Introduction
Starting a small business is a process that requires determination motivation and general know-how in regards to how to operate a business and ensure that it remains profitable despite the various challenges and risks that may be available in the business environment one wants to venture in. as such, several steps should be carried out to ensure that all details regarding the business are addressed and well planned for.
The steps as presented by Zahorsky include but are not limited to: the identification of the business opportunity the owner is willing to venture into. It should be the first stage and should be based on an individual’s passions, financial capability, and educational background that supports the business decision made (1). It should be noted, that the selection of a business venture is often a daunting task, especially if the potential investor is faced with numerous opportunities. As such, this is a very crucial stage, and much thought should be put into it before deciding on the venture to pursue.
Secondly, after deciding on the venture, the investor should create a comprehensive business plan which gives a detailed description of the business in regards to product, ownership, structure, competition, and amount required to start the business. Also, it is always important to mention the contacts and location of the business as well as its name and legal bearings. The third and final step is to find the funds required to start up the business.
Depending on its size, there are various avenues through which an individual can acquire the initial capital. These include but are not limited to Bank loans, inheritance, grants, and partnerships. With this in mind, this study shall delve further into a business plan and explain how each step should be followed and drafted to ensure the success of any business venture. To this end, the study shall describe the aspects that should be addressed while creating a business plan for starting a small business.
How to start a small business
Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most important segment within the business plan. It describes all the factors that the business plan hopes to address, therefore providing the readers with an overview of what the business entails and operates. This section should be written last after every other aspect has been satisfactorily addressed. Though optional, the executive summary should cover a maximum of two pages.
It means that the details presented therein should suffice in explaining what the business is all about within five minutes. As such, the executive summary should explain the essentials of the proposed business venture. To further expound on this, the executive summary should briefly describe what the product will be, the targeted audience (customers), the owner/s of the venture, and a forecast regarding the future of the venture.
Since this is often the first page of a business plan, the business owner should ensure that it is comprehensive, precise, and concise as well as enthusiastic. Such qualities reflect on the organization skills honed by the prospective business owner. In case the business requires capital from outside sources (e.g. bank loan), the executive summary should give precisely explain how much is required, how the money will be used, and how the borrowed money will, in the end, increase the profitability of the business. It is very important because it guarantees the lender that the money will be repaid within a given period.
Introduction
It is another equally important stage in writing a business plan. In this section, the business owner must give a brief history of the proposed business and why it is the most feasible venture. In this regard, the introduction should highlight the reasons as to why the owner chose the business and relate these reasons to his/her educational and experience backgrounds. In comparison to the executive summary, the introduction should be enthusiastic, truthful, and compelling to the reader. It should offer a detailed timeline of events that led to the final decision to start up the proposed venture.
Description of the business
It is the third stage of creating a business plan. In this segment, the business owner must describe the business he/she will be in and explain his/her role as well as the purpose of the business. Another key component that should be in the description is the mission statement. In most cases, the mission statement is a brief (30 words or less) testimonial, which explains the purpose of the business and acts as a guiding principle in all business endeavors.
After the mission statement, it is always advisable to include the goals and objectives that the business shall set to accomplish. According to Pinson and Jinnett, goals refer to the business destinations where the business owner hopes the business shall be at a given time, while objectives can loosely be defined, as achievement markers used to reach the set goals (75). After including these components, the owner should ensure that he/she explains what is of the greatest importance in the proposed business venture (develop a business philosophy).
In addition to this, the business owner should include brief statements regarding the targeted market, the industry the business is in, the growth of that industry over a given period (normally 5 years), the foreseeable long and short term changes within the industry, and how the business will be structured to benefit from these changes. Similarly, the description should include the strengths as well as competencies exhibited by the proposed venture.
In this regard, the owner should ensure that he/she explains the competitive advantage that the proposed venture has and give a brief description of the skills, experience, and strong personal aspects that he/she shall bring into the venture. Finally, the owner must describe the form of ownership that the business will adopt. The main forms of ownership, as described by Kennedy are sole proprietorship (single ownership), a partnership that encompasses two or more owners, corporations, and limited liability corporations (59). Understanding the various forms of ownership is instrumental in understanding the limitations and privileges each owner is legally allowed to have.
