Introduction
Stratasys is a printing and additive manufacturing business that has provided three-dimensional text reproduction and imaging services for the past close to 30 years (Stratasys par.1). The company creates systems and materials that are essential in 3D printing for producers, stylists and instructors, and individual clients.
The company’s main offices are based in Minnesota, although it has operations almost everywhere around the world, thus making it one of the leading 3D text reproduction solutions and additive manufacturing companies in the world. The company provides several solutions to its customers in four key areas, which include rapid prototyping, additive production, specialized services, and strategic advisory services.
The organization also has other areas of business such as the Stratasys Direct Manufacturing and Stratasys Advanced Materials, which are equally important areas that assist customers. The company, which currently has more than $3 billion market capitalization, is the world champion in three-dimensional text reproduction and additive production services; a position that it has held for close to ten consecutive years (Stratasys par.3).
The company is in the forefront in guiding technological research and development in the field of three-dimensional printing. With its current success, the business is likely to continue being the market champion in the short and long term. Scott Crump and Lisa Crump formed Stratasys in 1989. The company made its first three-dimensional modeler early 1990s. The company was very successful in its initial years.
It had its first initial public offering in 1994. In 1995, the company acquired IBMs rapid prototyping copyright. Stratasys developed its Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) technology, which is currently the best selling rapid prototyping technology in the world. Further, the company supplies approximately 45% of all additive production structures, thus making the world’s leader in the segment.
The company has also made important mergers and acquisitions that have solidified its position as the leader in three-dimensional printing technology. For instance, the Solidscape that was acquired in 2011 added new and important expertise to the company. Solidscape was the leader in high-precision three-dimensional printers at the time.
Further, in 2012, the company merged with an Israel-based 3D corporation, namely Objet. The move was an important addition to the company. Other acquisitions include MakerBot Industries, Solid Concepts, and Harvest Technologies.
How the Technology has Developed
The three-dimensional technology has evolved significantly over the years to its present state. The expertise is likely to continue developing as more research and more inventions appear. The technology did not begin with Stratasys. However, the company has made significant contributions ever since it began its activities in 1992. The 3D technology has its origin from the 1980s when ongoing research led to the development of the first additive production paraphernalia.
In 1984, Chuck Hull developed the first three-dimensional printing model that used an expertise referred to as the stereolithography where coatings were created through developing photopolymers using ultraviolet beam lasers. The first three-dimensional text reproduction machines were huge, massive, and highly costly and beyond the reach of many individuals and even companies.
The 3D technology continued to evolve until 1988 when Crump introduced the fused deposition production technique, which is now the industry’s principal 3D printing technology. The company continued to expand its activities. In 1994, it introduced the opening thermoplastic that was available for three-dimensional printing. In 2002, the first 3D machine under $30,000 was developed. Although this move was a breakthrough towards making 3D printers more accessible to the masses, newer models of $10,000 later emerged.
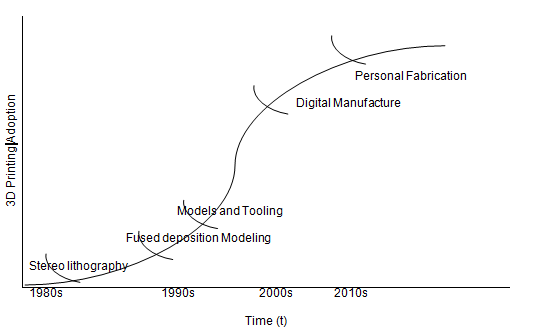
New technologies such as Models and Tooling, Digital Manufacturing, and Personal Production emerged later. For instance, Molds and Tooling was introduced in the late 1990s. The Digital Production technology was introduced in early 2000 while the Personal Production was introduced in 2010 (Lipson and Kurman 28).
The development of 3D printing technology is still growing. Many inventions are expected to revolutionize the industry. For instance, affordability is one of the major areas that the industry is likely to focus on in the quest of bringing the technology into the hands of the masses. Further, quality of printouts and new cost-effective technologies are likely to emerge. Concisely, the development of 2D technology has not reached its decline stage. There is still more developments that will enter the industry.
