, and environment.
Past investigations have demonstrated that construction execution in Saudi Arabia is poor. Acquisition framework is viewed as a fundamental factor that can expand the execution of undertakings (Elawi et al. 2016). Government delegates normally construct choices in light of cost when they obtain development ventures. Past examinations have demonstrated that low-offer is viewed as a noteworthy reason for development venture delay in Saudi Arabia (Elawi et al. 2016). At the point when contractual workers are chosen, the main concentration is cost. These low-offer tasks are influenced by substandard execution and postponements, which regularly prompts expanded expenses. The legislature of Saudi Arabia has burned through billions of dollars on development undertakings, and they select contractual workers as indicated by the most reduced offer. Nevertheless, these tasks are frequently influenced by taken a toll overwhelms. This demonstrates an inconsistency in how contractual workers are chosen in light of the fact that the framework depends on cost criteria, however this prompts extra spending amid the execution stage. Expanding venture execution in Saudi Arabia requires reexamining the acquirement conveyance framework.
Proposal Framework
- BV PIPS can manage essential delay causes in Saudi Arabia.
- The foundation of choosing project contractors in light of the most reduced offer does not mirror the genuine cost of activities.
- The NPMO must acknowledge and actualize the best practice execution framework (BV PIPS) in Saudi Arabia.
Objectives of the Proposal
- Recognize vital delay causes in national projects
- Show how BV PIPS can manage imperative delay components to enhance complex infrastructure in Saudi Arabia.
- Educate project owners to understand that choosing contractors based on cost causes poor execution of substandard development and cost overruns.
- Utilize BV PIPS model to distinguish how to expand construction industry execution in Saudi Arabia.
Literature Review
Infrastructure projects in Saudi Arabia have been confronted with performance issues. As per Al Turkey (2011), 75% of Saudi national projects were faced with delays. The authors revealed that poor estimation techniques and a deficiency project skill influenced construction delays. Some researchers evaluated complex national task to discover the reasons for delays in Saudi’s utility tasks. They explored among the proprietors, advisors, and project contractors understand who was in charge of task delays. They found that 65% of projects done between 1985 and 1994 were delayed. The proprietor and the advisor frequently accuse the contractor for project delays. However, contractors blame the proprietor and consultant for postponing completion timeline (Al Turkey 2011). Moreover, postponed ventures affect both the proprietor and contractor. The proprietor loses income in view of the uncompleted task, which drives him or her to lease transitory premises. Consequently, contractors additionally acquire overhead expenses, which shield them from getting another task (Assaf and Al-Hejji 2006).
The study revealed that government authorities, as proprietors of construction projects are influenced by disruptions in improvement designs, money related execution design, and restive communities where the project is situated. Consequently, site contractors are impacted through expanding time of venture, expanding overhead cost, and thwarting contractual worker from other business opportunity (Al-Kharashi and Skitmore 2009). It is important to note that project stakeholders expect to finish developmental projects on time. However, numerous past investigations discovered main considerations that influenced project performance on construction sites. Al-Karachi and Skitmore found around 112 components that cause project delays. They likewise got around 39 more factors from respondents in their investigation. Thus, we grouped the related causes in four levels: proprietor related causes, contractual worker related causes, advisor related causes, and other-related causes.
Vital Delay Causes in Saudi Arabia
Proprietor Related Causes
Proprietors assume a dynamic part in lessening venture delays. In this way, project period is thought to be a delay component. The proprietors cannot anticipate to what extent tasks will take (Mahamid 2013). Expansion time is one of the proprietor related deferred factors. Surveys show that proprietor endorsed expansion time on 87% of ventures (Mahamid 2013). Moreover, proprietors put off capital installments to different gatherings, which turns into another defer factor (Mahamid 2013). Another examination found that construction orders changed by the proprietor upset contractual workers’ calendars; causing project delays (Al Turkey 2011). Additionally, auditing and reconciling project records and expenditures prompted the deferment of activities. Additionally, suspension work on development projects by the proprietor influences the task’s execution. Therefore a bidding process can be viewed as a noteworthy factor that prompts the accomplishment of activities. Low-tender criteria, which is the framework in most Middle Eastern nations, is likewise viewed as a purpose behind the pervasiveness of task delays in Saudi Arabia (Al Turkey 2011).