Products and Services
Product and type
Under this subtopic, the owner must describe in detail the product or service offered. An in-depth description of the product must include the technical specifications, drawings, and photos of the products and, if possible, sales brochures. In addition to this, the business owner must elaborate on the factors, quality, and unique features that shall give the product or service a competitive advantage or disadvantage in a market setting.
Prices
In this segment, the owner should give a detailed analysis of the pricing mechanism and strategies used to ensure that all goods and services have the potential to bring back profits. In this regard, the owner should describe the structures that shall be developed to determine the price, fee, or lease of the goods and services available to the target markets.
Ownership
Owners
In this segment, the business owner should ensure that he/she provides adequate information about the owners of the proposed venture. What this means is that under this heading, the owner should mention in detail the form of ownership adopted by the proposed venture and why that choice was made. In this regard, the owner should ensure that the benefits and limitations of the ownership strategy to be implemented are well addressed.
Having done that, the owner should ensure that he/she includes the physical contacts of each owner, their educational, skills, and experience background, and their current occupation. Besides, copies of financial statements belonging to the owners should be attached and the role played by each owner in the running of the business is explained.
Required capital
It is also a very important part of the business planning process. In this segment, the business owner must give a detailed description of the amount of money required to start up the new business. In this regard, the owner should ensure that he/she gives specific and precise amounts needed to cover various costs during the business start-up. The owner should explain how the funds shall be used, why the expenditure will amount to the total figures suggested, and the duration through which the proposed amounts shall last.
Also, there should be a detailed explanation regarding the various sources of the capital (grants, loans, inheritance e. t. c.) and how the capital shall be distributed among the various business activities. In case a loan shall be used to supplement the available capital, the business owner should give a detailed account regarding the contribution the loan shall have in completing the project and how it shall improve the profit margin of the business. A detailed financial forecast should also be provided to highlight the duration the business shall take to repay the loan.
Profitability
The main aim of any business venture is to make profits. As such, it would be a worthwhile endeavor to highlight how the proposed venture shall make profits. On this note, the business owner should explain what the pricing strategies are and whether the business shall dwell on profit maximization or sale maximization within the start-up stages. Also, there should be a detailed description of how the profits shall be used.
In this context, the business owner should highlight the plans of the company and how the profits earned shall help achieve these goals. For example, the owner should specify whether the venture shall absorb the profits back into the business or share it with other owners. In both cases, the owner should give a breakdown of the profits into percentages and the criteria used to distribute the profits in the proposed manner. Besides, the owner should ensure that he/she designates a portion of the profits to serve the community. Giving back to the community is very important during the image building process. As such, every new business venture should ensure that it gives back to society as a sign of corporate responsibility.
Market description
The greatest mistake that a potential investor or business owner can make is to assume that the product or service they are bringing into the market is good enough to sell themselves. It should be noted that in as much as a product or service is the best, the business cannot succeed without the application of effective marketing. Effective marketing is all about research. As a business person, it is not a great quality to assume that you understand a market. A lot of time and effort should be employed in studying the market to ensure that the owner of the proposed business understands how various aspects affect the market.
Two types of research should be conducted regarding the market. The first king is the secondary research, which relies on printed literature to gain useful insight into market trends and an industry’s profile. The second type of research is known as primary research. It entails the gathering of potential market data by the business owner. It is the most important form of research because it gives accurate results due to the nature of activities required to give out conclusive findings.
During this research, the business owner should ensure that he/she collects relevant data about the targeted audience (Traffic in and out of the market at different times), competition, do surveys, and group-based discussions to understand what are the most pressing needs and preferences among the targeted consumers. Despite its importance, it should be noted that conducting professional market research is often very expensive.
However, Pinson and Jinnett reiterate that there are books and other resources that can educate small business owners on how to conduct commendable market research that is within their financial and physical capabilities (167). On the same note, the marketing plan should include specific statistics, figures, and sources of information as shall be gathered during the primary research.