The S-curve is an important tool that is used in ensuring that companies can track their evolution over the years (Foster 99).The following S-curve summarizes the evolution of the three-dimensional printing technology over the years:
Technological Limits
In the current rapidly developing world, digital technologies have evolved significantly. They continue to progress at a very high rate. In this case, it is important to note that no technology can be safe unless it also rapidly adapts to the occurring changes. The 3D printing technology has been used for more than 25 years, yet it has not reached its limits.
Consequently, it is without any doubt that while the technology will eventually reach its limit, it is still in its infancy in terms of adoption and development. There is more room for development. For instance, the current technological development only allows the use and application of 3D printing majorly for design purposes, as opposed to general use by the masses.
The main reason for such a limitation is that 3D machines are very expensive and consequently beyond the reach of many people (Bassoli 149). Therefore, there is more room for improvement towards making 3D printers more affordable to ensure that they can be adopted widely. Guaranteeing affordability will require the development of 3D printers with a price tag of less than $500. However, this dream may take some time to be achieved.
Secondly, ensuring that the technology is adopted widely will require the creation of the relevance of the printer for general and small industrial purposes, which will bring into the hands of many people. In the current state, 3D printers are mainly used for industrial purposes, as well as medical research.
Hence, many people are yet to recognize the relevance of such printers in their daily lives (Lipson and Kurman 24). Consequently, as the general population finds relevance in the 3D printers, the technology will grow even further in terms of affordability and application for general purposes. In this case, Stratasys and other firms in the industry will continue to experience growth and success as the technological changes open up more opportunities in the market.
Are there any Possible Disruptions?
Disruptions in an industry can lead to the success or failure of a company. As such, it is important to ensure that companies are in the forefront in noting and adapting to any changes (Utterback and Kim 114; McGahan 87). Stratasys has not experienced major disruptions in the past. However, the future may bring disruptions in terms of competition. For a very long time, Stratasys and other pioneer companies have dominated the industry.
However, new startups are emerging. Since the technology is still developing, the startups are likely to increase the competition in the market (Bassoli 151). Further, since more opportunities for the growth of 3D printing technology continue to be created in terms of affordability and application, companies that will manage to deliver on the two areas are likely to dominate the industry in the near future (Rengier 338). As such, it will be very important for Stratasys to ensure that it remains relevant through research and development.
Managing Diminishing Returns and Discontinuities
Based on what the company has demonstrated in the past 25 years of its existence, it suffices to declare research and development critical factors that can ensure relevance and competitiveness in the industry. Therefore, the company emphasizes research and development to improve its existing products and technologies.
Further, another important approach that the company focuses on is the acquisition or merging with like-minded companies, which can add value to the business. Such approaches will ensure that Stratasys manages diminishing returns and discontinuities that can arise from competition or the emergence of new technologies in the sector.
Conclusion
The 3D printing technology has developed and evolved over the years to its present state. Stratasys has played a major role in this development. The S-curve has shown that the industry has not reached technological discontinuity. There is still more room for development.
The fact that the industry is still developing implies that the likelihood of disruptions is high. However, through research and development, the company is keen on remaining relevant in the long term. Further, it uses research and development in addition to mergers and acquisitions to beat discontinuities and diminishing returns.
Works Cited
Bassoli, Elena. “3D printing technique applied to rapid casting.” Rapid Prototyping Journal 13.3(2007): 148-155. Print.
Foster, Richard. The S-curve: A New Forecasting Tool, London, UK: MacMillan, 1986. Print.
Lipson, Hod, and Melba Kurman. Fabricated: The New World of 3D Printing, New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons, 2013. Print.
McGahan, Anita. “How Industries Change.” Harvard Business Review 31.3(2004): 86-94. Print.
Rengier, Fabian. “3D printing based on imaging data: review of medical applications.” International journal of computer assisted radiology and surgery 5.4(2010): 335-341. Print.
Stratasys. About Us, 2015. Web.
Utterback, James, and Linsu Kim. Invasion of a stable business by radical innovation, New York, NY: Springer, 1985. 113-151. Print.