Contractor-Related Factors
Studies reveal that the primary drivers of project failures were ability deficiencies, poor estimation practices, and poor leadership (Al Turkey 2011). Therefore, project delay is a contractor-related deferred factor when the contracted workers lack foresight and booking aptitudes. Qualified site engineers may counteract venture delays because of their experience, learning, and capacity to handle a prepared workforce. The authors discovered many variables identified with site contractors, for example, clashing perspectives about subcontractors’ timetables in construction projects and poor subsurface conditions. A few site contractors do not expect the most noticeably awful things that could occur on the work site, for example, a high water table.
Another examination found that inadequate leadership, experience, and a deficiency of labor are significant reasons for venture delays. Poor site administration and supervision are likewise consistent with findings in previous studies on project delays and cost overruns. In addition, when a site contractor has income issues, it will normally influence the task’s culmination.
Advisor-Related Causes
Investigations uncovered that a portion of project delay elements can be connected to an advisor. A project advisor stands as a consultant and liaison that mediates between the contractor and proprietor. Therefore, an advisor or consultant influences project delays by creating configuration archives, evaluating, and approving site designs and records. In addition, consultants are associated with various variables that cause delays, for example, neglecting to discover slip-ups and errors in design records and inflexibility about arrangements. Furthermore, advisors or consultants need large amounts of involvement, keeping in mind the goal to play out their parts. Thus, construction task requires many site consultants to avoid inefficiency and delay tactics.
Other-Related Causes
It is difficult to order a few factors under the three fundamental classes of proprietor, contractual worker, and advisor. For instance, a postponement in material delivery is viewed as a factor that has a level of effect on project length. In construction projects, although it is hard to facilitate among stakeholders, correspondence and coordination improve the odds of accomplishing complex activities. Consequently, corruption causes delay projects and cost overruns. Government fraud, which is supervised by project personnel, causes delays for personal gains.
Low-Bid Technique and Cost Overruns
Project analysts have recognized that the utilization of an offer delivery strategy in light of low costs is a primary driver of cost overruns in Saudi Arabia. Choosing a site contractor based on budget cost is the most noteworthy factor of delays in task completion. As indicated in previous literatures project quality and time are not seen as being as imperative as low-bid offers. Task execution is influenced when contractors are chosen to reduce budget cost while disregarding time and quality (Holt et al. 1995). In the United Kingdom, the Finance Boards utilized performance bid form to evaluate contractors in view of a low-offer delivery framework, and results demonstrated that the bid costs were not huge (Wong et al. 2000). Besides, an examination distinguished that, paying little attention to the most reduced offer, the choice of qualified contractors among different bidders would positively affect project execution and cost (I Wong et al. 2000). Alternately, when site engineers are selected based on cost, unfit contractual workers are urged to submit offers (Wong et al. 2000). Therefore, national projects awarded to qualified contractors would expand the achievement rates of undertakings (Plebankiewicz 2009).
The choice of qualified suppliers is troublesome, as project proprietors confront multifaceted issues during the time spent settling on decisions in choosing qualified contractors (Elawi et al. 2016). Likewise, in Saudi Arabia, the choice of qualified contractors is influenced by numerous hindrances, for example, the trouble of basic leadership due to inexperience, absence of competent specialists, and hierarchical worry of accomplishing specific design, delivery time, and budget plan (Elawi et al. 2016). Another investigation recognized that the determination of qualified contractors is a test for the proprietors’ selection team, which directly affects the level of fulfillment and project performance (Price and Al-Otaibi 2010).
Specialists in the Saudi project sector have discovered that the contractor-determination technique does not meet customers’ desires, which influence many issues, for example, cost overruns, contractual worker disappointment, expanding changes, and low quality (Abu Nemeh 2012). Consequently, contract adjustments, cost overruns, temporary worker indebtedness, and substandard quality are caused when inadequate site engineers are granted undertakings by presenting the least cost.
An investigation revealed that bidders mean to win by presenting the minimal offer when the criterion is based on cost (Abu Nemeh 2012). Nonetheless, the likelihood that the real expenses of tasks are hidden increases if a cost-based determination is considered (Olaniran 2015). Another examination demonstrated that a contractor who has the minimal offer as a rule presents a gauge that is lower than the task’s budget (Abu Nemeh 2012). Thus, bidding with least value sum confronts benefit and misfortune issues.