These are some of the aspects that should be covered during the market description. The business owner should specify the industry under which the proposed business shall lie, give the total market size and explain the percentage of the market that the proposed venture shall own. Besides, there should be a detailed analysis of the current demand and supply in the target market as well as the growth and consumer preference trends that exist in the targeted market.
Similarly, there should be a summary highlighting the growth potential of the proposed venture and the opportunities that are available for a business of that stature. On the other hand, Kennedy asserts that a marketing plan is not complete if it does not consider the inherent barriers that a potential business may face while trying to enter an existing market segment (86).
As such, the business owner should ensure that some of the typical barriers are well researched and addressed. Examples of such barriers include but are not limited to: high capital, production, and marketing costs, brand recognition, technological hurdles, patents, training, and skills required by a particular market, unions, and trade barriers such as tariffs and quotas. Having addressed these, the business owner should also highlight the proposed strategies that shall be implemented to overcome these barriers. Also, there should be a detailed explanation of how changes in technology, government policies, economy, and industry shall affect the business and how the business shall survive through such changes without losing its primary focus and objectives.
Target market
In this segment, the business owner should give detailed demographics about the targeted markets. In this regard, the business plan should include details about the customers that the business shall target, their main characteristics, and geographic/physical location. However, it should be noted that the description may differ depending on whether the business shall sell to other businesses or consumers only.
Besides, the customers targeted may be categorized into groups. As such, the description should include their age bracket, gender, location, income, and educational levels, and social status among others. In cases where the targeted market shall be business customers (selling to other businesses), the description should identify the industry, location of the business, its size, and preferences in terms of technology, prices, and quality of goods and services offered.
Suppliers
In this segment, the business owner should identify the suppliers that shall be used to ensure that the business has a steady supply of required resources. As such, the business owner should identify the suppliers by providing their names and contact addresses, what they shall be supplied to the proposed venture, their policies regarding credit and delivery of goods and services, and their history and reliability.
The last section is the most important when it comes to choosing suppliers. A new business owner should look for suppliers that have been in the business for a long time and have proven to be reliable regardless of any hardship that may arise during various periods (slump and boom periods). Also, it is a known fact that suppliers who have been in the business for a while understand the challenges of starting up a business, and they may prove to be invaluable where other options have failed.
Similarly, the business owner should specify whether the business shall rely on particular suppliers or shall have more than one supplier. In this regard, there should be a detailed description of the goods that may need more suppliers mainly due to their sensitivity and impact on the business. It is always important for business owners to have back up suppliers for critical goods. Also, there should be a statement indicating whether the business shall be expecting any shortages from suppliers or delivery problems. Finally, the business owner should analyze and report whether the supply costs in the target market are fluctuating or steady and how the business shall remain balanced despite the changes in supply costs.
Competition
As businesses continue to emerge at an alarming rate, existing business owners are forced to employ cutthroat techniques to compete and eliminate weak businesses. All this is done in a bid to acquire a larger market share and profits. As such, it is always important to ensure that you study the potential competition before walking blindly into a market that is out to frustrate and kill your efforts.
In this regard, the business owner should describe the companies that the proposed venture shall compete with as well as the products that shall compete with yours. After identifying the competition, the business owner should categorize them in terms of their competition threat level. It means that the owner should describe whether the rival companies shall compete on every aspect of the business or some products. Besides, the owner should identify whether the competition shall extend beyond the products to the clients and location. Having done that, the business owner should give a detailed description of the strategies that shall be employed to ensure that any form of competition is mitigated if not eliminated.
Business owners should realize that there are indirect competitors in every market. As such, new businesses should stay alert and watch out for such competitors. For example, in most countries, the theater businesses have been suffering major losses due to an increase in video rental shops. Simple as it may seem, these rental stores are indirect competitions even though they specialize in a different business.
It is always important to develop a competitive analysis table which can be used to compare the proposed venture with major competitors. In this regard, the business owner should consider how the products and services compare with those offered by competitors. In evaluating the competition, a new business owner should tabulate a measurement matrix that shall be used to gauge the threat levels presented by each competitor. After carefully evaluating and categorizing the competition, the business owner should proceed to rate the proposed venture and identify where it shall fit in the market (Niche).
