Introduction
The purpose of this laboratory work was to determine the spring displacement as a function of the applied force and the type of spring used. Each of the five springs or elastic bands — Long Thick, Small Thick, Long Skinny, Red Tape, Normal Tape — was suspended vertically, and weights were attached to the lower end to increase the stretch of the spring or band. Determining the relationship between the value of the applied force and the stretch allowed the value of the regression tape slope and the spring constant to be determined.
Data
Table 1 contains the results of direct measurements of the distance and displacement of the spring or elastic band as a function of the value of the applied force. Instead of using an amplifier, the laboratory experiment used weights suspended from the spring or an elastic band. Knowing the value of the mass made it possible to determine the value of the applied force because the force of gravity came into play, determined by the formula F = mg, where g is the constant of the acceleration of gravity.
Table 1. Results of direct measurements for different types of springs
Normal
RED
Long Skinny
Long Thick
Small Thick
Results
Calculation
In this laboratory work, it was necessary to calculate force values based on the mass of the weights suspended from each specimen. For this purpose, it was assumed that the resultant force was determined by gravity alone, so the calculation of gravity for each test should have allowed the value of the applied force to be determined. This force is determined by the formula F = mg, where g is the acceleration of free fall or 9.807 m/s2.
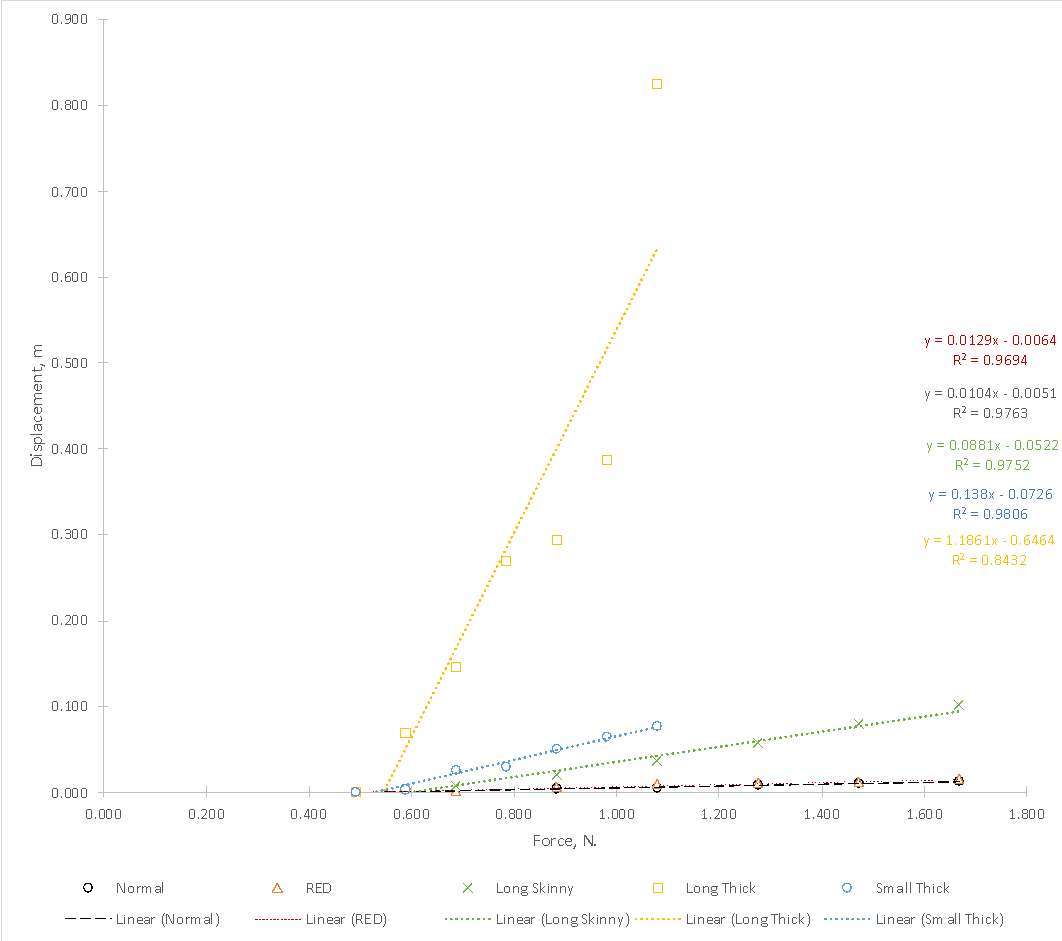
Thus, by multiplying each mass (considering the conversion to kilograms) by 9.807 m/s2, the value of the applied force could be obtained. A linear regression equation was found for Long Thick, 1.1861x – 0.6464, which can be used to determine the force required for a given displacement. Thus, for displacements of 10, 15, and 20 cm, the required force is 0.63, 0.67, and 0.71 N, respectively.
Graphs
The slope, the regression equation, and the coefficient of determination were determined for each of the five dependencies of the displacement on the applied force. The minimum value of this coefficient was 84.32% (for Long Thick), so the linear approximations were generally appropriate for each of the models.
All lines were ascending, indicating an increase in displacement with increasing applied force. The slopes in these equations determine the rate of increase in vertical displacement as the force increases by one N or the inverse value of the spring constant. Thus, in decreasing slope order, this rate of displacement was confirmed for the following materials: Long Thick > Small Thick > Long Skinny > Red tape> Normal tape.
Accordingly, the values of the spring (or tape) constant increased in this row because the more significant the slope, the smaller the spring constant (Dwivedi, 2023). It follows that Long Thick was the easiest to stretch because its spring constant is the lowest. The values of the intercepts, in this case, did not make physical sense and are an error of linear extrapolation.
Conclusion
The purpose of the present laboratory experiment was to establish the relationship between the vertical displacement of the spring or elastic band and the applied force; it was shown that, in general, the relationship between them can be defined as a linear upward one. This means that as the value of the applied force increases, the vertical displacement increases, but it is possible that when the critical point is reached, the spring material will rupture. It was found that the maximum displacement decreased in the Long Thick > Small Thick > Long Skinny > Red Tape > Normal Tape series, which means that the spring constant increased in this sequence. This supports the theoretical information about the relationship between the two variables since Hooke’s law states that F = -kx.
Reference
Dwivedi, K. (2023). Spring constant: Definition, formula, unit, calculation. Mechical. Web.