To win complex infrastructure using a low-offer delivery strategy, bidders have utilized a few procedures. A few bidders endeavor to find botches in the offering reports to help them in rolling out improvement requests and claims for additionally work. The term savage offering alludes to this approach, which is utilized to decrease project misfortunes. Hence, the real expenses are not reflected in some low-offer activities in light of the ceaseless request changes and claims that bidders utilize (Abu Nemeh 2012). Contractors use the technique to balance the misfortunes made by presenting a lower offer. Olaniran (2015) reviewed 54 development specialists to recognize the reasons for low venture execution identified with cost-based selection. Out of 22 distinguished causes, the most noteworthy positioned cause was that bidders decreased their overall revenues. The second reason was the low level of task control used by numerous site engineers. The third reason was the inadequacy of selected contractors. Subsequently, project performance can be influenced when contractual workers reduce their net revenues.
GCC Review
While reviewing literatures that described different circumstances and results of postponements in Saudi Arabia and other Gulf countries, researchers raised major concerns. The meaning of deferral in infrastructure industry is the time overrun in the undertakings that is approved by stakeholders. For the investor/proprietor, time defers causes loss of income. This is because of the nonappearance or deferral in funds generated from the proposed development after delivery. For a contractor, project delays cause cost overruns because of the remuneration of wages for delayed time, overabundance employ charges for plant and hardware, material and space use, loss or damage of project materials, and inflation. Any project lifecycle can be characterized into three classes, which include conceptualization/pre-development stage, plan, and the development stage. A large portion of the reasons for delays occurs amid the development stage because unexpected dangers are constantly included (Olaniran 2015). Different delay elements could be ordered in view of the immediate and aberrant outcomes upon the money related budget of the undertaking. Delay components could be sorted into forgivable and unpardonable postponements. Unpardonable deferrals are the ones caused solely by the supplier, sub-contractual workers, or material vendors. There is no pay to the contractor worker for this situation and the contractor is obliged to continue with their activity or pay for the damage to sold items. However, if damages are excluded in the contract agreement, payments could be made to the contractor as genuine expenditures.
Excusable project postponements are non-compensable, which are caused by different agents for example, sudden acts of the administration, project termination, natural disasters. The supplier in these cases does not have the privilege for budgetary remuneration; however, they have the privilege to time expansions. The second sort of understandable deferrals are compensable, which is caused by the activities or demonstration of the investor/proprietor or consultants, for example, outline changes or late arrival of designs. In these cases, the contractor collects extra cost from the proprietor as circuitous expenses for the additional overhead costs (Olaniran 2015). There are two categories of reasons for the delay that could be ordered into inward and outer causes. Internal reasons for delay are caused from the three primary stakeholders, which include investors, contractors, and consultants. However, external causes of project delay are influenced by cataclysmic events, deficiency of building materials in the market, Inaccessibility of appropriate hardware, and changes in government’s laws and policies.
Thus, different examinations have been performed in GCC nations with a plan to decide the reasons for delay on infrastructure projects (Mahamid 2013). The best positioned reasons for delay are summarized below. Project deferrals happen in each venture and the sizes of these postponements shifts impressively from one undertaking to another. At the beginning, it is fundamental to characterize the genuine reasons for delay keeping in mind the goal to limit related expenses in any construction work.
Hirsch and Catchim (2012) contend that erudite people, for example, Plato believed in human inadequacy to foresee the future. Plato’s statements indicate how doubtful they were setting up plans for the future and executing venture proficiently. Scientists have contended that there is no development venture without hazard, suggesting that in a few cases, infrastructure tasks are unplanned. Hazard can be supervised, limited, shared, exchanged, or acknowledged yet it cannot be ignored. In their investigation, Hirsch and Catchim (2012) contend that dangers are considered as non-specific to construction ventures. Delays caused by an activity may not cause project delays. However, delays caused by project stakeholders could conceivably influence the task finishing. Time overruns may happen simultaneously with different deferrals and every one of them may affect the project timeline. One of the central points that record for overrun dangers is the nonattendance of institutional governance that would uphold responsibility among stakeholders. Such regulation would create an interest for information about the genuine dangers that is often truant today.
