Introduction
International trade is often referred to as bilateral trade where different countries engage in trading activities. International trade has been very instrumental in providing crucial goods and services to various countries. International trade can also involve the exchange of capital goods across territories. International trade has been made possible by the increasing globalization and an increase in population.
In this case, countries need services and goods from other nations to ensure the satisfaction of the growing demand. International trade has been very instrumental in promoting world peace as countries’ relations are improved as through trade relations. The improvement in technology has been critical in promoting international trade where rising multinational corporations are emerging.
Infrastructure is the major determinant in international trade because it facilitates the movement of products across national borders. The two countries should facilitate the interaction in the trade through improving their transport and communication sector. This will enable citizens to share information and goods between them.
International trade is different from domestic trade in that the goods produced in the country are offered for sale to other nations that cannot produce such products. Thus, international trade enables the country to earn foreign exchange, which is important in stabilizing the economy (World Trade Organization, 50).
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is the largest state in the western Asia by land mass. It is located in the middle eastern part of Asia with neighbors such as Iran and Kuwait and Pakistan. It is referred to as the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia because it was founded by King Abdul-Aziz bin Saud. It has a population of about 29 million people.
The country is an Arab speaking nation, and it is mostly known for its oil producing capacity in the world market. The country needs to import most of its food from other countries due to this high population and the climatic condition of the country. Saud Arabia uses the oil revenue to purchase these goods. The country’s production of oil is known worldwide.
Thus, due to the high demand for oil, the country can use the oil earning to import other goods that citizens require. Over the last few years, the country has had a violent regime. After the overthrow of the Al Qaeda in the country, the country has been able to restructure and focus on industrialization.
The country also imports labor force from the East African countries, especially the unskilled labor. The country has been improving its infrastructure so as to pave the way for industrialization. The country is a major partner in OPEC, which is a group of oil producing and exporting countries worldwide (World Trade Organization, 52).
Balance of payment
Balance of payment can be defined as all the monetary transactions that take place between countries and especially the trading partners. It includes the value of capital goods and service between two or more trading partners. The balance of payment is very helpful when constituting the value of export and comparing it to the value of import for a certain period.
A country is said to have a positive balance of payment if it exports more than it imports and vice versa. Saudi Arabia’s economy is largely controlled by oil, and this makes it possible for the country’s government to have a big control in the sector in order to safeguard the economy of the country.
It is the largest exporter of petroleum products in the world and thus oil becomes its main source of revenue for the country (World Trade Organization, 53). According to the World Bank report, petroleum accounts for over 45% of the country GDP and over 90% of the country export earning. Thus, the country relies so much on the proceeds from oil and other petroleum products (EconomyWatch Content Saudi Arabia Economy para 5). In the 2009 report, the country had a GDP exchange of $379.5 billion.
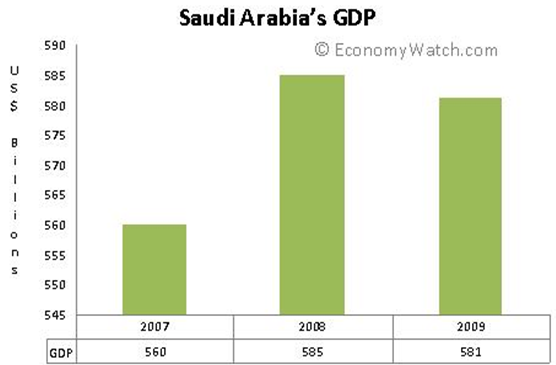
Source: (EconomyWatch Content Saudi Arabia Economy para 5)
The country has a positive balance of payment due to the high income from oil, and this has led to increased economic growth. Notably, the Saudi economy is growing at the rate of 4.6% per annum. The revenue earned from petroleum products has been channeled towards improving the industrial sector and create jobs for the citizens. In addition, some of the labor force is exported to other oil producing countries around the world (Kemp, 52).