Promotion
Simply put, promotion refers to the process through which a business informs the target market of all new products and creates incentives to encourage people to buy and test new products. The main question in this segment should therefore be: how do the customers get to know about the new product? This question shall enable the business owner to explore and choose the most appropriate promotional tools.
For example, if the owner decides that advertising shall be the best method of creating awareness, he/she should consider the media that shall be used, explain why it shall be the most logical option, and specify the number of times this method shall be used to promote the venture’s goods or services.
Also, there should be a summary of other options that shall be used in case advertising becomes more costly or complicated. For example, some businesses use trade shows, incentives, friends, and door to door selling as tools of promotion. In case the proposed venture shall utilize one of the alternatives, the business owner should give a detailed description of the benefits and costs of the option and how the decision to utilize this tool was reached at.
Similarly, the business owner should specify the image that the business shall want to purport through its dealings. To support this, there should be graphical backings such as logos, letterheads, and brochures among others. After deciding which promotional tool shall be used, the business owner should prepare a promotional budget that gives the specific amount of money that shall be used to promote the product. The budget should encompass monies that shall be used to promote the product before the business starts up and as the business proceeds.
Organizational chart
An organizational chart is a diagrammatic representation of an organization’s management flow. Organizational charts often vary depending on the number of employees, their roles, departments, and subordination. Small businesses adopt simple organizational structures where the power flow is in form of a pyramid.
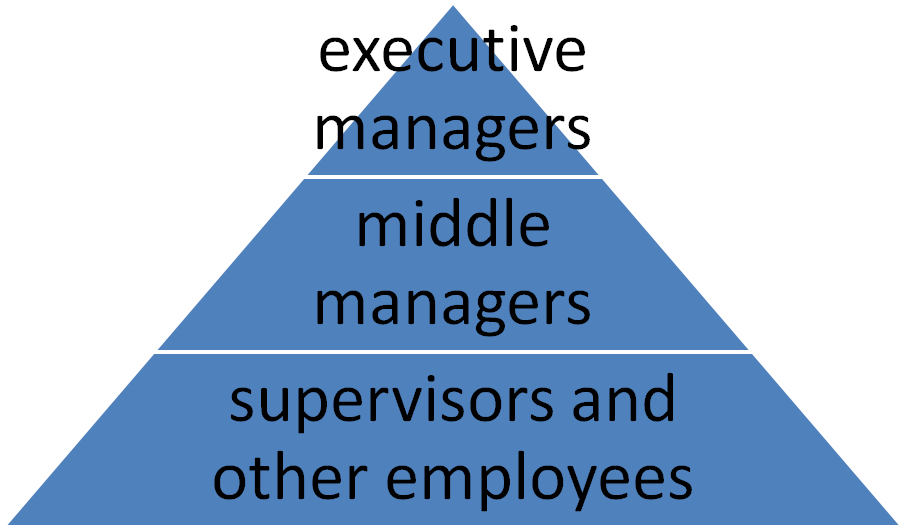
From this chart, it can be deduced that the lower level employees answer to middle management, who in turn answer to top executives. Depending on the business and human resource requirements, the business owner should select an organizational chart that shows how each employee shall contribute to the business and how power shall be distributed evenly across the business.
Operational plan
Equipment and facilities
It is always important to know how much a business has in terms of assets. It enables the owner to carefully plan the production capacity that a new venture shall be able to deliver within a given period. As such, the business owner should ensure that he/she provides a detailed list of all equipment that the business shall need to start up. It means that the owner should name the equipment and their relevance to various business processes.
In terms of facilities, the business plan should include the name and size of all facilities that the business shall acquire and require to have a successful start-up. For example, the business owner should ensure that he/she names the number of stores, warehouses, factories, and office buildings that shall be needed to guarantee the successful start-up of the proposed venture.
Similarly, this section should also highlight the methods that shall be used in acquiring this equipment and facilities. It is a known fact that the costs of starting a new business are inflated due to the monies used to acquire assets.