The idea of achievement in a project undertaking can be assessed when hazard measurements are characterized. In most ventures the assessment of performance or disappointment measurements relate to the customary limitations of time, cost, and quality parameters. Researchers observed that project performance must be assessed based on cost, plan, quality, and investor’s fulfillment (Al Turkey 2011).
To make progress, stakeholders must have a comprehension of conduct/designs of project factors and future control strategies. A significant number of literatures revealed that the inability to finish ventures on time keeps on being an unending issue (Al Turkey 2011). Nevertheless, as the pattern of cost overruns winds up noticeably extreme, various unfriendly outcomes, for example, project disappointment, diminishment of net revenue, loss of conviction of native in government financed ventures would surely occur.
Results of Time Delays and Cost Overruns
Some researchers contend that if project expenses or timetables surpass their arranged targets, investor fulfillment would be bargained, the financing profile will exceed the initial budget, and further delay in the calendar could occur (Al Turkey 2011). The resultant effect will include project termination or revocation. The experts revealed that project experts appear to give careful consideration to cost execution of ventures than time execution. A survey conducted in the United Kingdom, revealed that 58% of respondents dependably applies time controls to their venture, a further 19% showed that they apply time control procedures, and 11% respondents show that they do not apply time control amid their undertakings (Price and Al-Otaibi 2010).
Methodology for the Proposal
Based on previous articles on cost overruns and project delays, a review of literatures was carried out on complex infrastructure projects in Saudi Arabia. The review analyzed fundamental factors that caused delays in development projects. Likewise, a connection between low-value bidders and cost overruns were found. Based on the analysis, we proposed a model for best practices for the National Project Management Office in Saudi Arabia. The model if implemented, would enhance project completion and reduce cost overruns. The model is called the Best Value Performance Information Procurement System. This model has demonstrated a more elevated amount of project management than the low-offer framework. Moreover, contextual analyses that utilized PIPS were analyzed, which endorsed an abnormal state of execution with time, contract sum, and fulfillment.
Thus, the contextual investigation was conducted using SA as a sample specimen. We collected information concerning project delays on contracts that utilized the low-offer framework. Project contractors and engineers were instructed to ascertain delay causes from a proprietor’s point of view. Additionally, information included complete accessible concerning bidders and budget sum. Four complex infrastructure projects were chosen for analysis to inspect budget overruns overwhelms and demonstrate that expenses were higher than the first proposed costs. We also recognized the reasons for the budget overruns and demonstrated the technique for choosing contractual workers.
This exploration will endeavor to examine primary contributing components causing project late conveyance and spending cost. Likewise, the paper will propose remedies to address such factors utilizing successful management structure, project administration approach and undertaking administration best practices to limit as well as wipe out these impediments. The examination recognizes techniques for improving project management procedures and prompts the proposition of approaches to enhance the current unacceptable circumstance, with a specific goal to have positive results in Saudi infrastructure projects. At the end of the analysis, a model of BV PIPS that could be executed in Saudi Arabia was proposed. In summary, this proposal looked at the points below.
- Organizing reasons for project delays
- Organizing reasons for cost overruns
- Analyzing the current model (Low-bid procurement factor)
- Concurrence with the BV PIPS standards
- Concurrence with the proposed best practice
A study was gotten from 800 confidential project contractors and the results were subjected to factual examination to indicate legitimacy and unwavering quality of the outcomes.
Reasons for Delay Factors
After organizing project delay causes through survey, they were contrasted with deferred factors around the country, which were gathered from literatures. The correlation demonstrated the imperative factors facilitated cost overruns and project delays. The investigation at that point clarified how BV PIPS can manage critical delay components to enhance project execution in Saudi Arabia.
Reasons for Cost Overruns
After organizing reasons for budget overruns through survey, information of cost overruns was contrasted with BV PIPS execution.
Basis for NPMO Inclusion in Project Management Practices
Postponements in conveying infrastructure projects on time can make significant issues to investors, the government, and the economy. It has a genuine influence on money related responsibility, investor’s image, and the environment. The postponement in project delivery in Saudi Arabia is worsened because of sharp change in the cost of the materials. Thus, task proprietor inclusion, contractor capabilities, design outline, and project framework are vital elements for project delay in Saudi Arabia. The author examined delays in public sewage projects. As a result, delay components were coded and categorized for analysis. The author concluded that project delays occur most in government awarded contracts. Imperative causes are financial issues, changes in the plan and extension, delay in settling on choices and endorsements by the proprietor, troubles in obtaining work permits, and coordination and correspondence issues.