Saudi Arabia’s current account balance as from 2007 is as follows. The figures in US$(000,000)
Capital account balance in US$(000)
Saudi Arabia’s official national reserve in US dollars
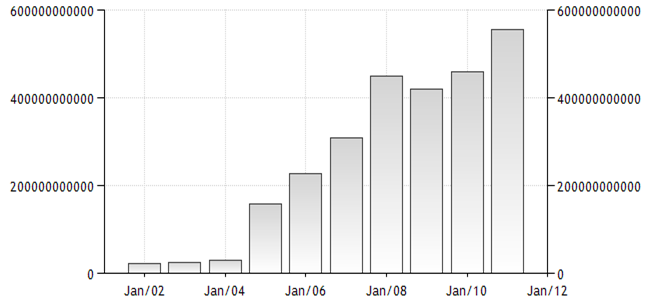
Source: (EconomyWatch Content Saudi Arabia Economy)
Membership in trading blocks
Saudi Arabia has been a member of OPEC since it was formed. The country is aimed at improving the condition of oil producing countries in the world. The country has also registered its membership with the World Trade Organization. The country aims at promoting world trade across countries and continents. It helps to safeguard all members from exploitation from industrial countries, which are efficient in production and may offer low prices for goods and services (Long, 68).
Top exports and imports
Saudi Arabia’s main exports include petroleum products, which are offered in the market worldwide. The oil producing country members control the price of oil worldwide due to the high demand and low supply of oil in the world. The price set is common to members of the organization, and this is usually geared towards maximizing the earning of such states.
The country is not able to grow enough foodstuffs for its large population due to the desert climate in Saudi Arabia. Thus, it imports most of the agricultural goods. The country has been importing drugs and labor force from other countries, especially from the East and Central African region.
The country’s economy is on the growth trend due to government policies that are geared towards shaping the economic recovery and industrialization through government control. The country has experienced low growth due to misuse of the country’s earning. This is due to the emergence of the terrorist group, Al Qaeda, and middlemen who controlled the oil sector.
However, after the election of a stable government, the country is improving (World Trade Organization, 60). The government has been involved in investing in other sectors of the economy to strengthen the economy. This was necessitated by over reliance on petroleum products for the country’s economy.
Investment in infrastructure and education has been helpful to the country’s economy through the creation of jobs and investing in the untapped sectors such as business. Saudi Arabia’s main trading partners include the US, China, Japan and European countries (Kemp, 37). The table below show major business partners of Saudi Arabia
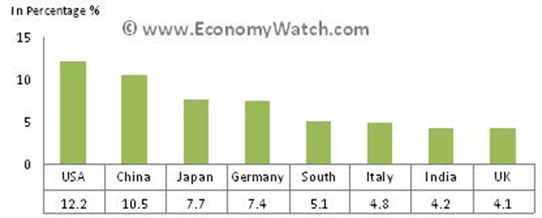
Source: (EconomyWatch Content Saudi Arabia Trade 1)
Saudi arabia’s top ten export apart from oil products include live animals and animal products, vegetable products, prepared foodstuffs and beverages, mineral products, chemical and allied products, plastic and rubber products, hides and leather, wood, textile and textile articles, footwear, cement and ceramic products, and finally machinery and mechanical appliances.
Saudi Arabia’s top ten imports include vehicles, aircrafts, cinematographic products, arms and ammunition, works of art, miscellaneous manufactured products, medical and surgical products, machinery and mechanical equipments, base metals and articles and finally precious metal and jewellery (Kemp, 37).
Foreign direct investment
Through the WTO, the country has been able to apply for loans that are geared towards improving the state of the country’s economy. The massive earnings from oil have been channeled to other sectors such as energy. This was meant to ensure a reliable energy source that is cheaper for the growth of the country’s economy.
Countries like the United States and Britain have been helping the country with investment in security through offering funds and machinery. These provisions of military machinery have helped the country to fight terrorism and other internal threats that may destabilize the government in the future (Kemp, 42).
Tariff policies
The current government of Saudi Arabia has established policies geared towards strengthening the country’s economy. Monetary policies have been very effective in the supply and demand of money within the country’s economy over the years. The monetary policy implemented by the central bank of Saudi Arabia has helped to reduce the levels of inflation, which was on the rise.
According to Economy watch, the inflation rate of Saudi Arabia stands at 4.3% (EconomyWatch Content Saudi Arabia Trade para 2). The other policy used by the government of Saudi has been the fiscal policy where the control of export and import has been made possible. Controlling the amount of import and export by a country is very important as it helps the government to stabilize the currency.
This policy is helpful in the control of the imports allowed into the country. This is crucial in safeguarding the local market from damping by other industrialized nation products. The policy safeguards the local industries from exploitation and subsequent closure of their operation when they fail to make viable sale and suffer losses.
Quotas have been used by the government to control the amount of export, especially in the oil sector in order to keep the demand and supply of the commodity on the global market under control. Through OPEC, the country can control the price of oil and thus safeguard against low pricing of this rare product on the market (World Trade Organization, 65).
