This paper is a strategic analysis of the best locations to establish new hubs for service and manufacturing processes of a new business. The calculations include weighted, center of gravity, location break-even, and transportation techniques. These methodologies will help in making recommendations about the best locations for setting up the two hubs described above. The principles underlying the proposals will also be explained.
Location of Service Hub
Weighted Technique
The weighted technique works by identifying important factors influencing the location of the service firm (Bag, 2016). The weighting process involves identifying values that spread from 0 to 1.00 (Wisdom IT Services India Pvt. Ltd., 2018). Using this measure, each factor is prioritized and its importance to the location decision evaluated. At the same time, a subjective score that may range from 1 to 100 is also evaluated to analyze the attractiveness of various locations (Render & Heizer, 2011). Thereafter, weighted scores are assessed. Considering there are three possible sites to locate the service hub of the new business, table 1 below identifies location considerations for the three sites and allocates different weights to them.
Table 1. Weighting Process.
The weighted scores for each of the sites highlighted above are derived from a multiplication of the factor weights by each of their scores. For example, the weighted score of staffing and climate issues is 0.30(80) = 24 points. Table 2 below explains the weighted scores for each of the factors indicated above.
Table 2. Weighted scores.
Based on the table above, site 3 has the highest factor rating. In this regard, it emerges as the most desirable location for the service hub.
Location Break-Even Technique
An assessment of three locations using the break-even analysis would help in ascertaining the cheapest location to set up the service hub (UMSL, 2017). Table 3 below shows the fixed and variable costs of each location.
Table 3. Fixed and variable costs of proposed locations.
Assuming there is an annual demand of 25,000 units, the best location for setting up the manufacturing hub would be achieved by computing fixed and variable costs for each location as outlined below.
- Location A: 650,000 + 50Q
- Location B: 350,000 + 65Q
- Location C: 400,000 + 55Q
The indifference pair for each of the locations identified would be achieved through the assessment below
650,000 + 50Q* = 350,000 + 65Q* = 400,000 + 55Q* (Q is the indifference demand)
An identification of the ranges of output will help to establish which location has the lowest cost for setting up the service hub. If Q = 0, location A, B, and C would cost $650,000, $350,000, and $400,000 respectively. If demand is less than 20,000 units, location A would have the highest cost of operation, while location B and C would have higher operating costs if the demand is higher than 20,000 units. Therefore, if the demand is greater than 20,000 units, location A should be chosen, and if it is less than this number, location B should be selected.
Location of Manufacturing Hub
Center of Gravity
Assuming the current business purchases its raw materials from four groups of suppliers who use 40-foot trucks (each with a capacity of 38,000 pounds of raw materials), the location of the four suppliers and the volume of goods supplied will emerge as highlighted in figure 1 below.
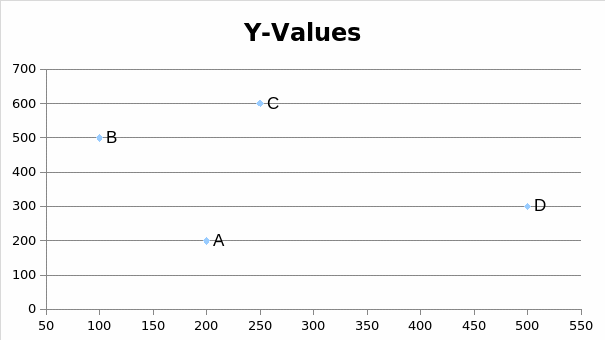
The locations of the four suppliers are highlighted in the figure above as A, B, C, and D. The annual number of trailer loads transported per year is highlighted in table 4 below.
Table 4. Loads supplied annually.
Using the center of gravity method, the location of the distribution center is calculated below.
Calculations for X-axis
200(75) + 100(105) + 250(135) + 500(60) = 238
75+ 105 + 135 + 60
Calculations for Y-axis
200(75) + 500(105) + 600(135) + 300(60) = 444
75+105+135+60
The results for the X-axis and Y-axis highlighted above provide the location for the manufacturing plant. Nonetheless, it is important to point out that this location is a product of straight line distances. Realistically, the actual roads leading to the facility may follow a circuitous path (Mageto, 2016).
Transportation Technique
The transportation technique evaluates the load and distance taken to transport goods from the manufacturing center to the market. The formula highlighted below is borrowed from MCU (2017) and is used to compute the straight line distance between the transportation points.
The desired outcome will be achieved by finding a location with the lowest value because it would mean that the same facility attracts the lowest transportation cost. If the above formula is used to evaluate the three sites with the coordinates highlighted below, the following equations would suffice.
- Site A: x1=360, y1 = 180
- Site B: x2=420, y2 = 450
- Site C: x3= 250, y3 + 400
The results would be 184.4, 170, and 269.3 for sites 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
The formula for load distance will be computed using the following formula, which is also borrowed from MCU (2017)
The results for the three sites are 125,063, 99,789, and 77,555 for sites 1, 2, and 3 respectively. Since the third site has the lowest load distance value, it emerges as the ideal location for setting up the manufacturing hub. This location is also close to the result noted in the center of gravity method.
Conclusion
This study shows that weighted, center of gravity, transportation, and break-even techniques are instrumental in determining where to set up manufacturing and service hubs of the new business. The location of the service hub was identified through the application of weighted and break-even techniques, while the location of the manufacturing hub was identified by applying center of gravity and transportation techniques. Site 3 emerged as the best location for setting up both hubs.
References
Bag, D. (2016). Business analytics. London, UK: Taylor & Francis Mageto, J. (2016). Facility location. Web.
MCU. (2017). Location planning and analysis. Web.
Render, B., & Heizer, J. (2011). Operations management: Flexible version (10th ed.). New York, NY: Pearson.
UMSL. (2017). Operations management. Web.
Wisdom IT Services India Pvt. Ltd. (2018). Location models. Web.