Experts argued that contractor’s performance is a significant reason for delay. Thirteen noteworthy measures were considered. These measures are identified with contractual worker resources and abilities. They distinguished contractual worker execution as one of the real reasons for delay in projects in Saudi Arabia (Al Turkey 2011). Al Turkey (2011) talked about the primary driver of disappointment in the construction industry in Saudi Arabia by studying 68 contractors and around 34 unique reasons for disappointment. The examination presumed that absence of experience, poor estimation rehearses, awful decisions in controlling organization’s strategy, and national droop in the economy are the extreme variables. The author considered the primary driver of postponement in complex infrastructure projects. The review secured an arbitrary example of contractors, consultants, and proprietors. They assembled the delay causes into nine noteworthy categories. The groups include financing, materials, legally binding connections, changes, government relations, labor, planning and control, hardware, and environment (Elawi et al. 2016).
Elawi et al. (2016) researched time execution of various sorts of development work in Saudi Arabia to decide the reasons for delay and their essential as indicated by each of the project members, proprietor, and site managers. The examination incorporated a field review of 23 site engineers, 19 specialists and 15 proprietors. Proprietors and contractors both showed that ineffectual arranging and planning by site engineers is one of the deferral to the undertaking; poor administration, poor site administration and supervision of consultants. Proprietors indicated that reasons for delay are identified with corruption and poor performance. The study showed that proprietors and advisors acknowledge most minimal bidder is the most astounding successive factor of deferral, while site engineers considered serious purposes of postponement are identified with proprietors.
In the absence of corruption, contractor determination has been done based on the costs offered by bidders. In choosing a contractor in the present project condition, numerous proprietors do not consider the cost as the single determination model: rather they focus on a blend of a few parameters, for example, value, notoriety of the bidders, history of past undertakings, significant development quality pointers, arranged illustrations, recommended development strategies to mention a few. Thus, the contractor’s choice is not a clear methodology performed by simply arranging the offers in view of the offered cost. This stresses the requirement for options that supports quality decision tools in allocating team engineers for national projects. Such programming arrangements align with the required laws and controls in choosing the site engineer within the sight of an assortment of subjective and quantitative elements.
Absence of Knowledge about Regulations
Keeping in mind the goal to encourage the offer and acknowledgment components of national projects, the National Management Office is mandated to supervise tenders and the bidding process. To enhance the adequacy of the articles of the ordinary contracts and to expand the productivity of the development division of the nation, lawful experts are permitted to issue revisions to a few articles in accordance with contract policies or translate the legitimate wording of the related archives.
Primarily because of the irregularities in the language and phrasing of the redresses issued by various supervisory units, we take note of that proprietor, advisors and contractual workers feel that the amendments and understandings cause superfluous postponements and deplorable disarray. Consequently, experienced legitimate specialists are not generally accessible when proprietors and site agents have inconsistent translations of the recently issued redresses: regardless of the possibility that lawful counsels are accessible, their administrations can be exceptionally costly and hence not included in the overhead cost of complex projects. Thus, the distortion of the remedies and conflicting phrasing of such rectifications can prompt exorbitant lawful question amongst contractors and investors. This raises project expenses and encourages unanticipated deferrals in the project timeline. To diminish this defer factor’s effect, we prescribe setting up a solitary outlet to distribute ordinary contracts and in addition the related revisions and understandings. This channel must be supervised by the management office. Thus, deploying an effective channel may lessen conflicting interpretation, which will relieve the perplexities and misinterpretations of the proprietors, contractors, and experts. As a result, delays and cost overrun causes by contract regulations will be addressed.
Projects Controlled by the Government
In Mecca, the government for an assortment of reasons characterizes project infrastructures. Once the government characterizes all the development ventures, it expects to dispatch amid a specific financial year. The time traverse and spending plans for these development ventures are resolved essentially because of political contemplations. Deficient consideration is characterized during such evaluation. Once an undertaking is established by parliament and a financial plan is approved, the administration calls for tenders. Advisors and contractors examine the courses of events and write proposals. If they presume that the appointed spending plan and established timetables are not reasonable, the administration sends corrections to the parliament.
