Introduction
Modern society is characterized by a high degree of complexity and is based on interaction and communication between groups or individuals. Companies actively use this aspect to generate product value for users. In particular, they use network effects to increase the number of participants in their network, which not only attracts more users but also generates product value for network members. Several main types of network effects affect a product’s value, increasing it and providing a competitive advantage to companies. Spotify and Airbnb are examples of the most successful use of various network effects to continuously generate the value of the network members’ products and increase their defense in the market.
Network Effects Definition and Overview
The principles of network effects in modern society and business are fundamental to the development of a competitive company. James Currier underlines that “every new user has the value in your product to other users who are using the product or will use the product” (NFX, 2020, [0:00-0:11]). Thus, the more people use the product, the more valuable it becomes to other existing and potential users. This factor also ensures the company’s growth and development, which provides a competitive advantage in the market.
Factors Affecting Product Value
Network Effects Types
Network effects are particularly significant in contemporary, highly digitalized society. In particular, there are four key defensibilities today, including network effects, embedding, scale, and brand (NFX, 2018). These factors allow companies to create value that cannot be copied or replicated, which increases the company’s competitive advantage in the market (Pidun et al., 2020). As part of technology startups, network effects account for more than 70% of the total value generated by the company (NFX, 2018, [0:20]). There are various types of network effects, which fall into major categories, including direct, two-sided, data, and social. A detailed network effects map is presented in
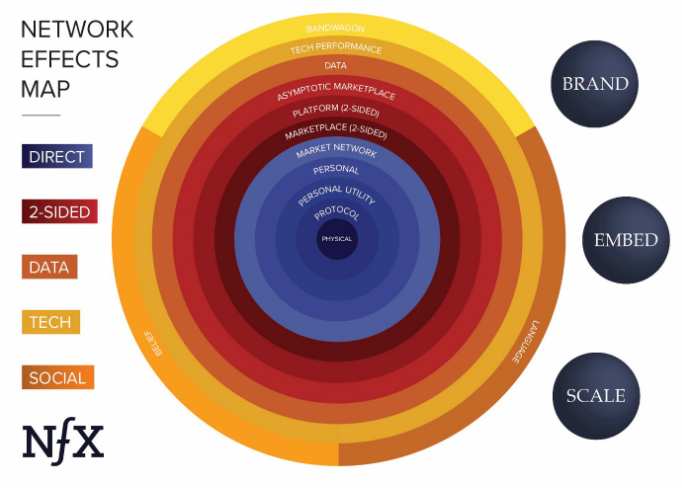
Fig. 1 and describes 13 types of effects as their impact on the value of a company’s product decreases.
Direct Network Effects
Direct network effects are the simplest and most powerful factors influencing business success. As shown in the map in Fig. 1, this broad group includes five effects: physical, protocol, personal utility, personal, and market network. The physical network effect is based on physical nodes and links, as a network of telephones and wires between them. This effect is the most defensible since it has a direct network effect, as well as “lends itself to the addition of other defensibilities; namely, scale effects and embedding” (Currier, n.d, para. 31). Businesses based on this type such as railway networks or electric networks, require large initial investments. Thus, most of the products and services offered by such companies are utilities that cannot be accessed through other effects.
The network effect protocol occurs when communication standards are set by the creator of the node and are available to anyone who can connect to the network using this protocol. For example, the latest blockchain technologies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are created according to this principle. The personal utility network effect is built on the principle of personal communication between network members. The main disadvantage of this effect is that when the network is disrupted, people using it experience direct harm from the inability to maintain personal communication. Examples of these networks are instant messaging tools or applications such as WhatsApp or SMS.