Non-tariff barriers
Non tariff barriers are geared towards controlling the amount of export and import into the country. The government of any country can control the amount of goods and services that citizens can import or export at any given time. This is a strategic approach towards safeguarding the country’s local industry from exploitation from other industrialized nations.
Such countries may carry out damping of their goods and services in the local market. Damping may lead to flow of cheap and poor quality goods on the local market. In this case, the local industries may suffer reduced sales volume and thus close down leading to loss of jobs and decline in economic growth.
Saudi Arabia uses non tariff barriers to control the amount of goods mainly from neighboring countries that may find their way into the local market. The government has put a quality standard for any import made in the country, especially on the industrial goods and services (Suwaidi, 98).
Culture and Business Practices
The term culture can be defined as the way of living of a group of people and the way they carry themselves, their practices and their beliefs. Saudi Arabia has been a good business partner with most East African countries. In this case, Saudi Arabia has established good relations with her trading partners that are geared towards improving their trade ties.
The culture of the country has been well protected by the government. The country is an Arabic speaking nation, and it is mostly known for its oil producing capacity. In this regard, the country is regarded as one of the major stakeholders in the production and exportation of oil and other petroleum products. The country is mostly inhabited by the Muslim community with a few numbers of Christians and other denomination.
The culture of the country has been cultivated from its former generations who have helped shape the country as it is today (Kemp, 48). According to World Bank records, the country has a population of about 29 million people who are actively involved in various sectors of the economy. The country has about 2 million illegal immigrants who have been attracted by the rich oil sector that provides jobs to them.
The country has a rich culture where people have confidence in the kingdom and the leadership of the king who has shaped the history of the country. The business culture of the Saudi is very rich dating back to the 12th century where people were involved in the long distance trade. The Saudi Arabians have a good trade relation with neighboring countries who include Kuwait and Iran where they have exchanged their culture over the years.
The business relationship that Saudi Arabia has established with the East African countries is very important to the economies of these countries through the exchange of goods and services. Most Saudi Arabians are staunch followers of the Sharia law where a severe punishment is given to the wrongdoer. It is these beliefs that have made the country stand out among other Arabian countries in the Middle East (Suwaidi, 45).
The country has had close ties with the United States mainly due to the defeat of the Al Qaeda group in neighboring Afghanistan. In addition, the foreign investment that the US has injected into the country’s economy has worked to enhance the relationship between the two countries. The country has also been exporting petroleum products to the US, and this has helped improve the trade ties between the two countries.
The exchange of technology between the two countries has been possible when it comes to the issues of oil exploration and other research undertakings. The United States also exports some of its labor force in the country. The two countries also undertake joint military exercises and military exchange programs that have proven to be beneficial for both countries.
The country has adopted a better democracy through mentorship by the US. In this case, Saudi Arabia has allowed women to participate in the democratic process, which was not the case in the past. The good relations between these two countries have created better trading ties between the two countries (Long, 68).
Conclusion
Saudi Arabia has had a rich culture that can be traced from the past. Many nations recognize Saudi Arabia due to the country’s enormous resource of oil deposits that act as the major income earner for the country. The government of Saudi Arabia has been involved in the control of the oil trade worldwide as it is its major export. The country is also one of the leading nations in crude oil production.
The country uses revenue from the oil industry to facilitate other development projects to facilitate the industrialization of the country. The government has established policies that help in shaping the country’s economy to reduce on reliance on oil. The focus has been to invest in other sectors such as the industrial and agriculture sectors.
The country enjoys good business relations with its trading partners that include Iran, Europe, the United States, and African countries among others. Through this interaction, the government of the country is strengthened, and the promotion of world peace and coexistence is enhanced.
Works Cited
EconomyWatch Content. Saudi Arabia Economy. 2010. Web.
—. Saudi Arabia Trade, Exports and Imports. 2010. Web.
Kemp, Geoffrey. The East Moves West: India, China, and Asia’s Growing Presence in the Middle East. Washington, D.C: Brookings Institution Press, 2012. Print.
Long, David E. Culture and Customs of Saudi Arabia. Westport, Conn. u.a.: Greenwood Press, 2005. Print.
Suwaidi, Ahmed A. Finance of International Trade in the Gulf. London u.a: Graham & Trotman, 1994. Print.
World Trade Organization. Protocol on the accession of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia =: Protocole d’accession du Royaume d’Arabie Saoudite = Protocolo de adhesión del Reino de Arabia Saudita. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007. Print.