This wasteful technique causes over 18% of the deferrals under law, control, and other general imperfections. This situation encourages budget overruns and project delays (Elawi et al. 2016). Keeping in mind the goal to stay away from such deferrals, extraordinary consideration ought to be paid to proactive arranging and risk management. For example, the government could create different hazard profiles and classify projects base individually. Once the profiles are proposed, government ought to create and keep emergency courses of action for various tasks in view of the hazard profiles. In addition, contractors and experts could survey the hazard profiles and emergency courses of action to get a superior assessment about the budgetary suitability of the undertaking, venture timetables, and project risk.
Without a doubt, political unsteadiness directly affects the hazard profile of development ventures at different levels. Political instability and other hazardous factors influence money related unsteadiness and builds the danger of cost overrun and project delays. This reality ought to be taken into full thought at all phases of the strategy of characterizing an administratively supported task, including when the government characterizes a project. Reducing political instability will mitigate a wide range of dangers. Along these lines, government and parliament are prescribed to diminish the political precariousness by making a typical dialect through procuring undertaking and risk management practices.
Proposing Best Practices for the National Project Management Office in Saudi Arabia
Instead of utilizing the low-offer value technique, another acquisition strategy, BV PIPS, can be adjusted in Saudi Arabia to enhance the execution of undertakings. BV PIPS has demonstrated to build execution in development ventures. In this framework, contractors are chosen in light of their execution while giving the most checked cost. The contractors provide a proposal that incorporates the delivery data through a particular strategy. Alzara et al. (2016) distinguished the significant time overrun factors that facilitate poor execution in Saudi Arabia and perceived BV PIPS as an answer for defeating this time-overruns hazard factors. Therefore, we propose the Best Value and Performance Information Procurement System for National Project Management Office in Saudi Arabia.
Best Value and Performance Information Procurement System (BV/PIPS)
Dr. Kashiwagi conceived BV PIPS in 1991. The model reduced hazards in undertakings and improved contractor’s performance. BV PIPS applies an uncommon delivery condition that limits basic leadership, administration, and control (Elawi et al. 2016). In 2008, the International Council for Building authorized a gathering to play out an examination utilizing literature exploration to identify creative methodologies in development reported an expansion in execution of activities (Hirsch and Catchim 2012). The examination separated through more than 15 million articles, looked into more than 4,500 papers, and distinguished the PIPS/PIRMS as the framework that had distributed records demonstrating an expansion in development execution of numerous tests. Execution of tasks is influenced when they depend on value and cost (Hirsch and Catchim 2012). At the point when the strategy is value based, projects demonstrate elevated amounts of execution, and when it depends on cost, they indicate substandard execution.
BV PIPS concentrates on finding and utilizing qualified contractors to expand the execution of undertakings. Execution measurements of PIPS ventures were completed on the spending plan, time, and quality. PIPS have been tried with more than 1,900 undertakings with $8.3 billion task value. These task measurements demonstrate a 98% rate of accomplishment in 6 nations and 31 states (Kashiwagi 2011). PIPS expand venture execution and productivity while lessening project delays with the low-bid strategy. The PIPS procedure comprises of four stages: pre-capability (discretionary), selection process, interpretation, and implementation.
The BV PIPS Process
- Pre-capability stage: This discretionary stage instructs contractors about BV PIPS. It also shows contractors how to submit proposals to demonstrate project execution.
- Selection stage: This stage has four channels to locate the best value contractor. In channel one, contractual workers ought to submit task ability and their value, which contains three records: level of skill (LS), value included (VI), and hazard appraisal (HA). Each of the three archives ought to be three pages at maximum. The second channel is a meeting deciding the contractual workers’ skill. The meeting is for the key individuals who will take every necessary step, for example, project supervisors to check whether they are specialists with a reasonable vision for the undertaking as it advances. The third channel is the advisory group organized criteria, which measures the past performance. Measurement scale could be numbered from 1– 10 or rates. The fourth channel is a strength check for the most proper contractor who gives data to limit hazard with the least cost.
- Interpretation stage: This is the most critical stage of the BV PIPS process. In this stage, contractors explain the project plan and offer. The contract worker in this stage ought to clarify what is outside the space of the venture while streamlining the proposition for the proprietor. Contractors and project proprietor ought to illuminate all perspectives identified with the undertaking by giving a timeline from the earliest starting point of the venture to the end, including the task scope, a turning point plan, and a hazard administration design.