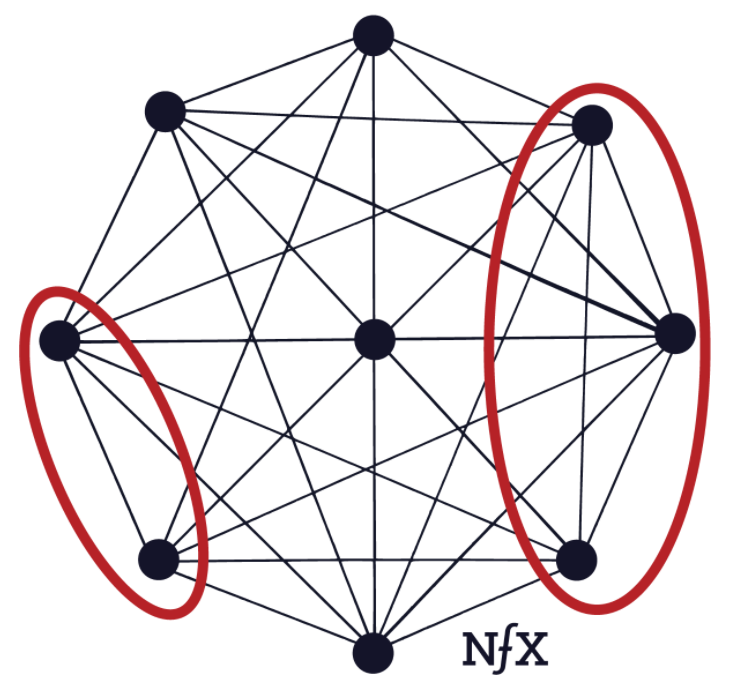
A personal direct network effect occurs when a product provides individual value to network participants. In particular, this is due to the fact that the reputation and personality of network participants are associated with and influenced by the product. In contrast to personal utility networks, this type of effect is not used for vital communication and is less personal in nature. Thus, when leaving the network or destroying it, users do not receive much damage. An example of such networks is Facebook or Twitter, where people can build long-term personal interactions. Finally, market networks are direct communication between marketplace participants. Thus, this effect is very similar to personal but focuses on interactions within a particular market. Examples of this effect are companies like HoneyBook or DotLoop that provide services to other businesses. Fig. 2 shows a typical structure of the direct network effect, which is built on nodes and links between them.
Two-Sided Network Effects
This group is also often called indirect effects, as it describes the interaction of demand and supply, which generate indirect value for each other. However, network participants on the same side also generate direct value when interacting, which explains the two-way nature of these effects. Most importantly, direct influences often negatively affect the value of a product, while indirect influences outweigh these factors to generate positive value. As shown in Fig. 1, there are three main network effects data types: marketplace, platform, and asymptomatic marketplace.
The marketplace network effect implies the presence of sellers and buyers. More opposing parties generate more value for the product. In this case, direct interaction on one side generates a negative value, which is offset by indirect influence. Examples of companies using this effect are marketplaces such as Amazon and eBay, matchmaking apps (Tinder or Craiglist, and payment instruments (Visa or American Express). The platform network effect is similar to the marketplace, but on the one hand, there are the creators of a product that is only available on a certain platform, and on the other, users. This effect is used by the creators of operating software, including Microsoft OS, and iOS, as well as the creators of game consoles and other similar systems.
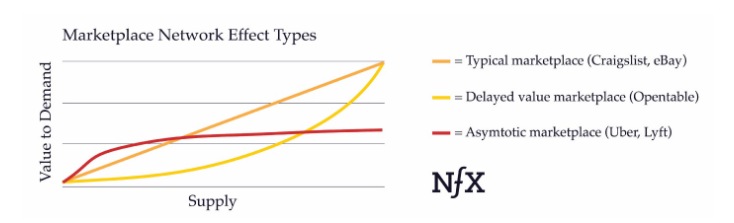
The asymptomatic marketplace network effect differs from the two types described in that they offer a rapid increase in value at the start of product implementation and a decrease in efficiency as the company develops. Typical and deferred value marketplaces, in turn, offer businesses the opportunity for stable growth in the generated value (the factor is illustrated in Fig. 3). This model is the most vulnerable and represents the least competitive advantage for companies but allows a quick start. Examples of companies successfully using this network effect are Uber and Lyft.