However, some options may lower such costs. They include leasing, hire purchase, borrowing, and renting. For example, the business venture may require cars to facilitate the transportation of goods and services between the business, clients, and suppliers. However, buying new cars is not very wise at this point. As such, the business owner may decide to outsource or rent a mode of transportation that is within a reasonable financial cost. Therefore, this section should also specify the available options that can be used to acquire the assets and at a reasonable cost.
Organizational processes
In this segment, the business owner should give a detailed explanation of how the daily operations of the business shall be carried out. Besides, there should be a precise description regarding the location of the business, the people and the processes that shall be carried out, and the surrounding environment. To ensure that nothing is left out, the business owner should subdivide the different aspects and processes and address each as a subtopic.
For example, underproduction, the owner should describe how and where the goods shall be produced. It should be followed by a compact analysis that explains the methods of production. For example, the business owner should explain what production techniques and costs shall be used, how the business shall maintain and promote quality control, how the business shall deliver customer service and product development (Kennedy 45).
On the same note, the business owner should give detailed descriptions of how the processes shall work, the resources needed to ensure success, and the manpower requirements that shall monitor and evaluate each process. For example, in regards to production techniques, the business owner should indicate whether the business shall use capital intensive or labor-intensive methods of production. Also, there should be a detailed explanation regarding the merits and demerits of the production method that shall be utilized and how the business shall maximize on both ends.
In regards to location, there should be a summary of all the aspects that shall make the selected location feasible for the types of processes that shall be carried out. In this regard, there should be a summary that explains the qualities that shall be needed in a location and the type of location the business shall have. On this note, there should be a description of the amount of space that shall be needed to set up the whole venture, the type of buildings that shall be required to enable efficiency, zoning details of the proposed location and the availability of power and other utilities in the proposed location.
Another key element that should be considered under operational plans is access to the business. Under this subtopic, the business owner should ensure that he/she explains how the proposed location shall be convenient to transportation and the suppliers. Also, an explanation should be provided as to how the business shall in future expansion and remain accessible to customers and how close it is to transport hubs (bus and train stations, outstanding transport and communication infrastructure, and room for future expansion in the proposed location).
Operational hours
Under this heading, the business owner should specify the number of hours that the business shall be operating each day. If the new venture shall be able to work for more hours (exceeding 8), there should be an explanation that shows the criteria and strategies that shall be used to divide labor and time. If the business hopes to implement a piece-work system, this should be expressed and explained in this section.
Legal Environment
It is another equally important portion of any business. In this stage, the business owner should ensure that he/she describes the licensing and bonding requirements that shall be needed before starting up the business. Also, the business owner should indicate whether permits shall be used or not. In case they shall be used, a detailed description of the type of permit required for that kind of business should be given. In addition to this, the business plan should highlight how the business shall conform to the health, workplace, and environmental regulations set by various authorities.
Also, there should be a provision and explanation of any special regulation that may be designed for the industry the proposed business shall be in. similarly, the business owner should ensure that the zoning and building requirements are well described as well as the codes that regulate these factors. Also, this section should be used to address the issue of insurance coverage (who shall get it, why, how shall it be financed, and so on) as well as that of the existing, purchased, or pending trademarks, patents, and copyrights.
Personnel
It is an integral part of the operational plans that a new venture hopes to achieve. Under this segment, the business owner should ensure that the number of employees that the business shall have is given, the type of input that the laborers shall bring into the venture (skilled, unskilled, or professional labor), and the criteria that shall be followed in selecting and recruiting the right employees.
Besides, this section should also provide useful information regarding the quality of the staff that shall be hired, the pay structure that shall be used to compensate them for their efforts, and the training methods that shall be implemented to ensure that the employees enhance their performance, are motivated and committed to the proposed venture.
On the same note, this section should also highlight the division of labor. In this regard, the business owner should explain the roles of each employee, whether there is a drafted job description form for employees and whether the venture shall use contracted workers in situations where the employees do not suffice. Also, this section should give a detailed description of the requirements needed for a particular job and how these requirements shall be matched with the qualifications of the employees.