- Execution stage: This last phase has the contractual worker present a week by week hazard report (WHR) to the proprietor. The WHR is given as Gantt report that clarifies the task exercises and any deviations from the underlying arrangement as far as time, cost, and quality are concerned. The WHR additionally gives a point of reference plan, execution estimations, and a hazard administration design. The report contains an outline of all WHRs and gives every contractor execution and any hazard that ought to be centered around.
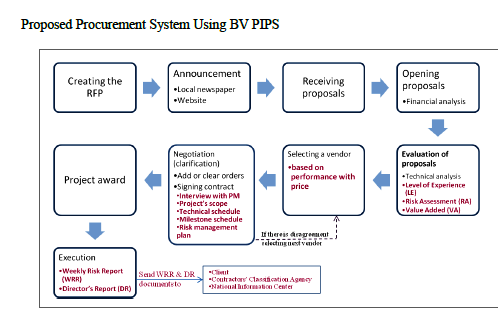
Proof of Procedure
The past examination discovered 27 critical elements that delayed national projects in Saudi Arabia. This investigation demonstrates that BV PIPS can manage these delay factors. Best value diminishes administration, basic leadership, and control by using skill and expanding straightforwardness. These standards help proprietors in decision making to build the endorsement rate of configuration records. At the point when the institution builds straightforwardness and declines control, the association’s progress improves, which comprehends many variables identified with the proprietor. Thus, the existing bidding process can be replaced with the BV PIPS model, which utilizes many stages to choose the most elevated performing contractor who is the best value.
The proposed obtainment framework utilizing BV PIPS in Saudi Arabia uses the accompanying procedure:
- The primary stage includes the demand for the proposition.
- In the second stage, offers are declared in daily papers and online sites.
- In the third stage, proprietors get the recommendations and check them to coordinate directions.
- When the board of trustees and time allotment schedule are recognized, the fourth stage is prepared for money related examination and is organized by most reduced cost.
- In the fifth and sixth stage, the board of trustees assesses the level of skill (LS), hazard evaluation (HE), and values included (VI) records.
The advisory group approves bid selection based on the project requirements
- If acknowledged, the minimal bidder moves to the transaction stage with the board of trustees. In the seventh stage, the board of trustees should meet the project administrator to check whether the contractor is a specialist. Additionally, the bidder ought to present the project extension, specialized calendar, breakthrough timetable, and hazard administration design. In light of these prerequisites, the board of trustees ought to have the capacity to check whether the bidder is a specialist. If the bidder and the council are not ready to discover shared conviction, the board of trustees should then choose another bidder.
- After marking the agreement with the contractor, bidding move to the eighth stage, which is the project approval phase.
- In the ninth stage, the contractor moves to the execution phase. Here, the contractor ought to present a week-by-week hazard report (WHR)) to update the agency on the project timeline. This process will limit project delays and cost overruns. These reports help with expanding straightforwardness among venture parties, which will build the accomplishment of the undertaking.
The most well-known delay factors, which caused deferrals to ventures in Saudi Arabia, can be unraveled through the utilization of BV PIPS. In particular, delay components are tackled through stages. These stages have many channels that help project proprietors discover contractors based on performance.
Conclusions
Based on the proposed model we can summarize the benefits of BV PIPS. The proposed model will enable stakeholders give careful consideration to project implementation. Planning is the most fundamental segment of project management and the greatest weapon against cost overruns and delays. Therefore, stakeholders must analyze the project scope, which is documented for referral purposes. The proposed model assists the organization to evaluate each bid based on the contractor’s performance. In numerous intricate undertakings, you may need to use external contractors to do some portion of the project. Before you employ a merchant, consider previous performance, logistics delivery, delivery date implementation, and project quality. Mandating the country’s NPMO to organize the project management practice would regulate the project scope. Battling extension implementation is the greatest test for a project chief. The engineers need to include their preferred designs, the customers begin requesting things that were not initially approved, and the testing group needs an adjustment in a portion of the design. While a portion of the progressions may be called for, an uncommon design adjustment may cause delays. Thus, the NPMO must control and persuade to avoid delays and cost overruns.