Data Network Effects
The data network effect describes how an increase in the amount of data leads to an increase in the value of a product. In turn, the growth in the value of the product is associated with the generation of a large amount of data. The interaction between the quantity and quality of generated data, as well as the mode of its usage, can affect the value of a product in different ways. However, the increased use of data and the improvement of the quality of information products leads to an increase in the value of the product for users. Companies that actively use this effect include Google, Amazon, IMDB, and others.
Tech Performance Network Effects
This aspect describes a situation where the performance of technology grows with an increase in the number of users. A large number of users or devices on the network will make the technology more convenient, cheaper, and more accessible. A feature of this effect is that each new node increases the performance of the technology for all other nodes of the network. Basically, this system is actively used by peer-2-peer technologies and companies based on them, including BitTorrent, VPN services, Hola, and others.
Social Network Effects
This type of effect generates product value solely through the interaction between people. This group is the most difficult in the long run but can offer a great competitive advantage. Social network effects, including language, bandwagon, and belief, are a form of brand defensibility because they are based on the influence of people’s psychology. However, these aspects still represent a network effect since their effectiveness also depends on the number of nodes and connections within the system.
Language is the most common factor that increases the value of a product. In particular, the more people use the brand name in the speech, the more recognizable and defensible it becomes. Language is also a predicate of international development since, for example, a company with a name in English will be much easier to promote globally than using local languages. For example, the company name Google already has a generic designation for Internet search, which greatly increases the value of the product. Belief works in a similar way: the more people believe in the value of a product, the more value it generates. The simplest example of this effect is religions or ideologies that exist solely due to belief and has no physical embodiment. The bandwagon network effect also engages people’s psychology by putting pressure on them to join a movement or group. A good example is Slack, which created a prejudice among tech companies that using their product is what makes a successful business. Therefore, the utility and the product do not match the opinion created around it.
The Exploitation of Network Effects Examples
Spotify
Spotify has become one of the pioneers in using the principles of network effects. This streaming application allows any user to create a profile on the platform as well as share their own or others’ playlists. Additionally, users can add each other as friends, see what music other users are listening to, and create joint playlists. It is also important that the application is integrated into other media platforms and allows users to share their music on Facebook pages and other resources. Recently, the company added the ability to share remote listening for users. Thus, Spotify actively uses several network effects, which together constantly increase the value of the product.
First of all, Spotify uses direct effects, including personal utility and personal effects. The personal utility effect is to provide users with the opportunity to communicate with each other and express themselves, as well as search for communities. The personal network effect consists of giving users access to music and various playlists, which creates value in itself. More musicians and listeners in the network generate more and more value for all its participants. The company also uses the two-sided network platform effect, as Spotify delivers value exclusively within its platform, gaining additional value and defensibility. Moreover, the company uses the sided network marketplace effect to provide value-generating interaction between musicians and listeners. Finally, Spotify is actively integrating social networks such as language and bandwagon to promote the brand as well as set trends that influence public opinion. Together, these factors allow the company to constantly increase the value of its product, making it more and more indispensable in the market and increasing its competitive advantage.
Airbnb
Airbnb is another example of the successful use of network effects, but the company utilizes fewer factors than Spotify. In particular, the company model is based on the interaction of hosts and guests, which is a typical example of the marketplace network effect. Thus, the platform provides network participants with the opportunity to interact. In turn, more users generate increased value and attract new members. In turn, the constant growth of the network increases the value of the company’s product and provides a competitive advantage in the market.
Conclusion
Network effects are built on the interaction of system nodes and links to generate product value. As one can see from the examples of Spotify and Airbnb examples, companies can use various factors to attract more users and increase the company’s competitive advantage. The most important thing about network effects is that the process does not require any special investments or strategies from the company. The product itself generates value if it is useful to users, which is the main driver of value growth.
Reference List
Currier, J. (n.d) The network effects manual: 13 different network effects (and counting). Web.
NFX. (2018) Network effects predict the future of Facebook. Web.
NFX. (2020) What are network effects? Web.
Pidun, U., Reeves, M. and Schüssler, M. (2020) Why do ost business ecosystems fail? Web.