Another integral part of the operational plan is the Inventory. In this section, the business owner should explain the type of inventory the business shall keep. For example, the business owner should specify the raw materials the business shall keep, the supplies required, and the finished goods that shall be kept. Besides, there should be a detailed description of the rate of turnover and seasonal trends in inventory management.
Financial matters
It should be noted, that every new business is expected to have numerous startup expenses before it even begins normal operations. It is therefore very important that the business owner estimates these expenses accordingly and lay down a plan on how the required capital shall be obtained. As such, thorough research should be carried out to ensure that all expenses are accounted for and none is overestimated or underestimated.
Also, the business owner should liaison with financial experts so that they can assist in establishing the feasibility quotient of the proposed venture. As such, this section should also include the financial forecasts that the business is expected to follow and how it shall make profits within a stipulated period.
Primary investment and capital
Under this segment, the business owner should specify the amount needed to start up the business. It is a known fact that new businesses have unforeseen expenses. Failing to consider this may lead to a shortage of funds, which may lead to the failure of the business. As such, the best way to ensure that the business does not incur more expenses is to develop a contingency plan and budgets, indicating the costs on a higher-end (overestimated figures) and on a lower side (actual figures). However, the best way to tackle such eventualities is to ask for advice from people operating the same business as the proposed venture. In so doing, the business owner may discover certain costs and expenses that he/she may have overlooked or ignored.
Having covered this issue, this section should, therefore, provide a detailed description of how the funds shall be acquired and distributed within the business. Besides, the following documents should be provided to show how the capital shall be used and the duration it shall take for the business to start making profits and sustain itself. The documents include: “A 12-month profit and loss projection, a four-year profit and loss projection (optional), a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a break-even calculation (Kennedy 93).”
When combined, these calculations should provide a detailed analysis of the business’s financial plan and how it will remain relevant in the chosen environment. Another equally important aspect that should be provided in this segment is the opening day balance sheet. This report should include the assets and liabilities that the business shall have on the first day.
Funding sources
There are many sources of getting capital for a business. The business owner may decide to use personal finances, borrow from a financial institution or friends, grants, and inheritance or gifts. These are legal sources of capital, and it is up to the owner to decide which option best serves the needs of the business.
Summary
After carefully evaluating each of the components, the business owner should use this section to summarize the strong points and attributes of the business. In this regard, the summary should comprise a brief description of the business, the product or service to be offered, financial plan, operational and management plans, and a forecast of future expectations. A summary is an effective tool in ensuring that all bases have been covered and the chances of incurring risks have been minimized. Since most business plans are lengthy, the summary provides an avenue through which readers may reflect on various aspects without necessarily having to go through the whole plan again.
Appendices
In this section, the business owner includes other resources that shall be used to ensure that the business is a success. Also, all the diagrams, photos, and graphical materials should be recorded in this section as well as the tabulated data and statistics which apply to the business.
Bibliography
As mentioned earlier, the process of starting a business is a lengthy one and requires a lot of research. As such, it is ethically sound that the business owner gives credit to all parties that assisted in formulating the business plan. In cases where books were used to provide vital information, the sources should be well-cited and referenced.
Conclusion
Starting a business is seldom an easy undertaking, and in many situations, businesses have failed due to a lack of know-how by the business owners. As such, it is always important to ensure that the proposed venture is feasible before pouring all your investments into it. On this note, this study has provided a detailed step-by-step guideline as to how an individual may start a business. From this guide, a description of each stage has been provided and the aspects that should be covered addressed.
If followed to the letter, this may prove to be the differentiating factors that mark a successful from a failed new venture. However, drafting a business plan is only half the battle. There are unforeseen events that may crop up at the advent of the business. It is, therefore important that the business owner develops a backup plan to help the business get through such hurdles without affecting the progress or financial stability of the venture.
Works Cited
Kennedy, Joe. The small business owner’s manual: everything you need to know to start up and run your business. New York: Career Press, 2005. Print.
Pinson, Linda and Jerry Jinnett. Steps to Small Business Start-Up. USA: Kaplan Publishing, 2006. Print.
Zahorsky, Darrell. Starting a Small Business 101: The Essential Steps. 2010. Web.