The proposed model encourages automated project instruments and graphs. Appropriate planning is an unquestionable requirement in complex ventures. Improper planning can cause wrong cost estimations and project delays. Thus, Gantt diagram and other project tools would improve delivery timelines and mitigate cost overruns. The model ensures that stakeholders agree before project approval and implementation. Viable correspondence can help diminish deferrals by abstaining from project delay factors and improving the work plan. Finally, the proposed model allows the government to track progress report. A contractor needs to track project report using different measurements to quantify each activity. This will give early flags of undertaking delays, while additionally giving you chances to settle the issues immediately. The legislature of Saudi Arabia has burned through billions of dollars on development undertakings, and they select contractual workers as indicated by the most reduced offer. Nevertheless, these tasks are frequently influenced by taken a toll overwhelms. This demonstrates an inconsistency in how contractual workers are chosen in light of the fact that the framework depends on cost criteria, however this prompts extra spending amid the execution stage. Expanding venture execution in Saudi Arabia requires reexamining the acquirement conveyance framework.
The low-offer acquisition framework adversely influences the Saudi Arabian project execution. Fulfillment of the present (low-offer) framework is poor, as revealed in previous literatures. Cost ought not to be the main assessment factor. Contractors and government authorities must utilize the BV PIPS components for project approval. Thus, the level of understanding, hazard evaluation, and value-included records help proprietors to assess site engineers based on quality and performance.
References
Abu Nemeh, M. H. A. (2012). Multi-criteria decision making model for the selection of a construction contractor in Saudi Arabia (Unpublished master’s thesis). King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Saudi Arabia.
Al Turkey, T. (2011). The reality of projects in terms of organization and structure, and the reasons for success and failure In Saudi Arabia. Web.
Al-Khalil, M. I., & Al-Ghafly, M.A. (1999). “Delay in public utility projects in Saudi Arabia.” International Journal of Project Management, 17(2), 101–106.
Al-Kharashi, A., & Skitmore, M. (2009) Causes of delays in Saudi Arabian public sector construction projects. Construction Management and Economics, 27(1), 3–23.
Al-Sultan, A. S. (1987). Determination of construction contract duration for public projects in Saudi Arabia (Unpublished master’s thesis). King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia.
Alzara, M., Kashiwagi, J., Kashiwagi, D., & Al-Tassan, A. (2016). “Important causes of delayed projects in Saudi Arabia vs. PIPS: A university campus case study.” Journal for the Advancement of Performance Information & Value, 8(1).
Assaf, S. A., & Al-Hejji, S. (2006). “Causes of delay in large construction projects.” International Journal of Project Management, 24(4), 349–357.
Elawi, G. S. A., Algahtany, M., & Kashiwagi, D. (2016). “Owners’ perspective of factors contributing to project delay: Case studies of road and bridge projects in Saudi Arabia.” Procedia Engineering, 145, 1402–1409.
Hirsch, A., and Catchim, T. (2012). The Permanent Revolution: Apostolic Imagination and Practice for the 21st Century Church. John Willey & Sons, NY.
Holt, G. D., Olomolaiye, P. O., & Harris, F. C. (1995). “A review of contractor selection practice in the UK construction industry.” Building and Environment, 30(4), 553–561.
Kashiwagi, D. (2011). “Case study: Best value procurement/performance information procurement system development.” Journal for the Advancement of Performance Information & Value, 3(1).
Mahamid, I. (2013). “Contributions to schedule delay in public construction projects in Saudi Arabia: Owners’ perspective.” Journal of Construction Project Management and Innovation, 3(2), 608–619.
Olaniran, O. J. (2015). “The effects of cost-based contractor selection on construction project performance.” Journal of Financial Management of Property and Construction, 20(3), 235–251.
Plebankiewicz, E. (2009). “Contractor prequalification model using fuzzy sets”. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 15(4), 377–385.
Price, A. D., & Al-Otaibi, M. (2010). Analysis and evaluation of criteria for pre-selecting contractors in the Saudi Arabian construction sector. In C. Egbu (Ed.), Proceedings 26th Annual ARCOM Conference, 6–8 September 2010 (pp. 1141–1148). Leeds, UK. Association of Researchers in Construction Management (vol. 2).
Wong, C. H., Holt, G. D., & Cooper, P. A. (2000). “Lowest price or value? Investigation of UK construction clients’ tender selection process.” Construction Management & Economics, 18(7), 767–774.